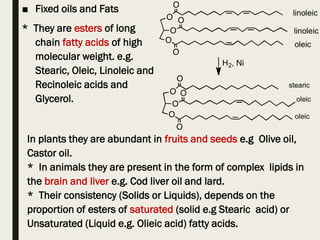
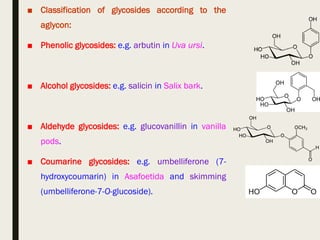
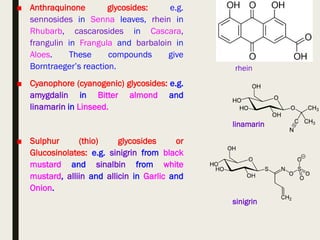
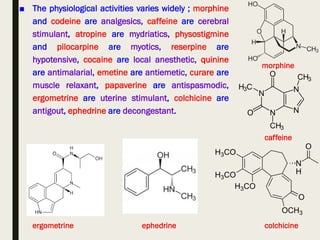
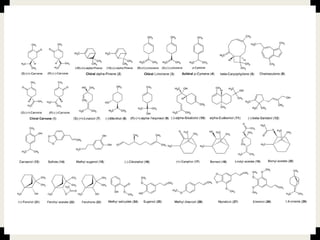
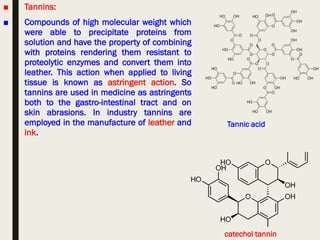
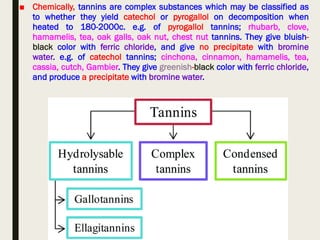
This document provides an overview of primary and secondary plant metabolites. It discusses starch, proteins, oils and fats as primary metabolites that plants produce for energy storage. As secondary metabolites, it covers glycosides, alkaloids, volatile oils, tannins, and bitter principles. For each type of metabolite, it provides examples of compounds and their characteristic chemical properties and biological activities. The document is intended as an introduction to the different classes of compounds produced by plant metabolism.