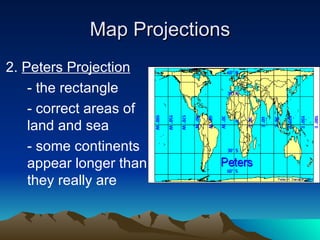
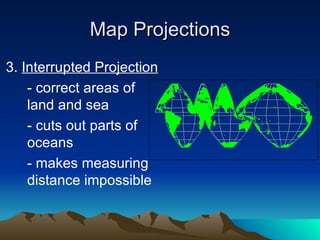
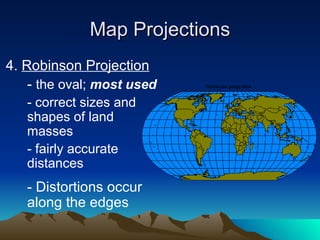
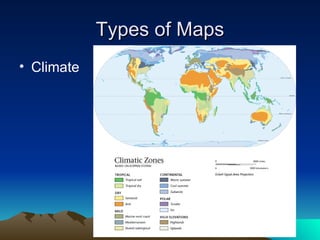
This document discusses different tools used in geography including map projections and types of maps. It provides details on four common map projections: Mercator, Peters, Interrupted, and Robinson. It also outlines three types of maps - physical, population, and climate maps. Additionally, it lists the four major landforms as mountains, hills, plateaus, and plains. Finally, it discusses climate and factors that influence climate such as latitude, proximity to oceans, and elevation.