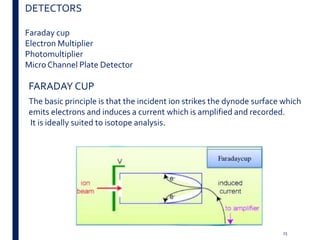
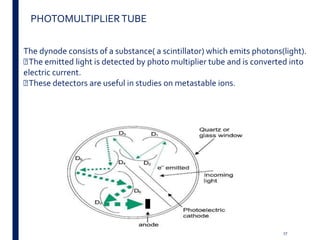
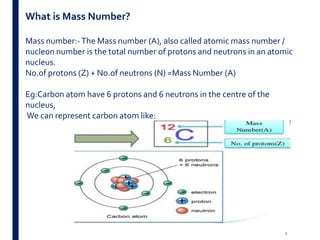
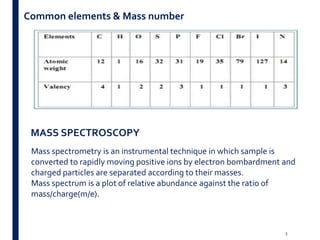
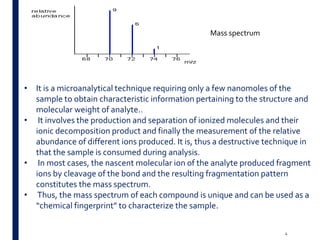
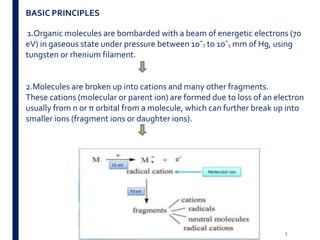
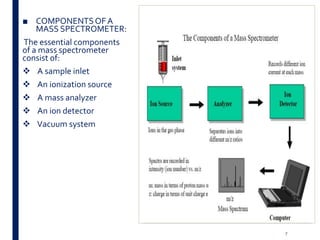
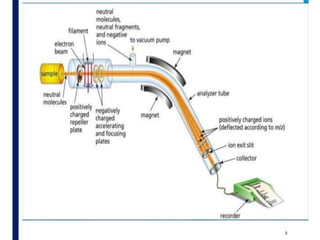
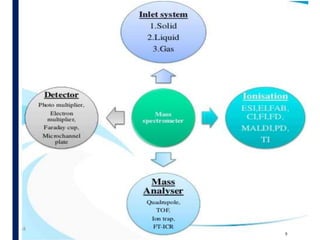
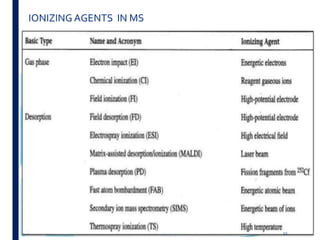
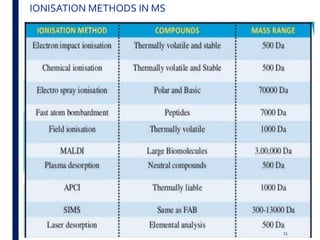
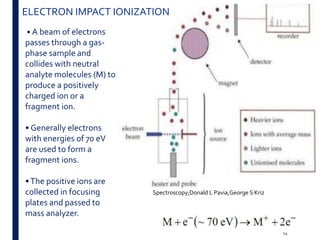
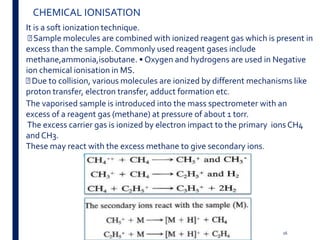
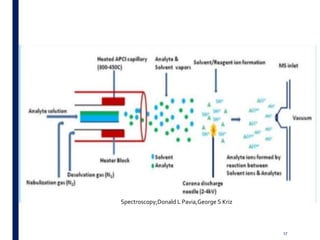
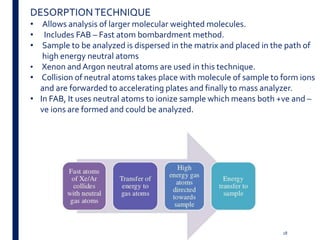
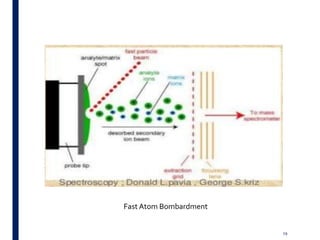
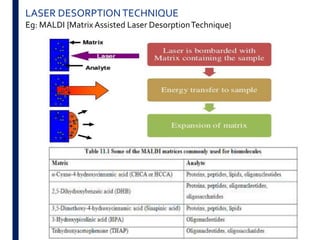
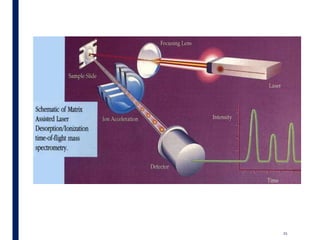
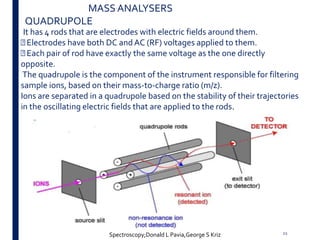
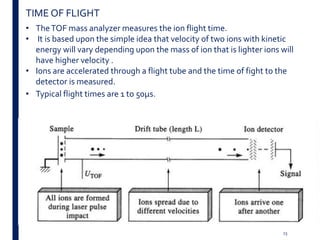
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. It operates by first converting molecules to ions, then separating and detecting these ions. The three main components are an ion source, a mass analyzer, and a detector. The document discusses the basic principles of mass spectrometry including ionization methods like electron impact ionization and chemical ionization. It also describes several types of mass analyzers such as quadrupole, time-of-flight, and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance analyzers. Common detectors include Faraday cups, electron multipliers, and photomultiplier tubes. Mass spectrometry is used to determine molecular structure and analyze organic and inorganic





![24
FOURIERTRANSFORM ION CYCLOTRON ANALYZER [FT-ICR]
A type of mass analyzer for determining the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of
ions based on the cyclotron frequency of the ions in a fixed magnetic field.
The ions are trapped in a Penning trap(a magnetic field with electric
trapping plates) where they are excited to a larger cyclotron radius by an
oscillating electric field perpendicular to the magnetic field.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/massspectro-181011141025/85/Mass-spectroscopy-24-320.jpg)