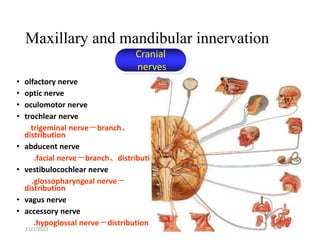
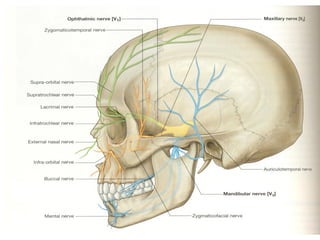
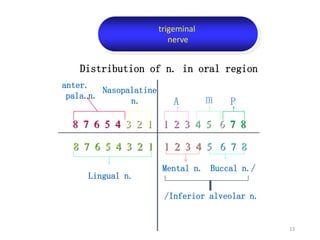
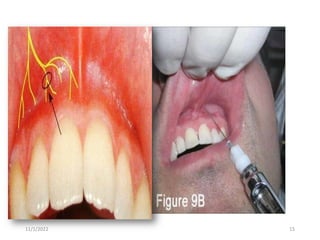
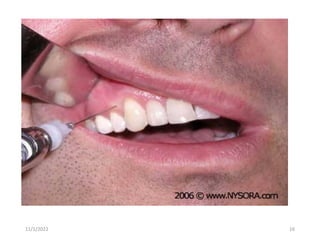
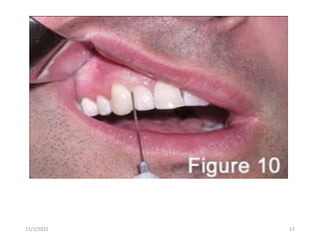
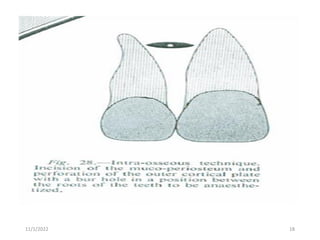
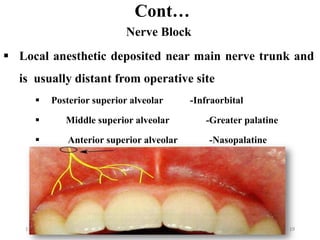
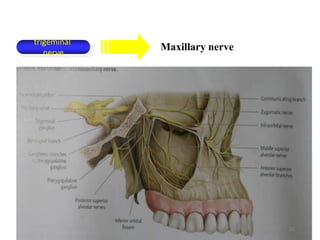
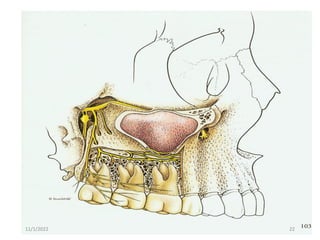
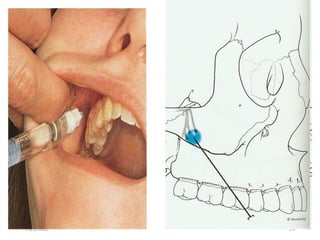
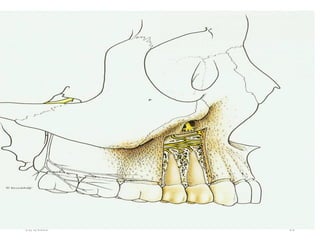
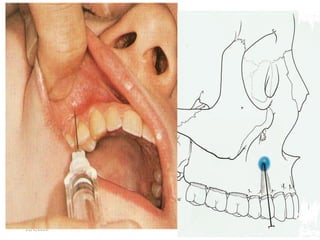
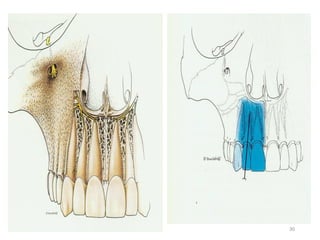
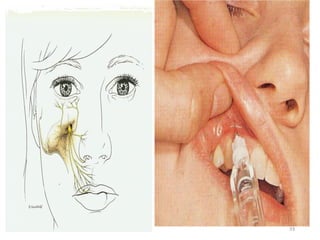
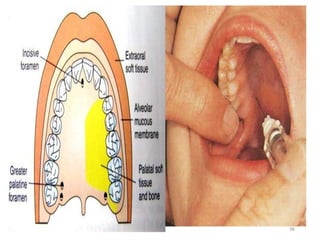
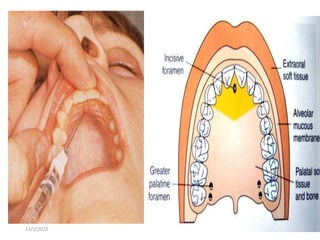
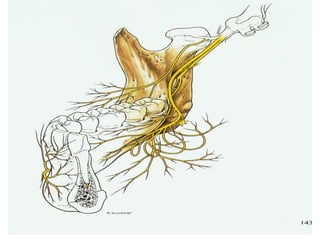
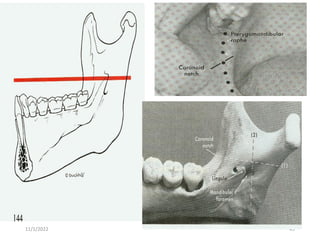
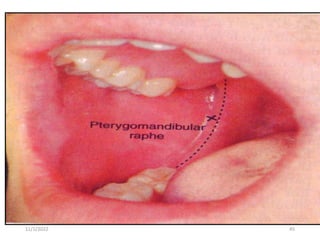
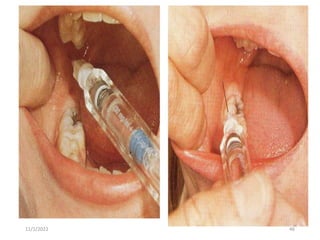
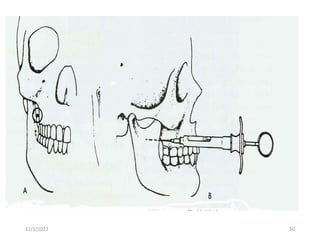
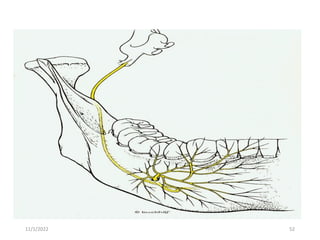
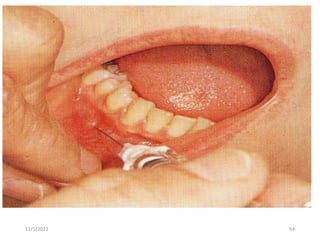
This document provides an overview of anesthesia considerations in dentistry. It defines local anesthesia and describes its role in decreasing pain during and after dental procedures. Various techniques for maxillary and mandibular anesthesia are outlined, including infiltration, nerve blocks, and specific block techniques for nerves like the posterior superior alveolar nerve. Advantages of local anesthesia are discussed along with precautions for safe injection and potential complications. Objectives of the seminar are to define anesthesia, understand its role in dentistry, identify different methods and limitations, and note advances in the field.