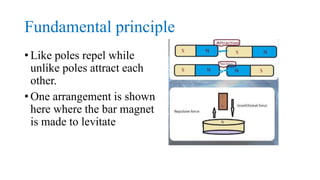
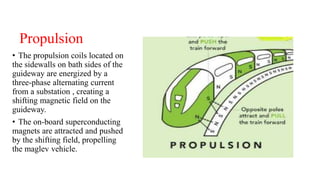
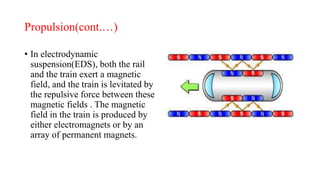
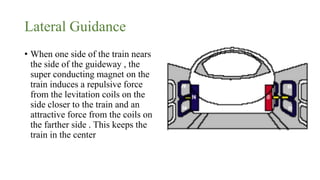
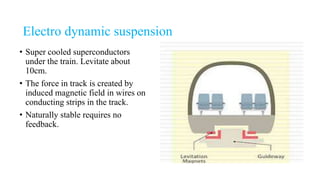
Maglev trains use magnetic levitation to float and propel trains along guideways without touching the track. There are two main levitation techniques: electromagnetic suspension uses electromagnets on the train and ferromagnets on the track to attract the train upwards; electrodynamic suspension uses superconducting magnets on the train that repel from induction coils on the track to levitate the train 10cm above. Propulsion is achieved through propulsion coils on the guideway that create a shifting magnetic field to push the on-board superconducting magnets. Lateral guidance coils ensure the train remains centered through attractive and repulsive magnetic forces.