Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX







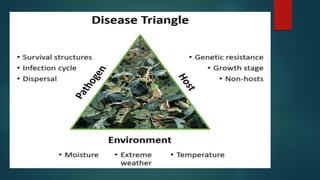










Integrated Disease Management (IDM) involves using pesticides only when disease incidence reaches economic threshold levels, promoting natural biocontrol agents. IDM uses cultural, biological, and limited chemical controls to keep disease below economic levels. It has four components: host resistance, biological control, need-based chemical control, and culture control like intercropping and crop rotation.

















