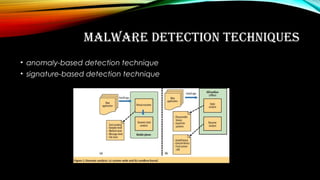
This document discusses data mining techniques for malware detection. It introduces the concepts of data mining, describes common types of malware like viruses, worms and trojans, and covers techniques for malware detection including anomaly-based detection, signature-based detection and clustering algorithms like k-means. Applications of data mining are also discussed along with potential advantages and disadvantages.