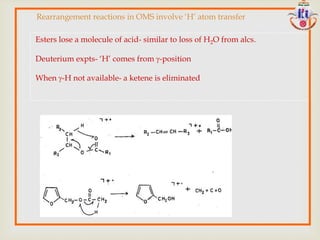
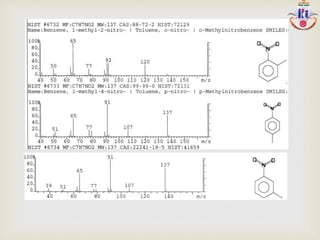
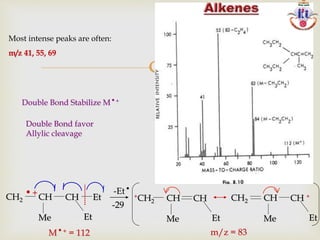
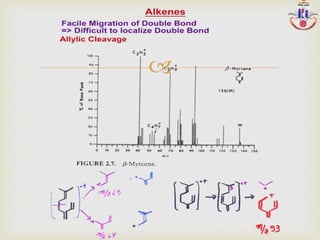
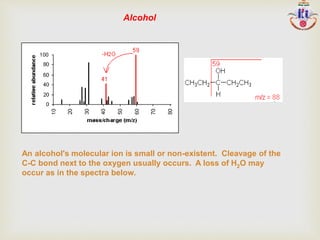
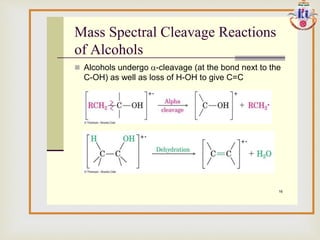
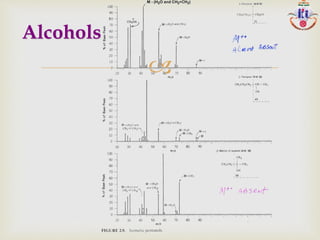
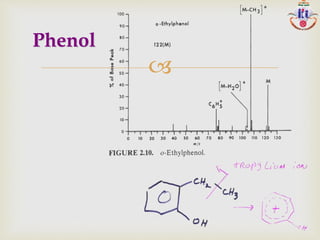
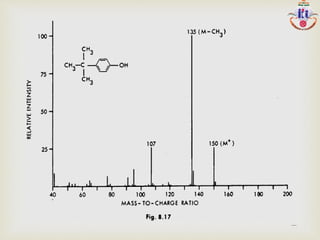
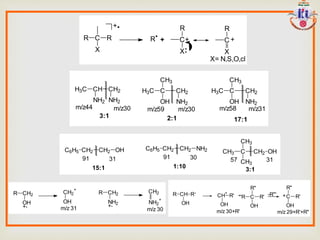
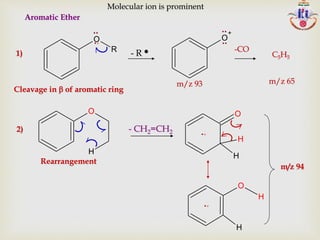
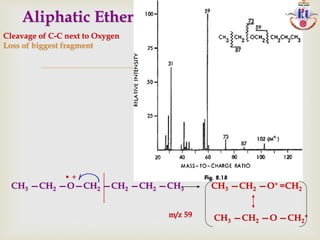
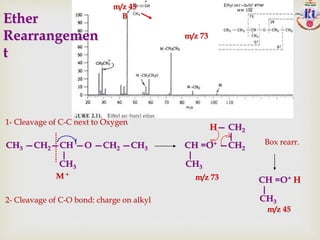
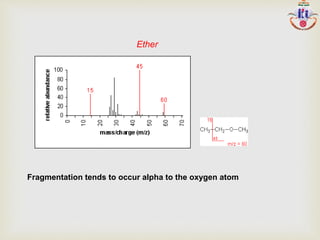
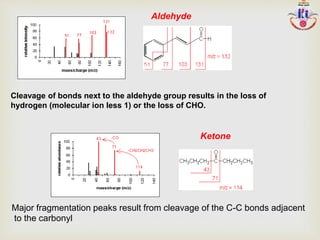
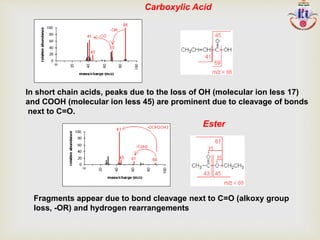
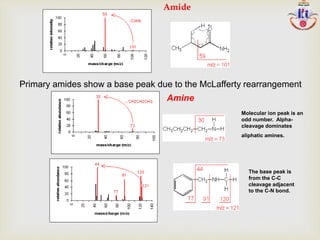
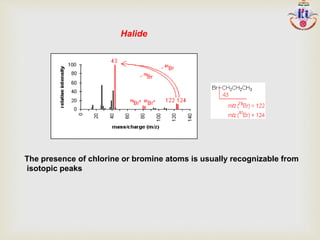
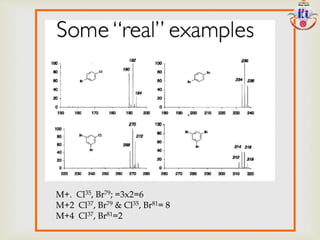
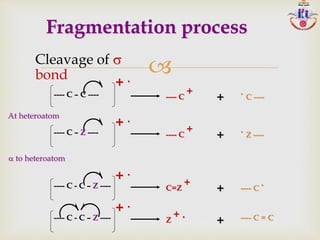
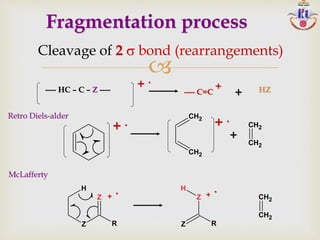
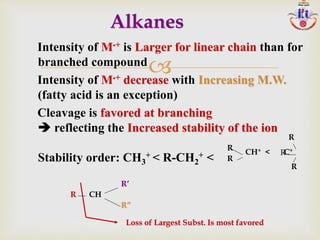
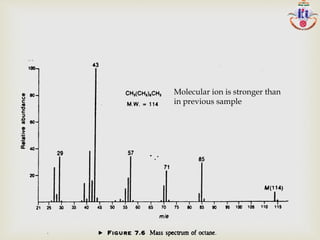
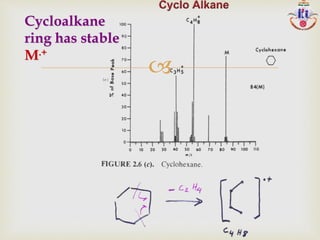
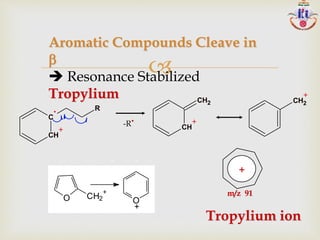
The document discusses various fragmentation patterns seen in mass spectrometry for different functional groups. For alcohols, cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond adjacent to the oxygen is common, as is loss of a water molecule. Aromatic ethers often fragment through cleavage of the carbon-oxygen bond or rearrangement within the aromatic ring. Carboxylic acids may lose a hydroxyl group or carboxyl group through cleavage of bonds adjacent to the carbonyl. The presence of halides is indicated by isotopic peaks from chlorine or bromine atoms.




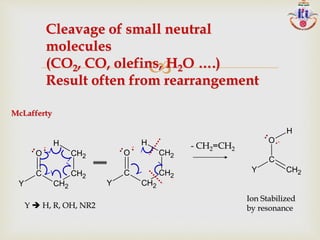
![Mass spectral reactions:
Unimolecular, competitive and consecutive
Ions with wide range of internal energy
ABCD + e- ABCD +• + 2e
ABCD + e- A +• + BCD•
AB+ + CD• A+ + B
AB• + CD+ C+ + D (I)
AD+ + BC• (II)
ABCD +• + ABCD [ ABCD ABCD ]+ ABCDA+(III)
“Cool ions” appear as M +•
(I) Simple cleavages
(II) Rearrangements
(III) ion-molecule reactions
MS FRAGMENTATION OF HYPOTHETICAL MOLECULE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msinterpretation-140618020105-phpapp02/85/Ms-interpretation-13-320.jpg)
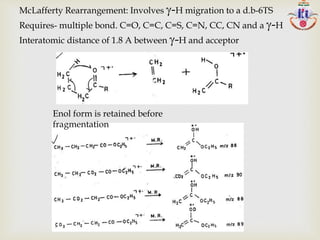
![Abundance of ions depends on:
Stability of the +ve charge in the cation or +.
ion stabilization- e- sharing –hetero atoms nonbonding
orbital CH3-C + =O CH3-CO +
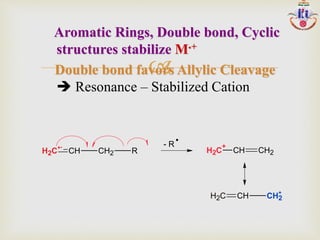
Resonance stabilization:CH2=CH-CH2
+ +CH2-CH=CH2
Stability of radical or neutral species
Steric arrangements of atoms or groups of atoms-
favoring Rearrangements
Stevenson Rule: ABCD+. A + + BCD• or A . + BCD+
Radical of high IE, Ion of low IE
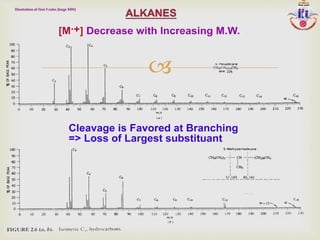
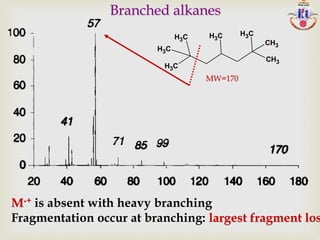
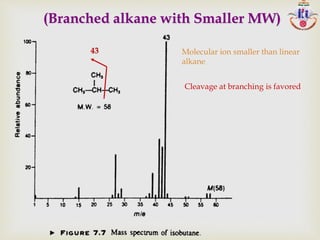
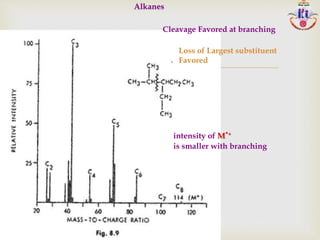
Loss of largest alkyl group-most abundance ion-exception
C2H5CH(CH3)-C4H9
+ [C2H5CH(CH3)+] >[CH(CH3)-C4H9
+ ]
> [C2H5CH-C4H9
+] > [C2H5C(CH3)-C4H9
+ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msinterpretation-140618020105-phpapp02/85/Ms-interpretation-14-320.jpg)
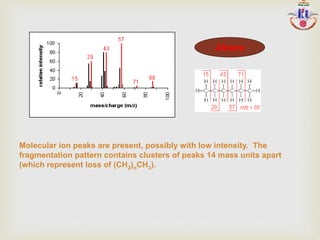

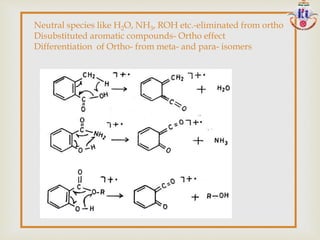
![
R CH2 CH2 Y R
x
CH2 Y R
+
CH2
+
Y R
x
R2
C
R1
O
C
R1
O
+
C
+
R1
O
- [RCH2]
- [R2]
larger
C-C Next to Heteroatom cleave leaving
the charge on the Heteroatom](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msinterpretation-140618020105-phpapp02/85/Ms-interpretation-32-320.jpg)