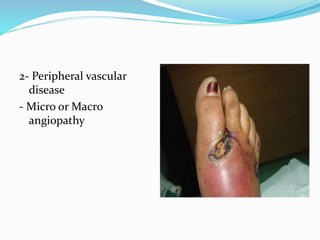
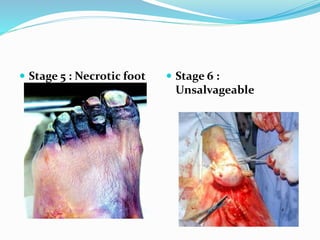
This document discusses the epidemiology, pathogenesis, pathology, classification, management, and treatment of diabetic foot. It notes that diabetic foot affects 15% of diabetics globally and can result in high rates of amputation. Management is multi-disciplinary and involves history, examination, investigations, prevention, wound care, offloading, revascularization procedures, and amputation if needed. Good diabetic control and foot care education are essential to preventing and treating diabetic foot complications.