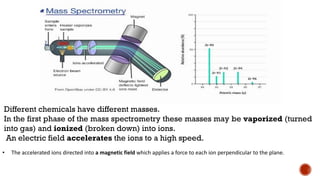
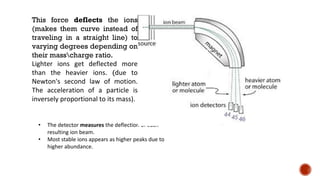
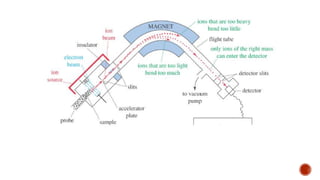
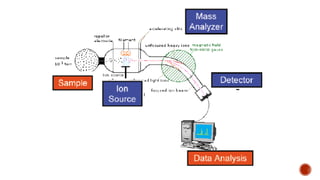
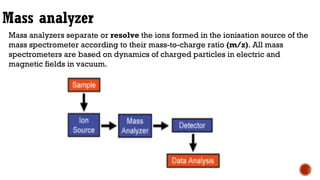
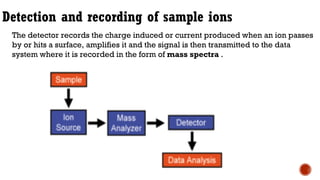
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles to identify molecules. It can be used to determine molecular weight, detect fragmentation patterns, determine molecular formulas, and analyze proteins. The technique works by ionizing molecule samples and accelerating the ions using electric fields before separating them using magnetic fields based on their mass-to-charge ratios. Lighter ions are deflected more than heavier ions. A detector then measures the deflected ion beams to produce mass spectra.