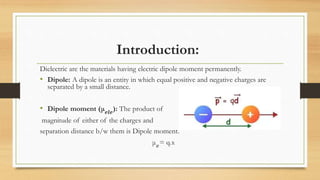
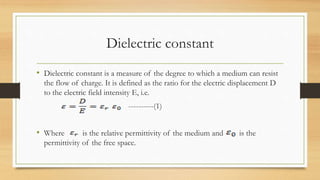
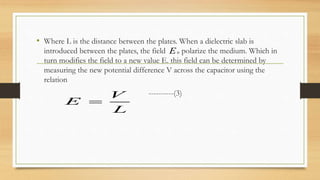
Dielectric materials can be polarized by an external electric field due to various polarization mechanisms. The dielectric constant is a measure of how much a material polarizes in response to an applied electric field. It is defined as the ratio of the relative permittivity of the medium to the permittivity of free space. The main polarization mechanisms are electronic, ionic, orientational, and space charge polarization. Electronic polarization occurs due to displacement of electrons relative to atomic nuclei. Ionic polarization is due to displacement of positive and negative ions relative to each other within molecules.