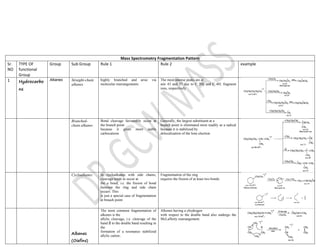
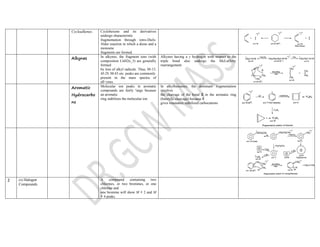
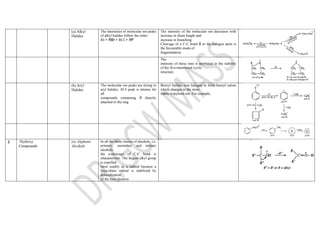
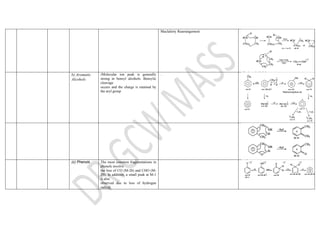
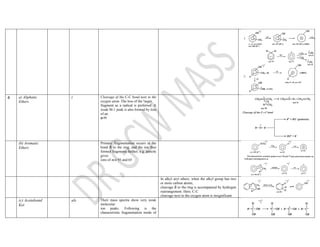
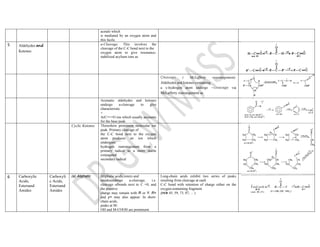
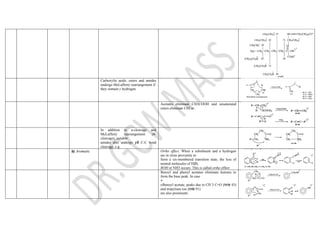
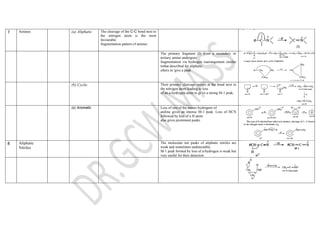
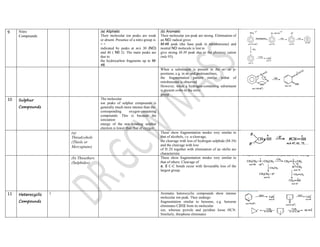
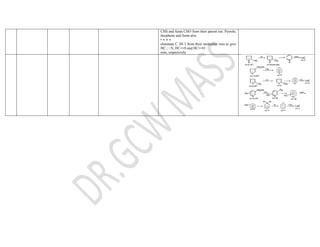
This document summarizes the common fragmentation patterns observed in mass spectrometry for different functional groups. It describes the typical bond cleavages and fragment ions formed. For example, it notes that alkanes commonly form fragment ions of m/z 43 and 57 due to C3H5+ and C4H7+ ions. Alcohols typically undergo alpha cleavage of the C-C bond next to the hydroxyl group. Aromatic compounds often involve cleavage of the bond beta to the aromatic ring. The document provides examples of characteristic fragmentation for each functional group class.