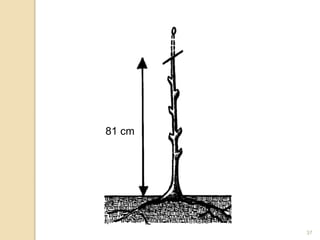
1) Fruit and nut trees are pruned and trained to develop a strong structure that can support heavy crops without breaking. Pruning is also needed to maintain size, remove undesirable growth, and stimulate flowering and fruiting.
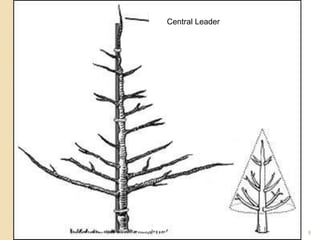
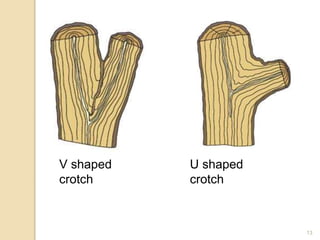
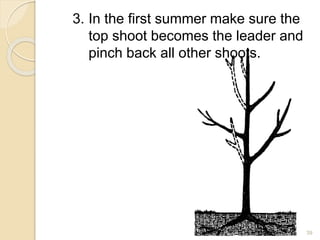
2) It is important to understand tree structures like the central leader, scaffold branches, and branch attachments when pruning. V-shaped crotches are weak while U-shaped crotches are strong. Watersprouts, suckers, and crossing branches should be removed.
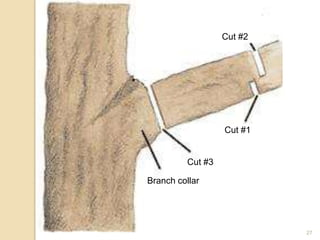
3) When pruning large limbs, an undercut should be made followed by a cut further out on the limb to allow it to swing away from the tree before being cut off close to the trunk to avoid stripping bark