This document summarizes information about Android malware, including its goals, installation methods, evasion techniques, and detection methods. Some key points:
- Malware goals include sending premium SMS, stealing banking info, adware click fraud, and ransomware. It can also mine bitcoin or exfiltrate personal data.
- It installs via repackaged apps, update attacks, drive-by downloads, or by misusing accessibility services. Packers encrypt the APK to evade detection.
- Evasion techniques include dynamic C&C domains, encryption, reflection, delaying attacks, and polymorphism/metamorphism. It also checks for emulators or debuggers.
- Detection analy

















![Detect if running in debugger
Check Debug.isDebuggerConnected(), Debug.waitingForDebugger()
Launch multiple threads and let one thread attach to another using
ptrace(), because a process can only be attached by one process.
[Packergrind paper]
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidmalwarepresentation-180711133900/85/Android-malware-presentation-19-320.jpg)








![Dynamic Analysis - Andrubis
Andrubis does “Stimulation” instead of passive wait or UI exploration.
1. Invoke all Activities (not just Main) found in the Manifest
2. Patch Android ActivityManager to start all background services
automatically.
3. Intercept calls to “registerReceiver” and use ActivityManager to
invoke them.
4. Broadcast common events such as SMS, WiFi+3G connectivity, GPS
lock, phone calls, phone state changes to trigger OS and App
behaviour.
Andrubis is now commercial - Lastline
[Weichselbaum, et al. Andrubis. Android Malware under the magnifying glass ]
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidmalwarepresentation-180711133900/85/Android-malware-presentation-28-320.jpg)
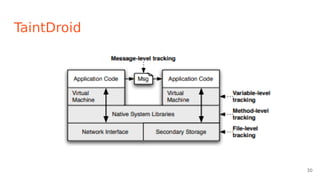
![TaintDroid
Leverages Android virtualized env. Assumes no app is trusted.
It labels (taints) data from privacy-sensitive sources
Transitively applies labels as sensitive data propagates through program
variables, files, and interprocess messages.
When tainted data are transmitted over the network, or otherwise leave
the system, TaintDroid logs the data’s labels, the application responsible
for transmitting the data, and the data’s destination.
[Enck, et al. TaintDroid - OSDI 2010]
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidmalwarepresentation-180711133900/85/Android-malware-presentation-29-320.jpg)

![How to beat the Packers
Some packers decrypt the original APK at known locations in RAM. Use
that to find and analyze the decrypted APK at runtime.
[ Strazzere talk at Defcon 14 https://github.com/strazzere/android-unpacker ]
DexHunter modified Dalvik runtime(ART/OAT) to trap ClassLoader.
[ Zhang, et al. DexHunter ESORICS 2015 https://github.com/zyq8709/DexHunter ]
PackerGrind
[ Xue, et al. Adaptive Unpacking of Android Apps ]
DaBID Debugger [Blackhat Asia 2015]
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidmalwarepresentation-180711133900/85/Android-malware-presentation-32-320.jpg)

![ML model over opcode sequences
ML : the holy grail !
Treat opcode sequence as text.
Formulate malware recognition as an NLP problem.
Feed the opcode sequence to a Neural Net.
System dynamically learns the length of the n-gram which is most
relevant.
[ McLaughlin et al. Deep Android Malware Detection. ODASPY 2017 ]
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidmalwarepresentation-180711133900/85/Android-malware-presentation-34-320.jpg)