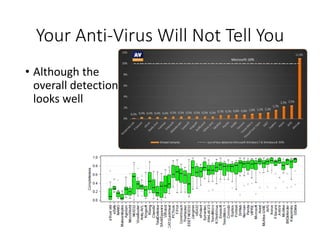
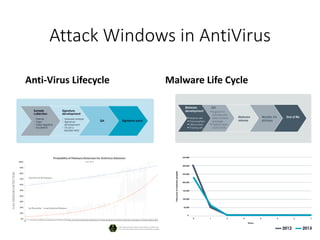
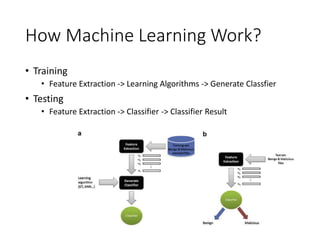
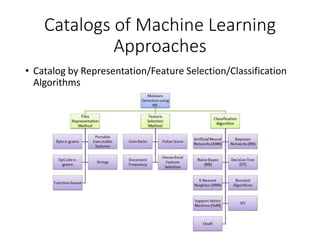
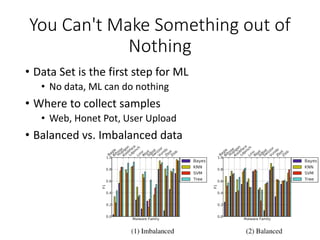
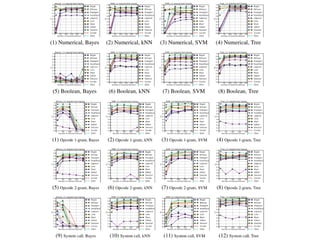
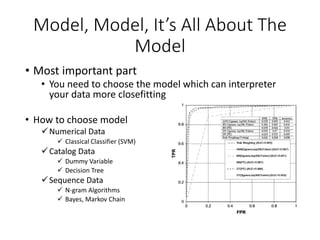
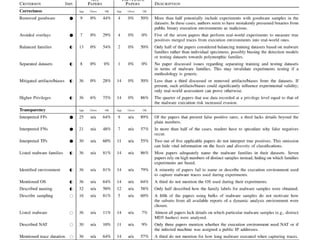
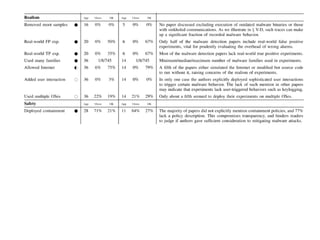
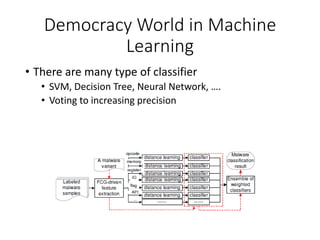
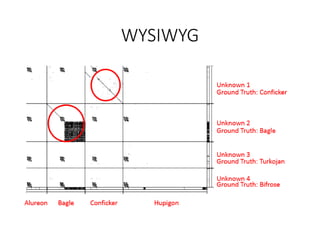
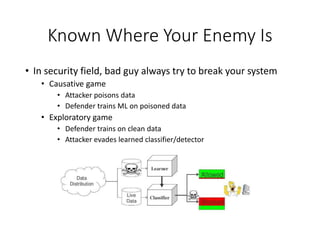
This document discusses machine learning approaches for malware detection. It notes that millions of new malware are created each year, making it difficult for signature-based antivirus software to keep up. Machine learning is presented as a potential solution by automatically constructing models to detect malware based on training data. However, the quality of the training data and features is critical, as machine learning risks producing garbage outputs from garbage inputs. Different machine learning algorithms and evaluation benchmarks are also discussed.