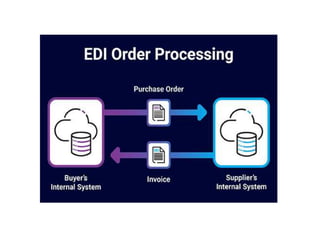
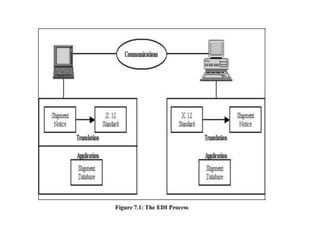
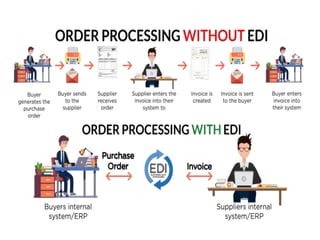
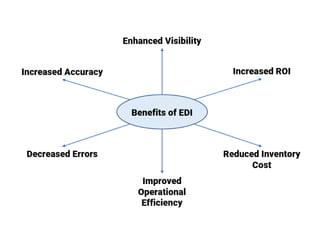
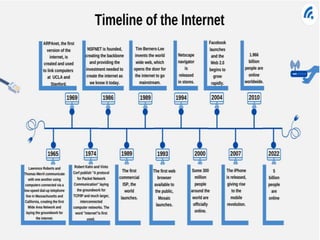
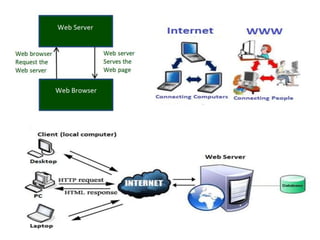
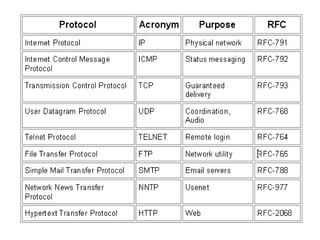
The document discusses electronic data interchange (EDI) and the internet. It defines EDI as the electronic exchange of business documents between organizations in a standardized format. Common documents exchanged via EDI include invoices, purchase orders, and shipping notices. The document also outlines several benefits of EDI for industries like retail, manufacturing, and automobiles. It provides a brief history of the internet and defines key terms like protocols and the world wide web. EDI is useful for regular exchanges between business partners in industries like supply chain management.