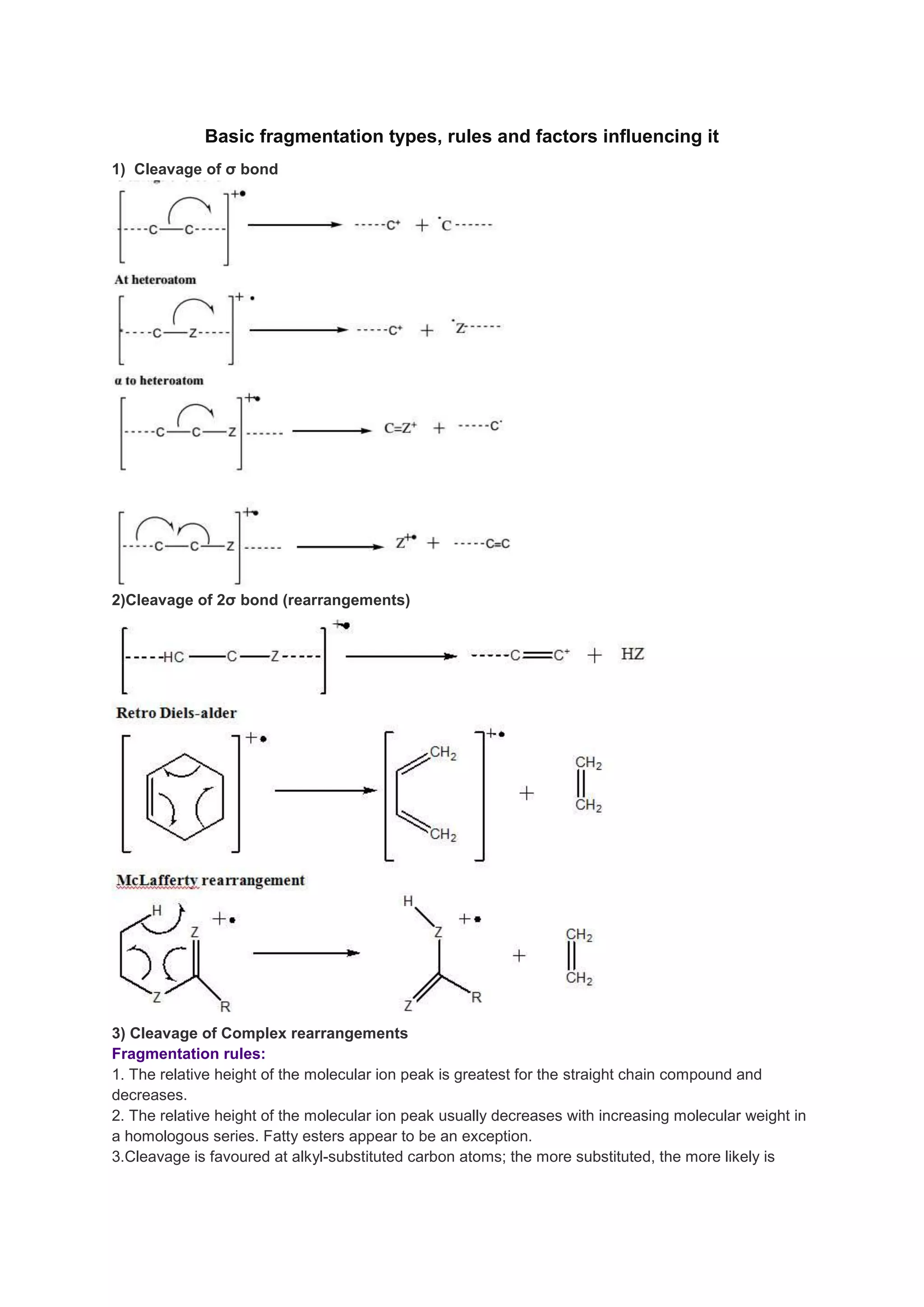
1) Basic fragmentation types include cleavage of σ bonds, cleavage of 2σ bonds with rearrangements, and complex rearrangements.
2) Fragmentation rules favor cleavage at alkyl-substituted carbon atoms and bonds next to heteroatoms. The molecular ion peak is greatest for straight chain compounds and decreases with increasing molecular weight and substitutions.
3) Factors that influence fragmentation include the number of fragment peaks, which provides information about the type of molecule, as well as the presence of common fragment ions that can indicate functional groups or structures.