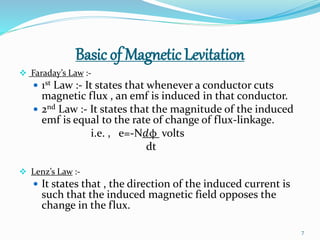
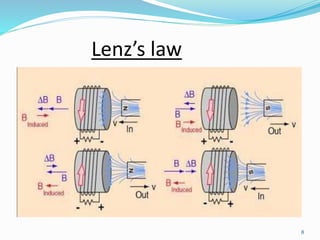
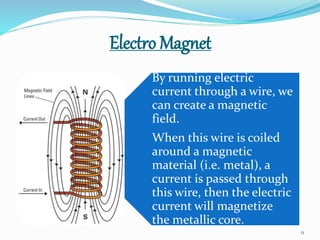
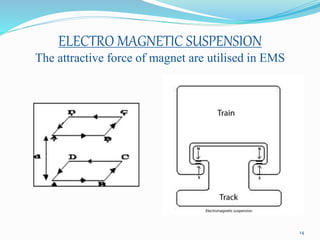
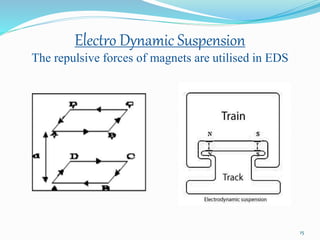
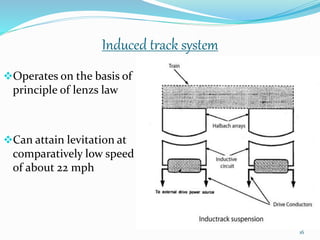
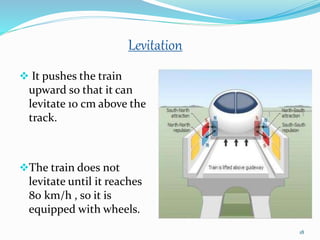
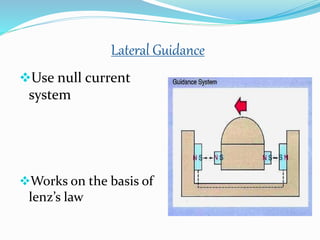
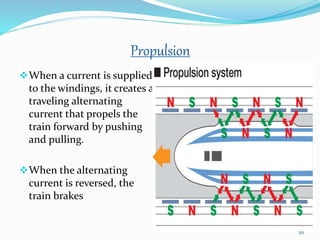
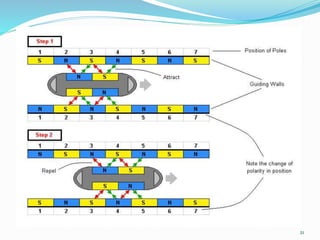
The seminar discusses magnetic levitation (maglev) technology, specifically focused on maglev trains that utilize magnetic forces for lift and propulsion, eliminating friction for high-speed travel. It covers the history, types of magnetic levitation, key technologies, advantages, limitations, and future prospects, highlighting their energy efficiency and environmental benefits. The conclusion emphasizes that maglev trains are a safe and efficient mode of transportation.