This document discusses concepts related to production planning and control, work study, and time study. It provides definitions and explanations of key terms:
- Production planning and control facilitates optimal capacity utilization, inventory control, production time efficiency, and quality assurance. It involves planning, routing, scheduling, loading, dispatching, follow up, inspection, and corrective measures.
- Work study aims to find the most efficient use of resources through analyzing work methods. It includes method study to evaluate and standardize work processes, and work measurement including time study to establish time standards.
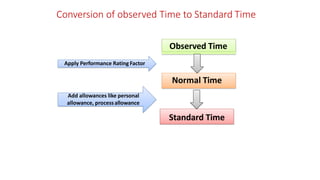
- Time study techniques measure times of job elements under specified conditions to determine the time needed at a defined performance rate, through stopwatch observation, normal