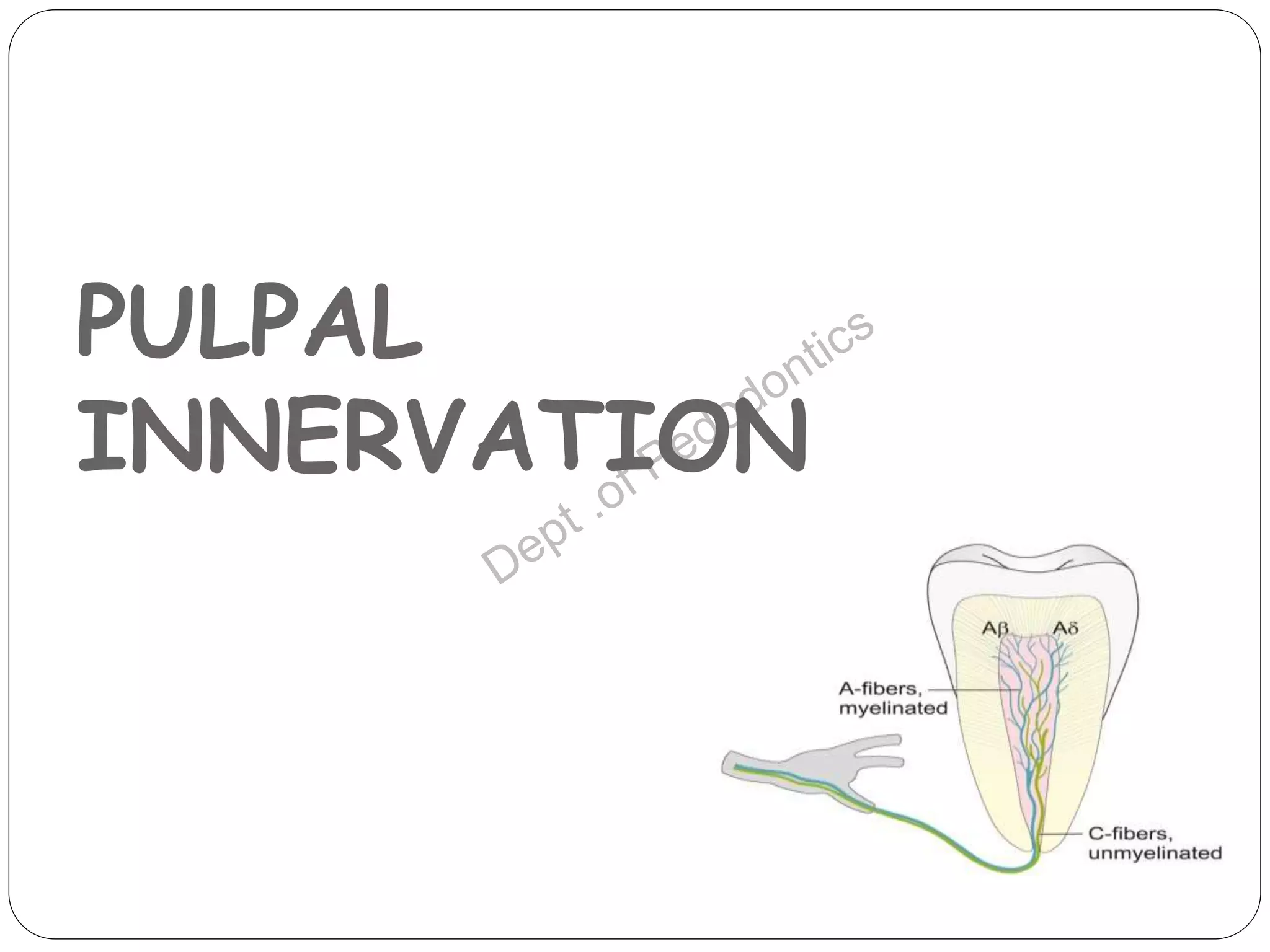
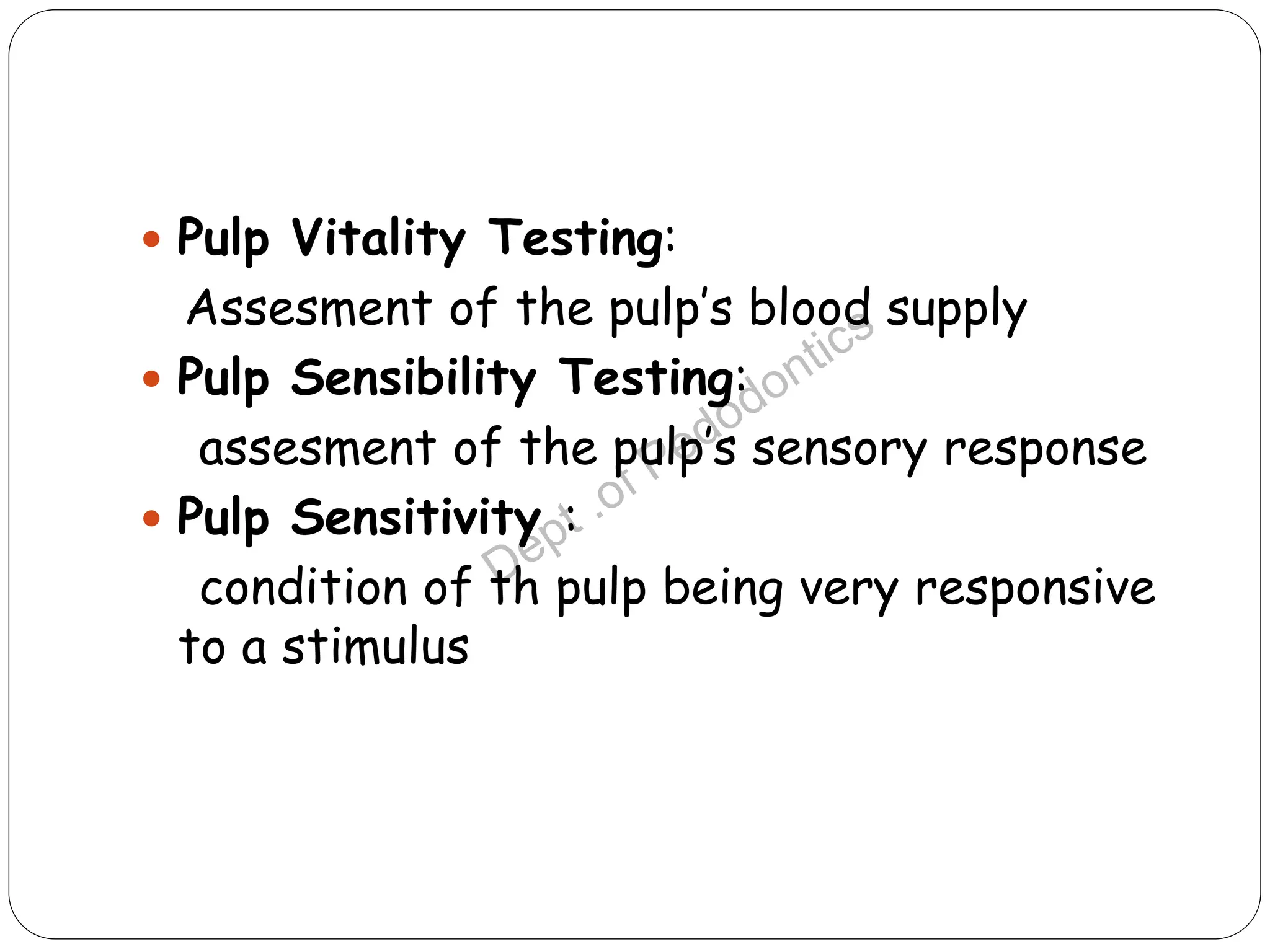
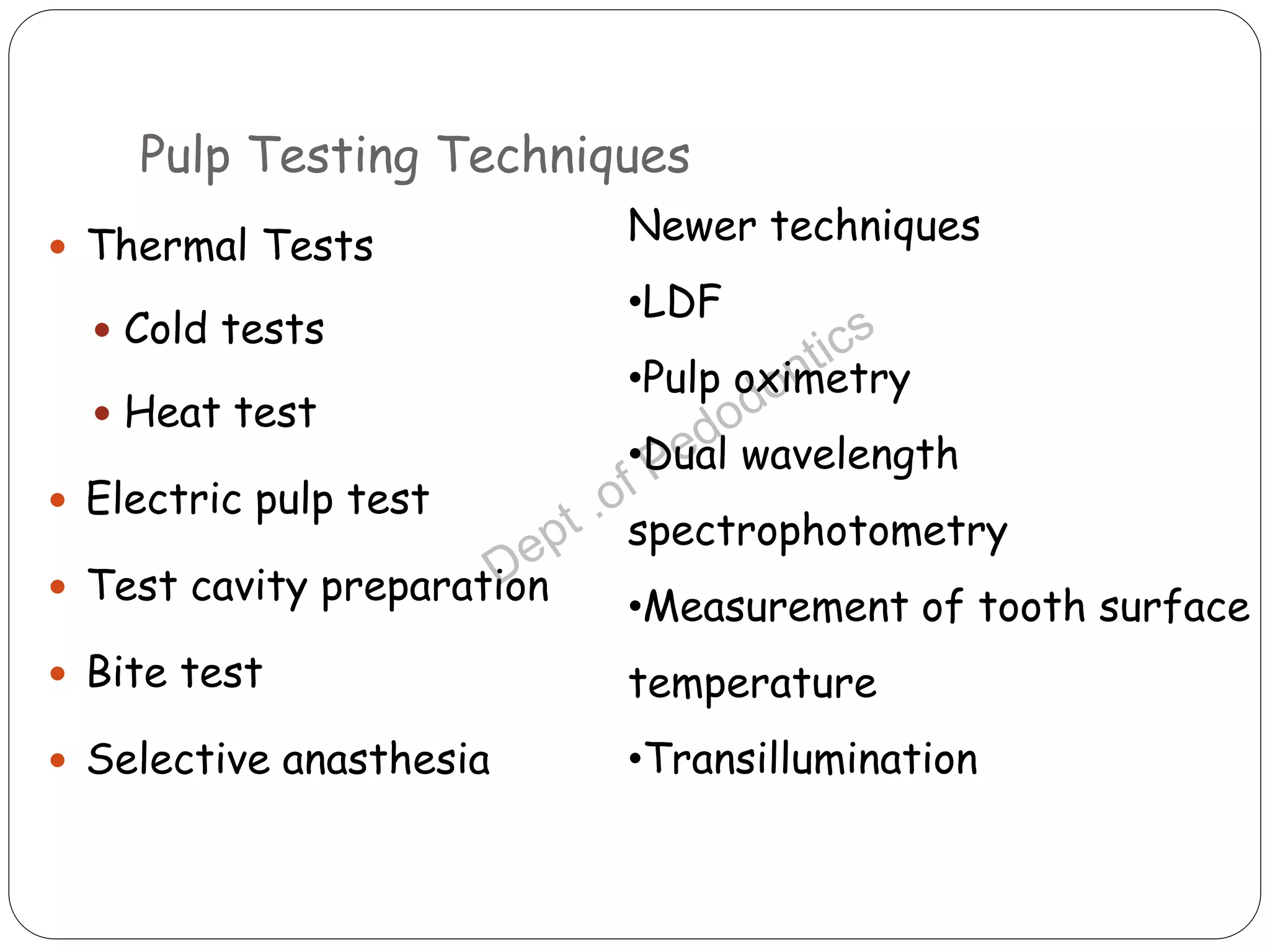
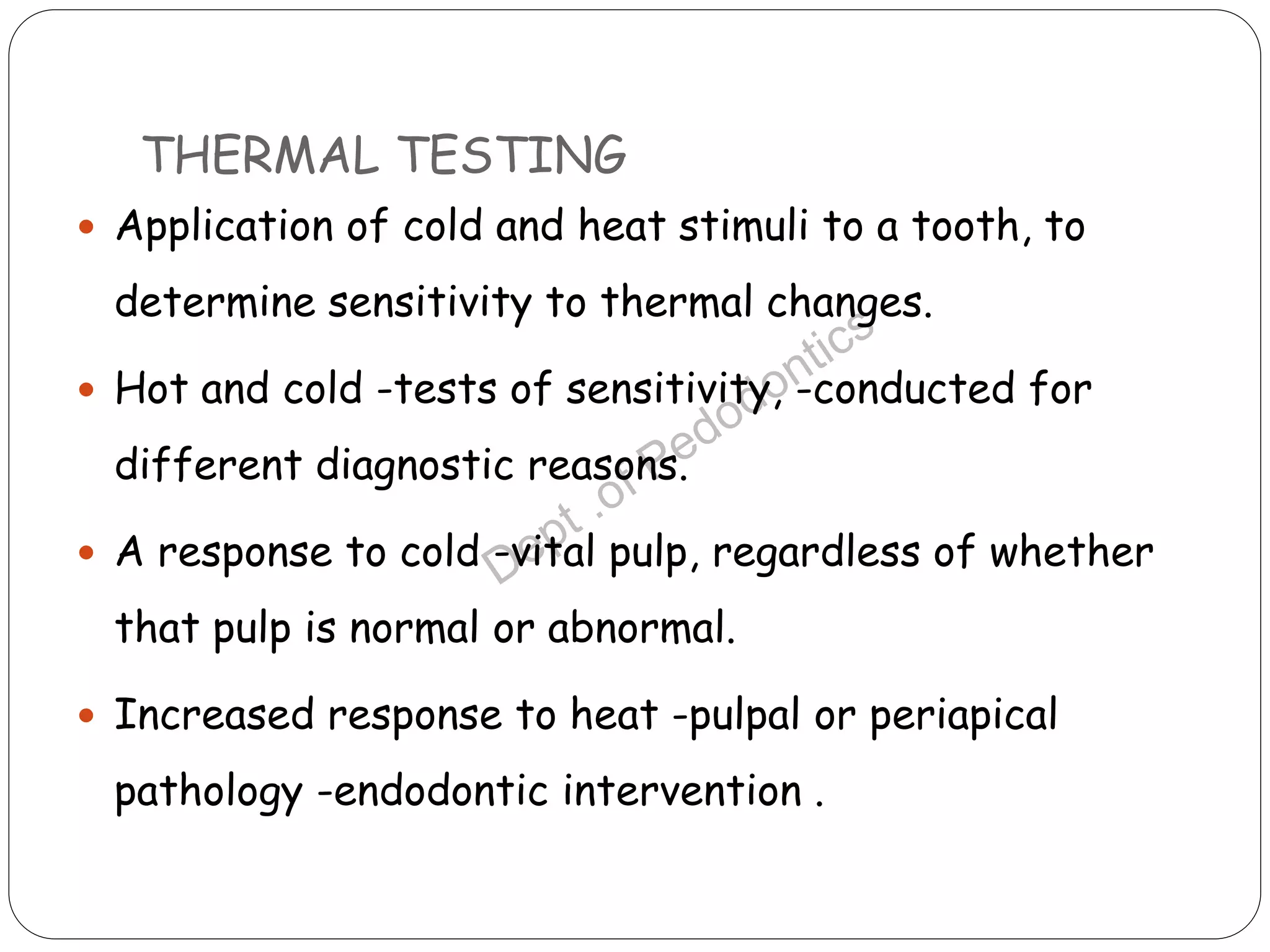
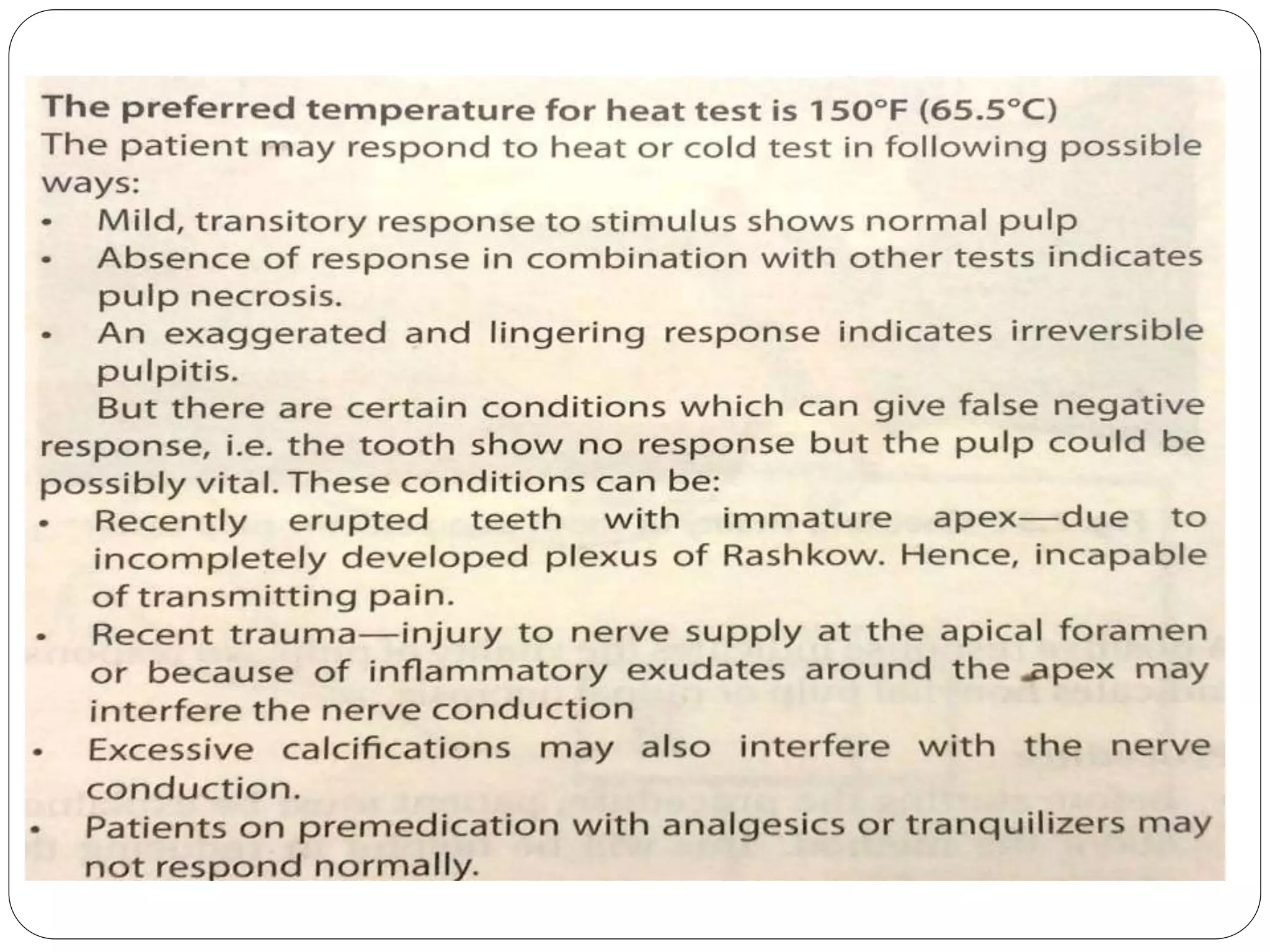
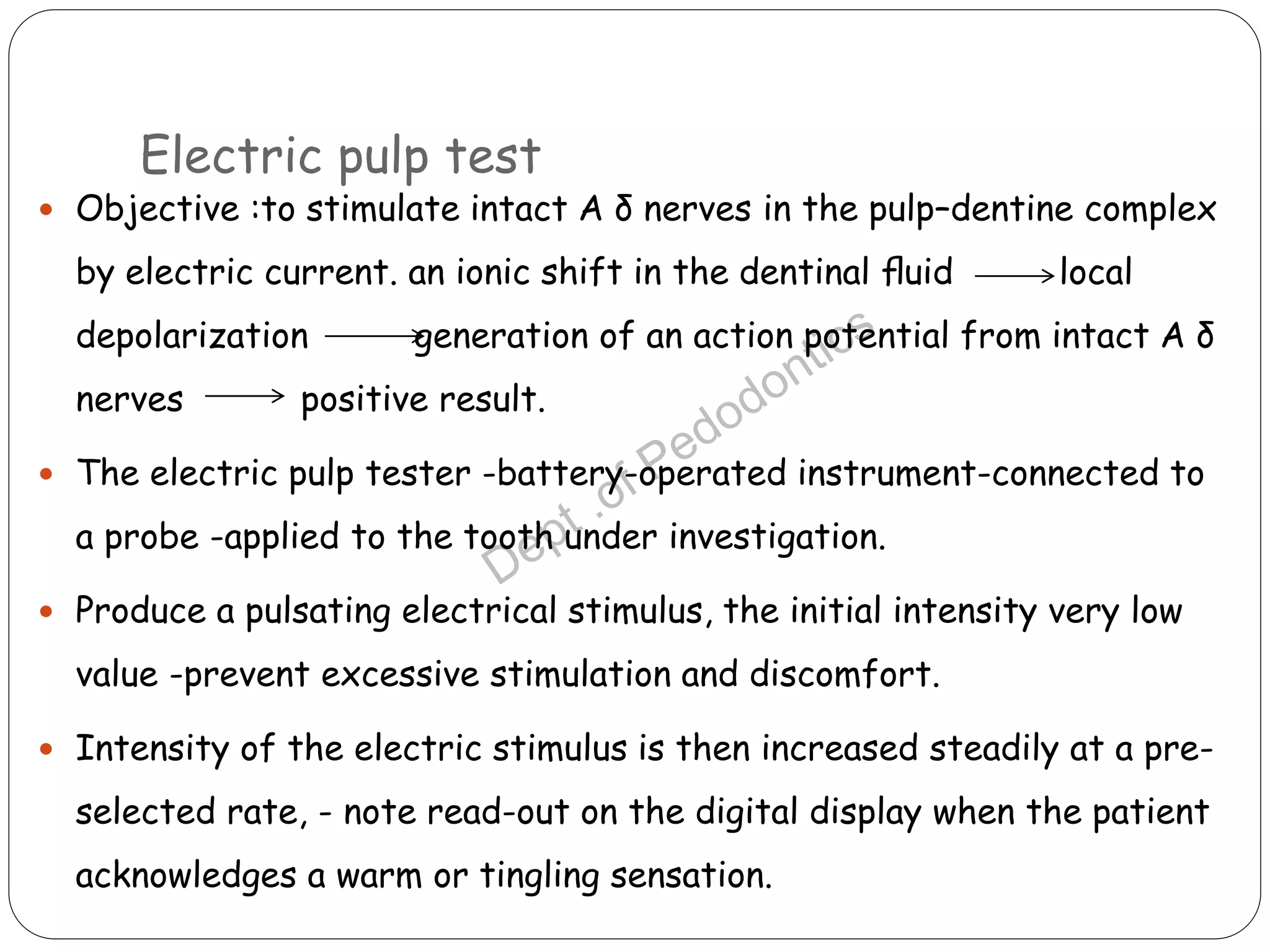
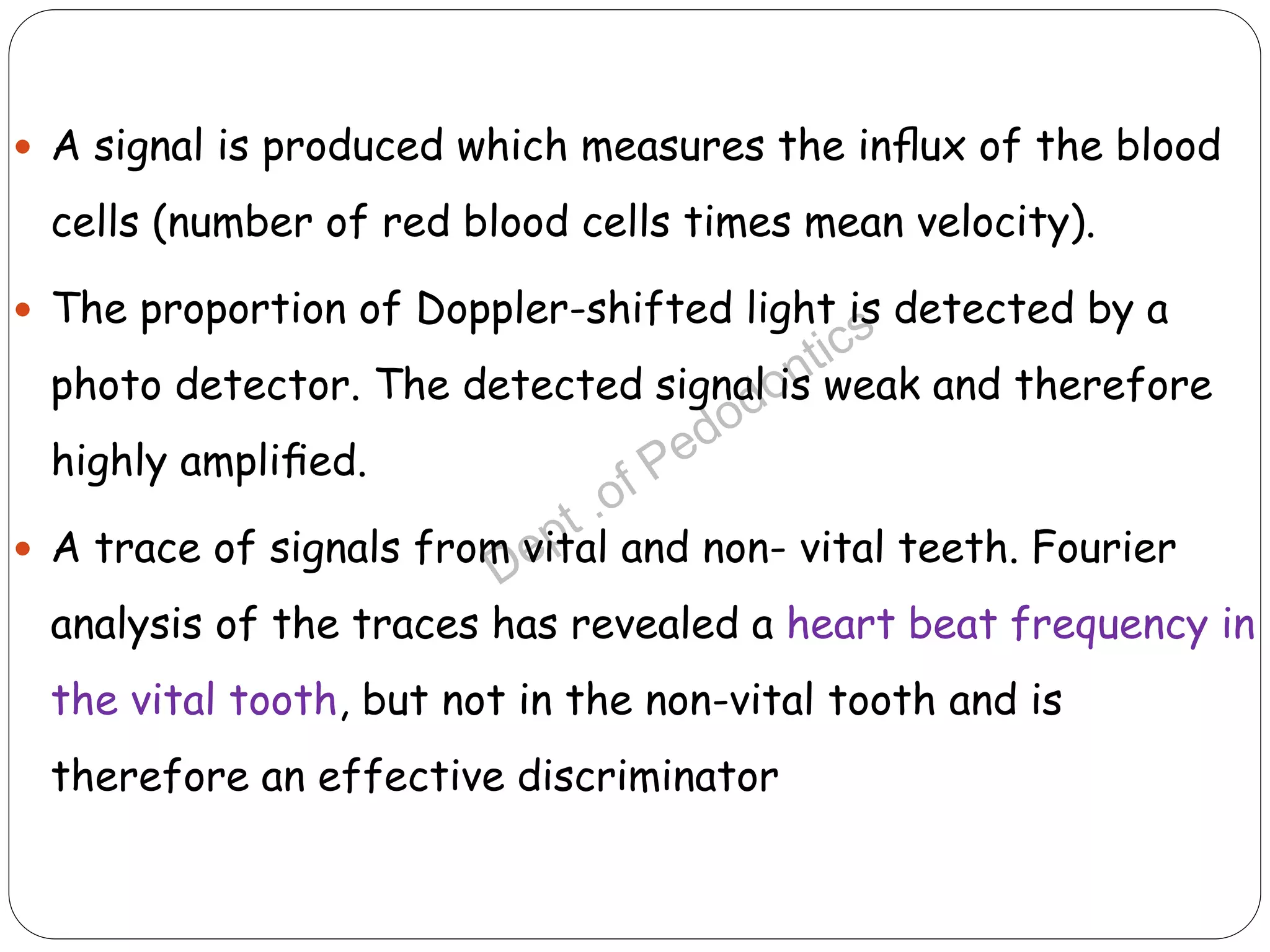
Pulp vitality and sensitivity tests are important diagnostic tools for assessing pulp status. Thermal tests using cold or heat are commonly used to stimulate pulp nerves. The electric pulp test provides a controlled electric stimulus to activate Aδ nerve fibers if the pulp is vital. Proper placement of the stimulus and interpretation of responses are needed for accurate results. Additional tests like bite testing can identify cracked teeth or evaluate periapical pathology responses. Combining history, examination findings, and multiple test results provides the best assessment of pulp conditions.