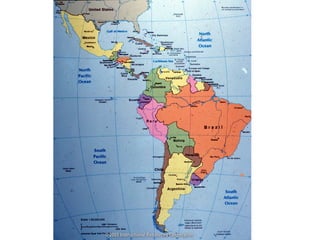
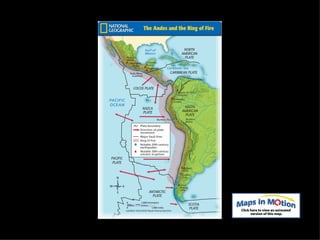
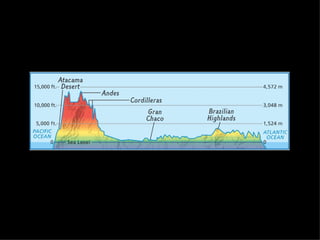
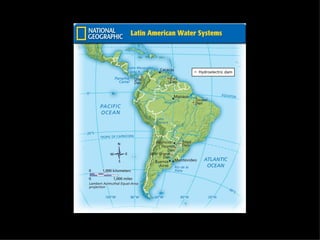
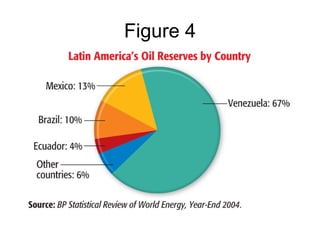
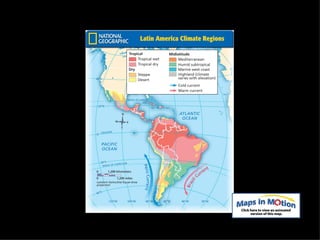
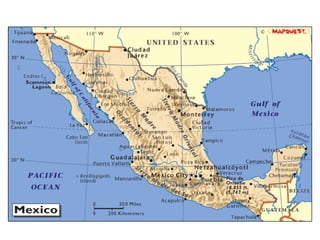
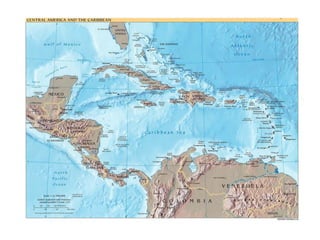
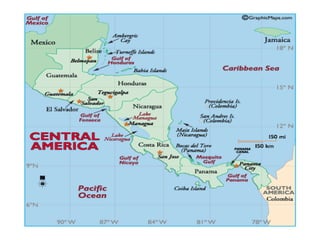
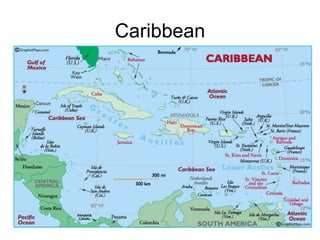
The document provides an overview of the geography, climate, economy, and people of Latin America. It notes that Latin America spans from Mexico to South America, covering around 8 million square miles. The region has diverse terrain including mountains, plains, rivers, and rainforests. The climate varies from tropical to temperate. The economy is based on agriculture, industry, and services. The population is around 500 million people and includes many ethnic groups.