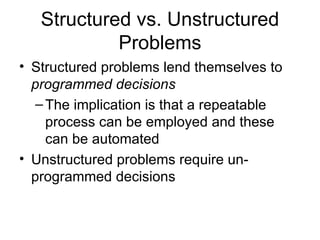
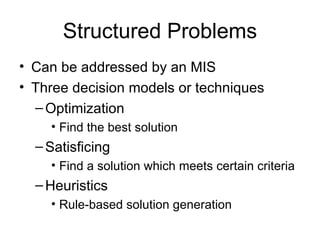
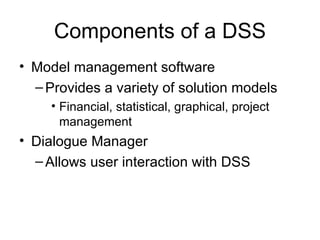
Management Information Systems (MIS) refers both to the study of information technology in business settings and to systems used to support operational and tactical decision making. There are different types of problems including structured problems, which can be addressed by programmed decisions and automated systems, and unstructured problems, which require unprogrammed decisions and can be addressed using decision support systems. The goals of an MIS are to provide managers with information to help with regular operations, control, organization, planning and decision making.