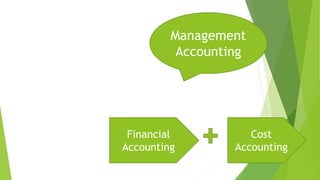
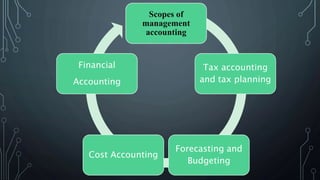
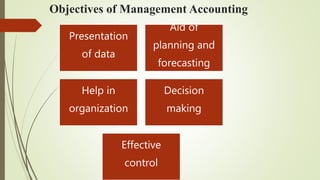
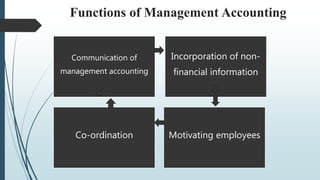
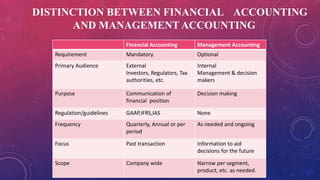
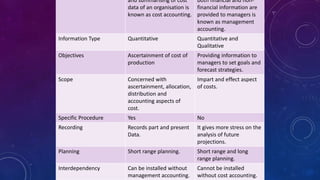
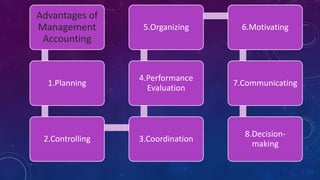
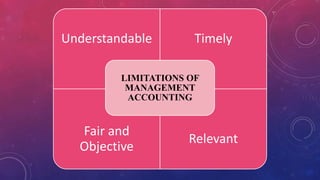
Management accounting involves the use of accounting information by managers for decision-making, planning, and control within organizations. It encompasses various scopes such as forecasting, budgeting, and cost accounting, providing both financial and non-financial information to aid in strategic planning. The document also outlines the tools and techniques of management accounting, its advantages, and distinctions from financial accounting.