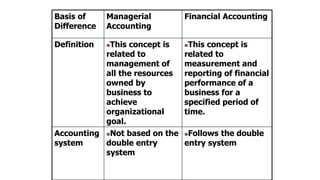
This document discusses management accounting concepts including definitions, classifications of costs, and the differences between management accounting and financial accounting. Management accounting is a tool that assists management in decision making and planning by providing both financial and non-financial information. It considers both quantitative and qualitative factors and future orientation. Costs can be classified in various ways including by element, function, inventoriability, traceability, and behavior. Management accounting differs from financial accounting in its focus on internal users, future orientation, and use of non-monetary factors.






![What is Financial Accounting?
• Financial accounting is the preparation and communication of financial
information to its users.
• Financial accounting is based on Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles[GAAP].
• It records only monetary transactions.
• It is fully guided by GAAP.
• The data and information which financial accounting provides is
historical natured.
• Under financial accounting, the reports are generally prepared for a
certain specified period.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managementaccounts-230108020410-aa94bfa0/85/Management-Accounts-pptx-7-320.jpg)