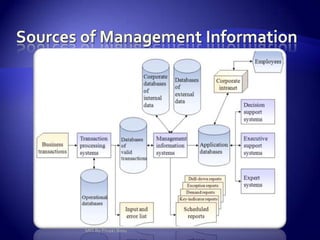
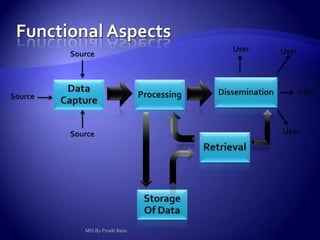
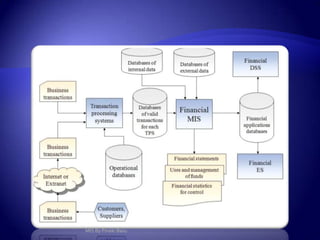
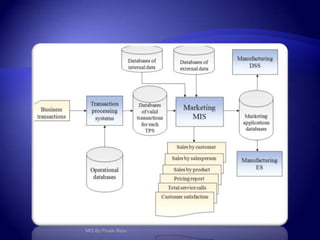
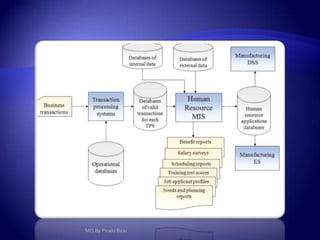
Management Information System (MIS) provides flexible and speedy access to accurate data for personal, professional, organizational, national, and global use. MIS processes data into information that is communicated to various departments in an organization to aid in decision making. It has various subsystems and outputs like scheduled reports, key indicator reports, and demand reports that provide information to managers. MIS takes inputs from various sources and uses information technology to collect and process data for management.