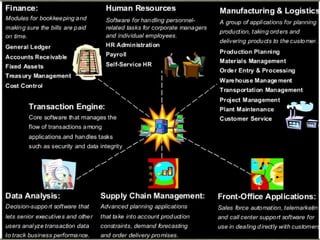
This presentation discusses the use of information technology in decision-making processes for businesses, covering the distinction between structured and unstructured problems and their respective approaches. It highlights the importance of gathering accurate data from various sources to aid managers in effective operations and provide various reporting formats. Additionally, it addresses how technology can facilitate group decision-making, particularly in time-sensitive environments with dispersed participants.