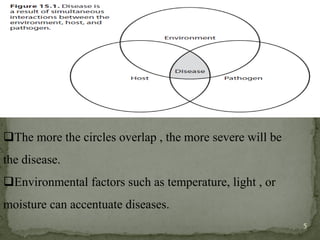
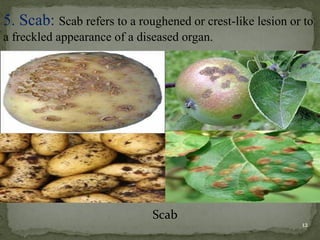
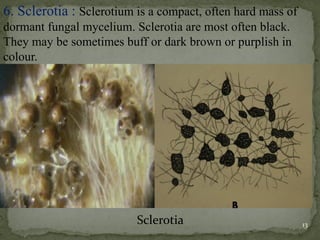
This document provides an overview of plant diseases, categorizing them into infectious and non-infectious types, and detailing the conditions required for disease development. It discusses the disease cycle, symptoms of diseases, and various control methods, including exclusion, eradication, and resistance. Key examples of plant diseases and their specific symptoms are also described.