- Geography is the study of Earth's physical features, people, places, and environments. It examines how humans interact with their surroundings and how locations are connected.
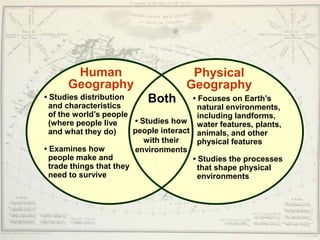
- There are two main branches of geography - human geography focuses on people and societies, while physical geography examines natural environments and processes.
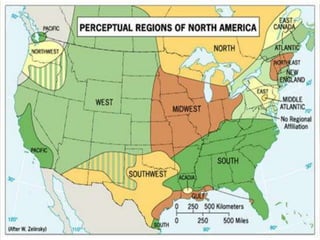
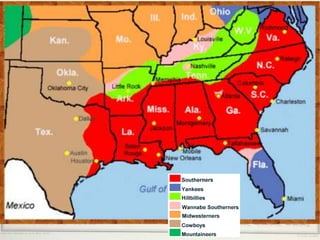
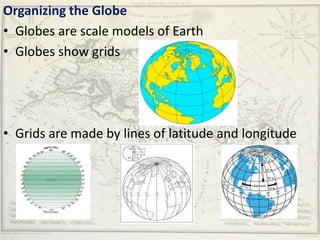
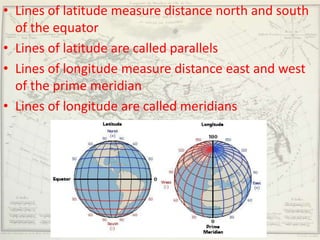
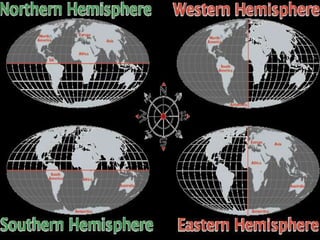
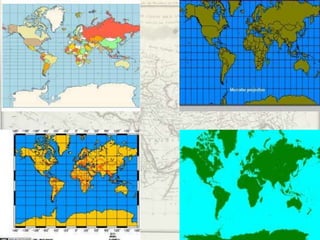
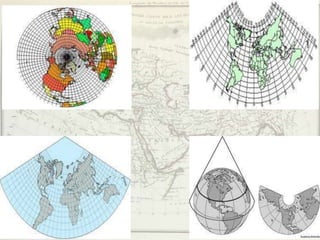
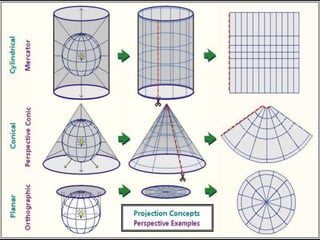
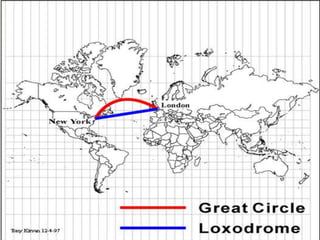
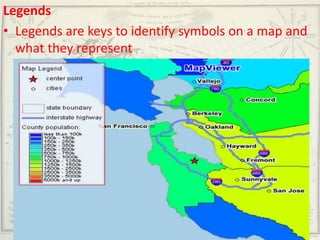
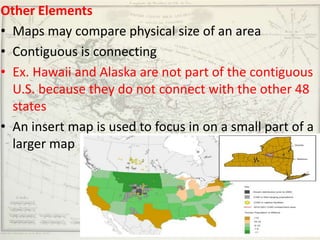
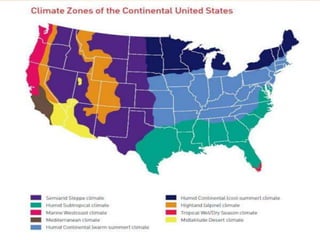
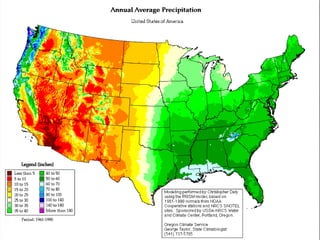
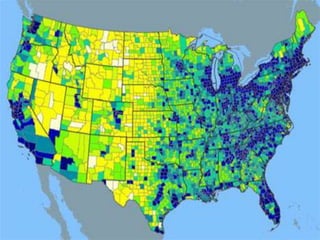
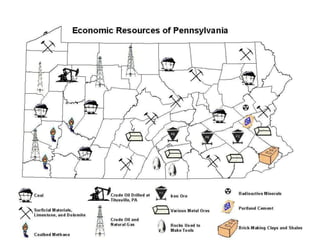
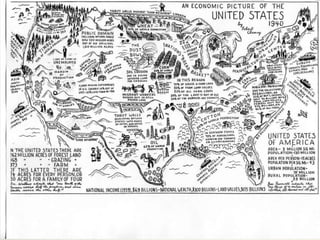
- Geographers use various tools like maps, globes, and diagrams to analyze spatial patterns and regions at different scales. They work in fields like cartography, meteorology, education, and land use planning to understand the world.