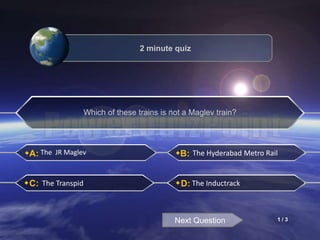
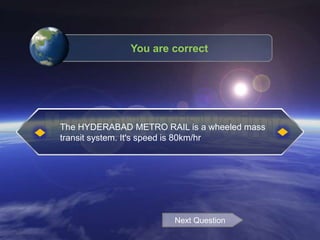
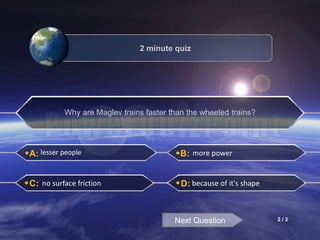
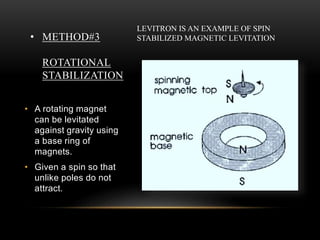
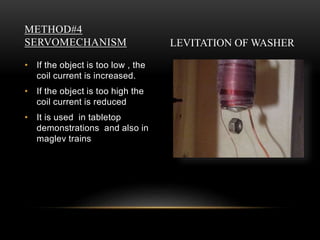
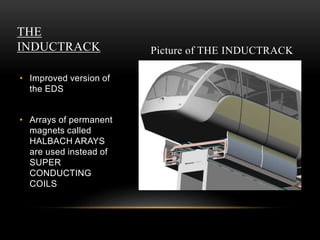
The document discusses different methods of magnetic levitation or maglev. It describes 4 main methods - diamagnetism, superconductors, rotational stabilization, and servomechanism. It provides examples of using each method to levitate small objects like graphite or large objects like maglev trains. The document also discusses the working of maglev trains in detail, covering electromagnetic suspension and electrodynamic suspension systems. It highlights the advantages of maglev trains like very high speeds and less maintenance compared to wheeled trains.
![MAGNETIC LEVITATION
[MAGLEV]
BY
Sathish & sai charan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-1-320.jpg)
![LEVITATION MEANS TO RISE
OR HOVER IN THE AIR
Levitation as shown in magic shows and
movies [not possible without tricks]
TRICKS AND ILLUSIONS USED SPECIAL EFFECTS USED](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-2-320.jpg)




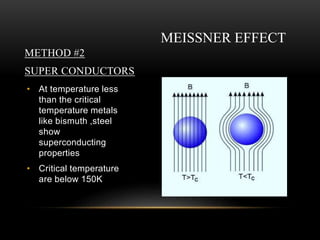




![MAGLEV
TRAINS
• Two types of maglev
trains have been
developed.
1. EMS MAGLEV
TRAIN developed in
GERMANY
[TRANSRAPID]
2. EDS MAGLEV
TRAIN developed in
JAPAN.[JR MAGLEV
shown in picture ]
The highest recorded speed of the
JR MAGLEV train is 581 kilometres per
hour (361 mph),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-14-320.jpg)
![ELECTROMAGNETIC
SUSPENSION[EMS]
• Electromagnets
controlled by
computers are used.
• They are present on
the sides and the
underside of the train.
• Attraction between the
steel track and
magnet on the
underside levitates
the train.
How does the train rise?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-15-320.jpg)
![ELECTRO MAGNETIC
SUSPENSION[EMS]
GUIDING MAGNETS
• Magnetic forces may
not be constant on
the two sides.
• So ,electromagnets
are controlled by
computers to keep
the train in the
center.
front view of guiding magnets
side view](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-16-320.jpg)
![• Picture showing aluminium
windings
ELECTRO MAGNETIC
SUSPENSION[EMS]
PROPULSION
• Aluminium three
phase windings are
present in the track.
• When a current is
supplied to the
windings, it creates a
traveling alternating
current that propels
the train forward by
pushing and pulling.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-17-320.jpg)
![ELECTRO MAGNETIC
SUSPENSION[EMS]
BRAKING
• When the alternating
current is reversed, the
train brakes.
• Different speeds are
achieved by varying the
intensity of the current.
• Only the section of track
where the train is
traveling is electrified.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-18-320.jpg)
![ELECTRO DYNAMIC
SUSPENSION [EDS]
LEVITATION
• In electrodynamic
suspension (EDS), a
repulsive magnetic
field between the train
and the track levitates
the train.
• . Superconductors
cooled by liquid
helium or liquid
nitrogen are used in
the train and the track.
The JR-Maglev](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-19-320.jpg)
![ELECTRO DYNAMIC
SUSPENSION [EDS]
PROPULSION
• The train is naturally
stable.
• An alternating
current runs throw
the track.
• For braking it moves
in the reverse
direction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-20-320.jpg)

![ADVANTAGES OF MAGLEV TRAINS
• An average speed of
300mph is achieved.
• Time taken to reach
destination is as
good as an airplane
[including check in
and check out time ].
• Safer as there is no
risk of derailing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/magneticlev-170821152823/85/Magnetic-lev-23-320.jpg)