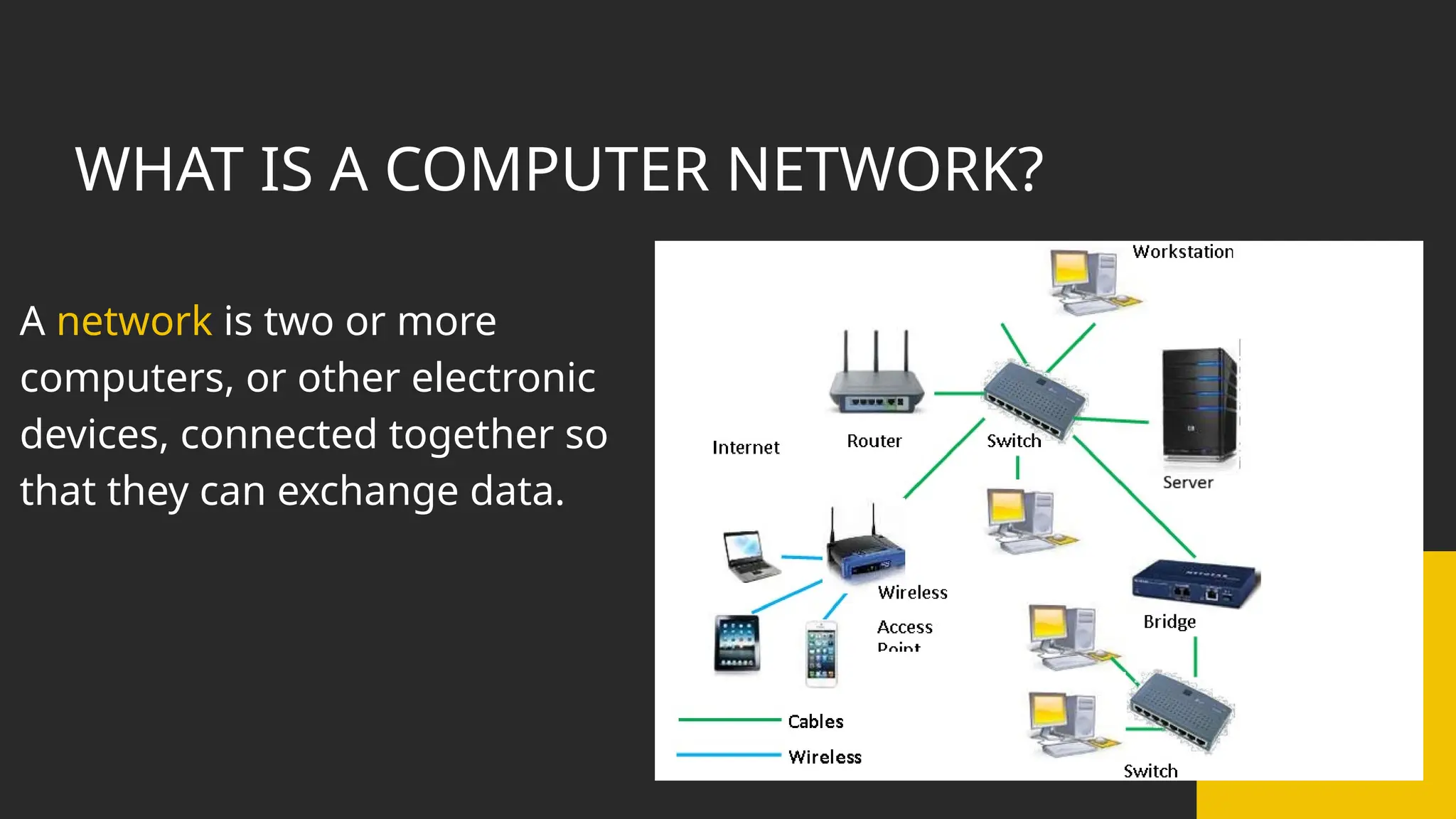
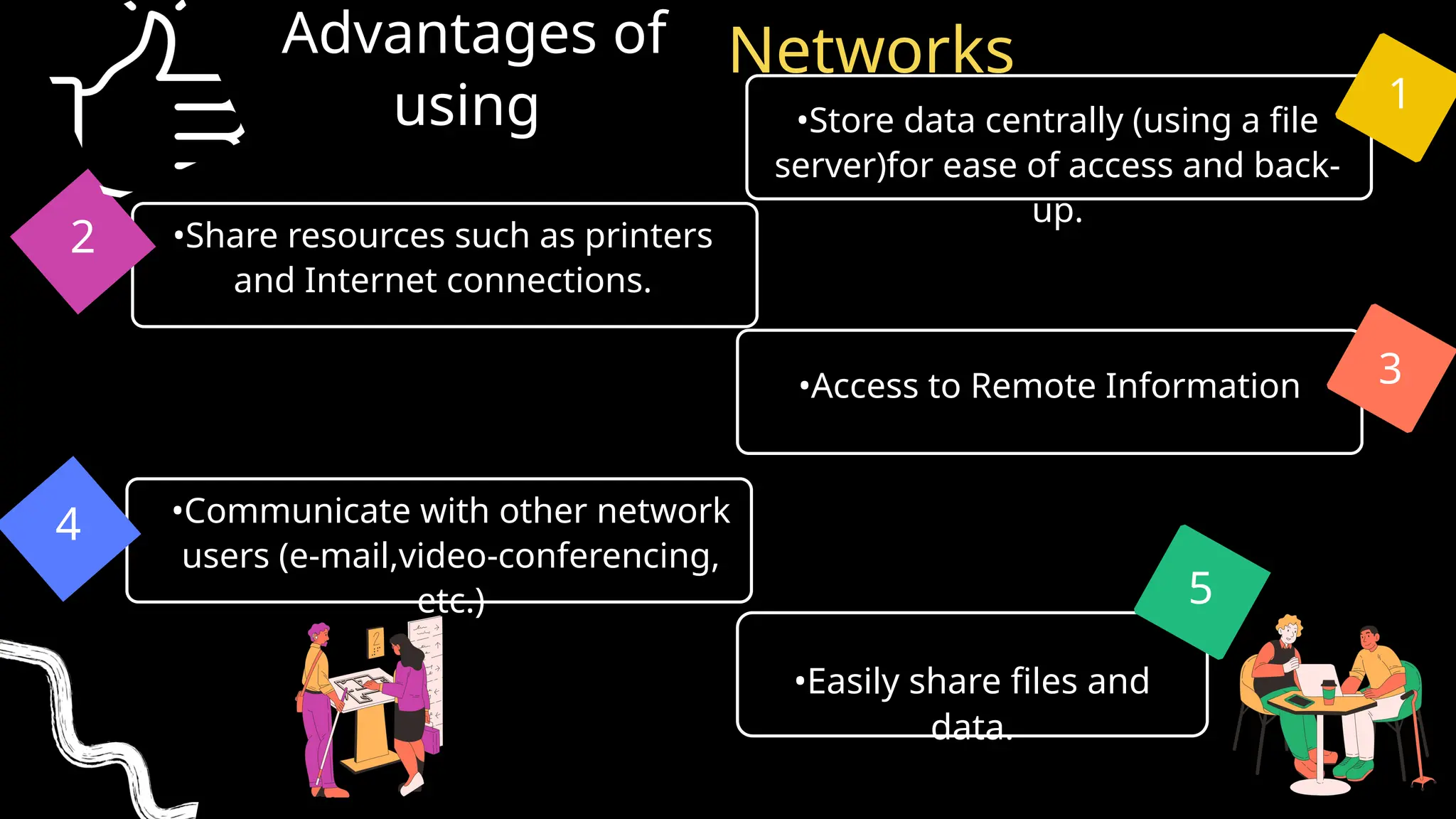
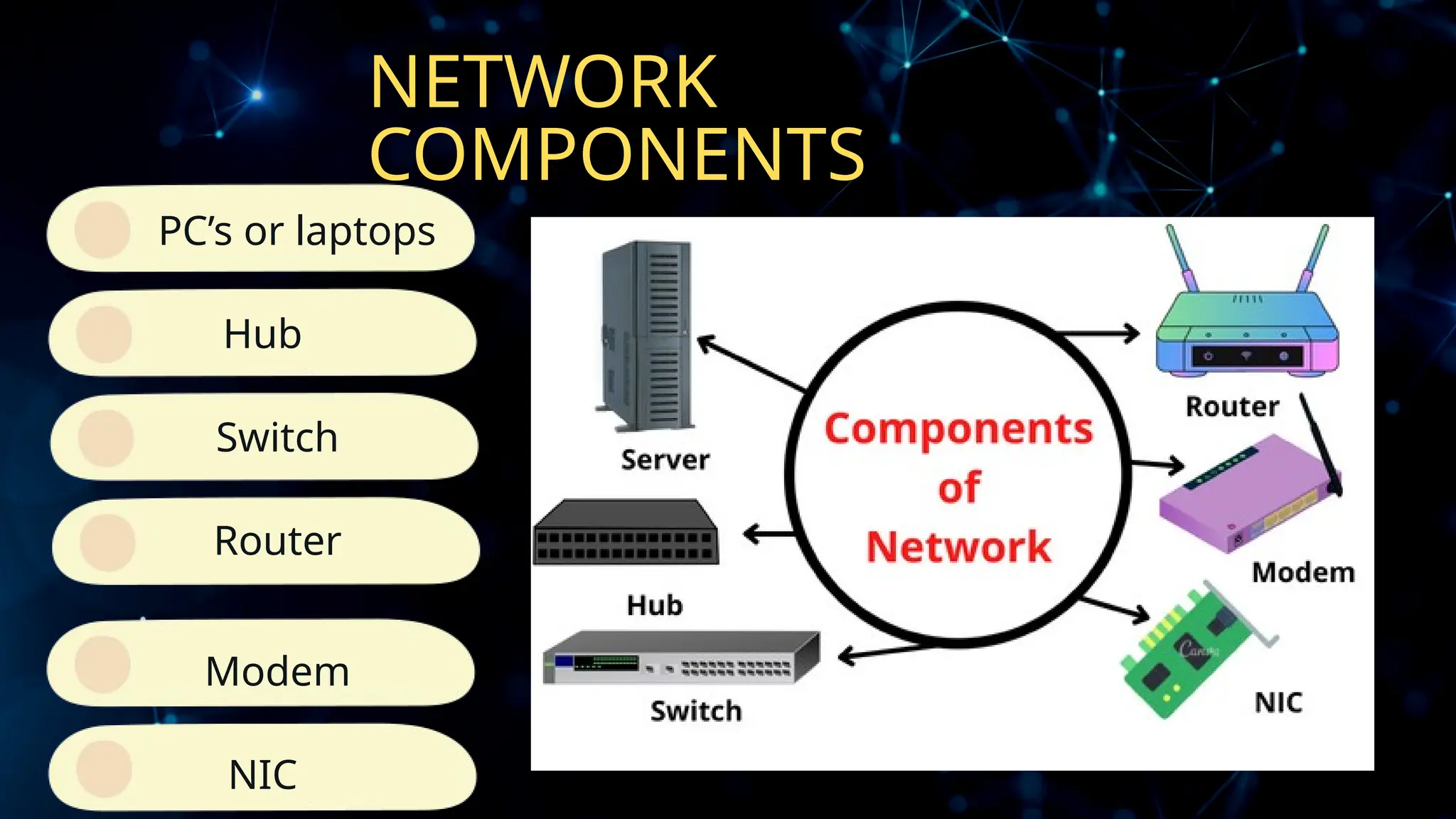
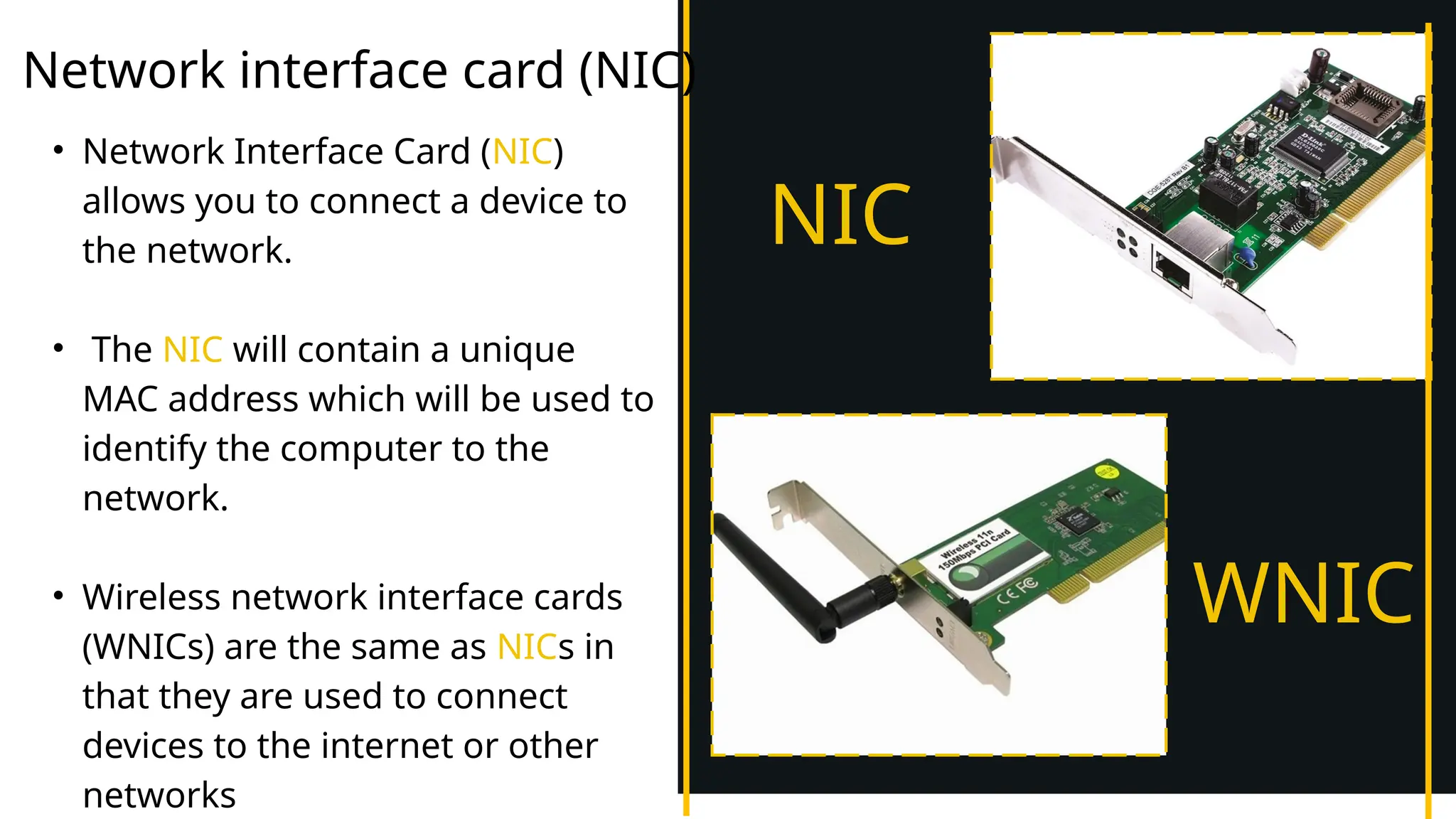
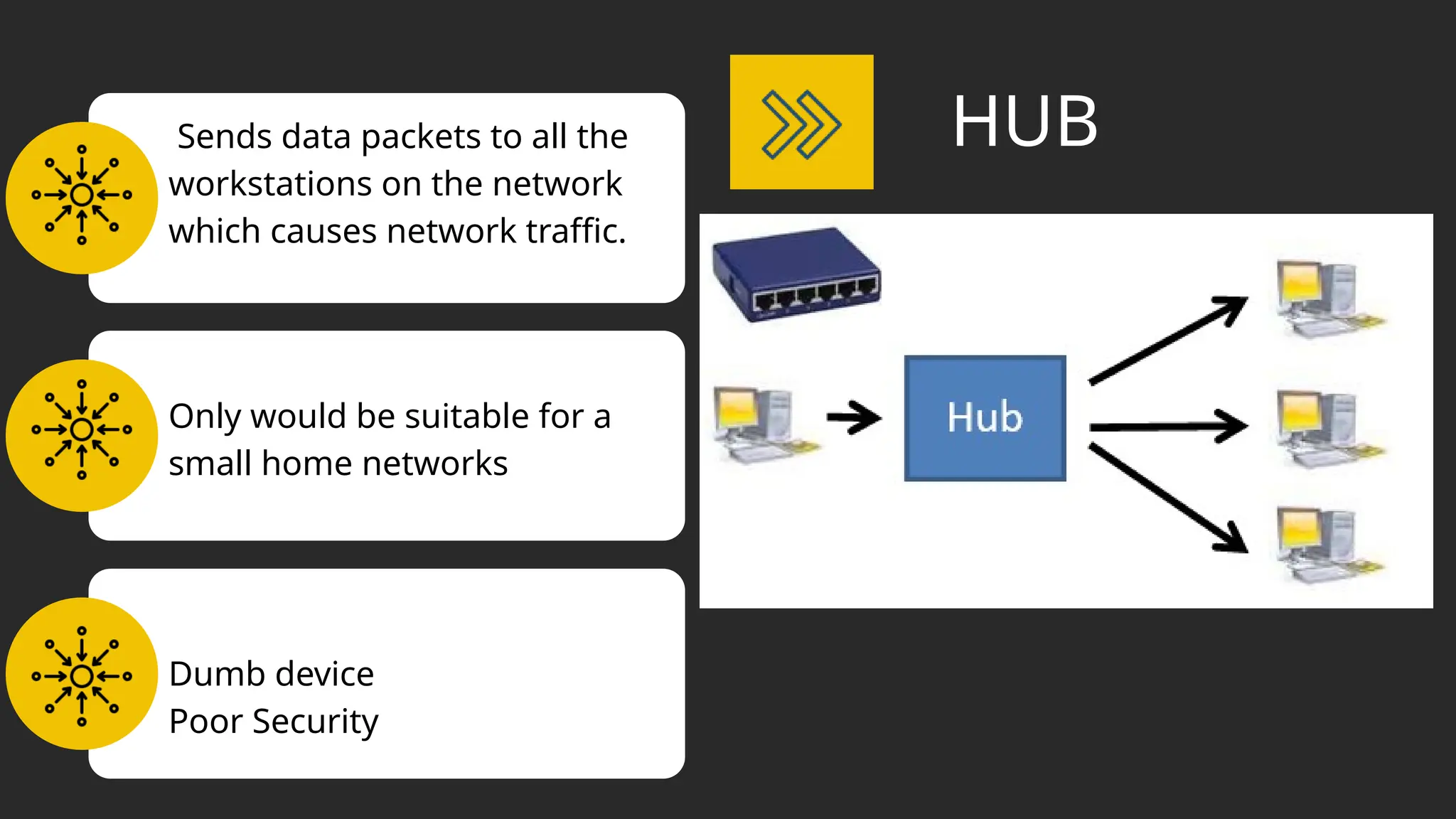
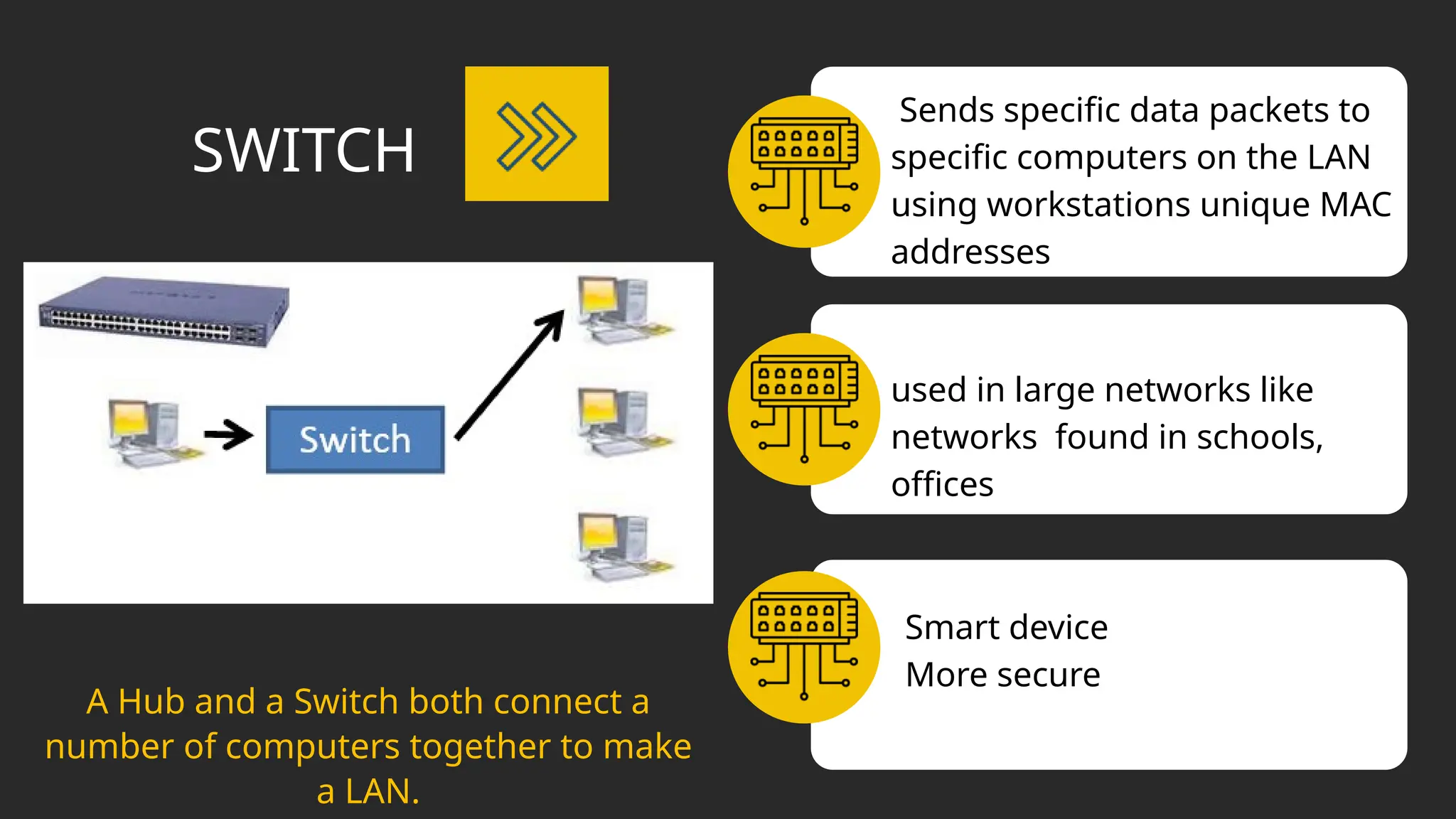
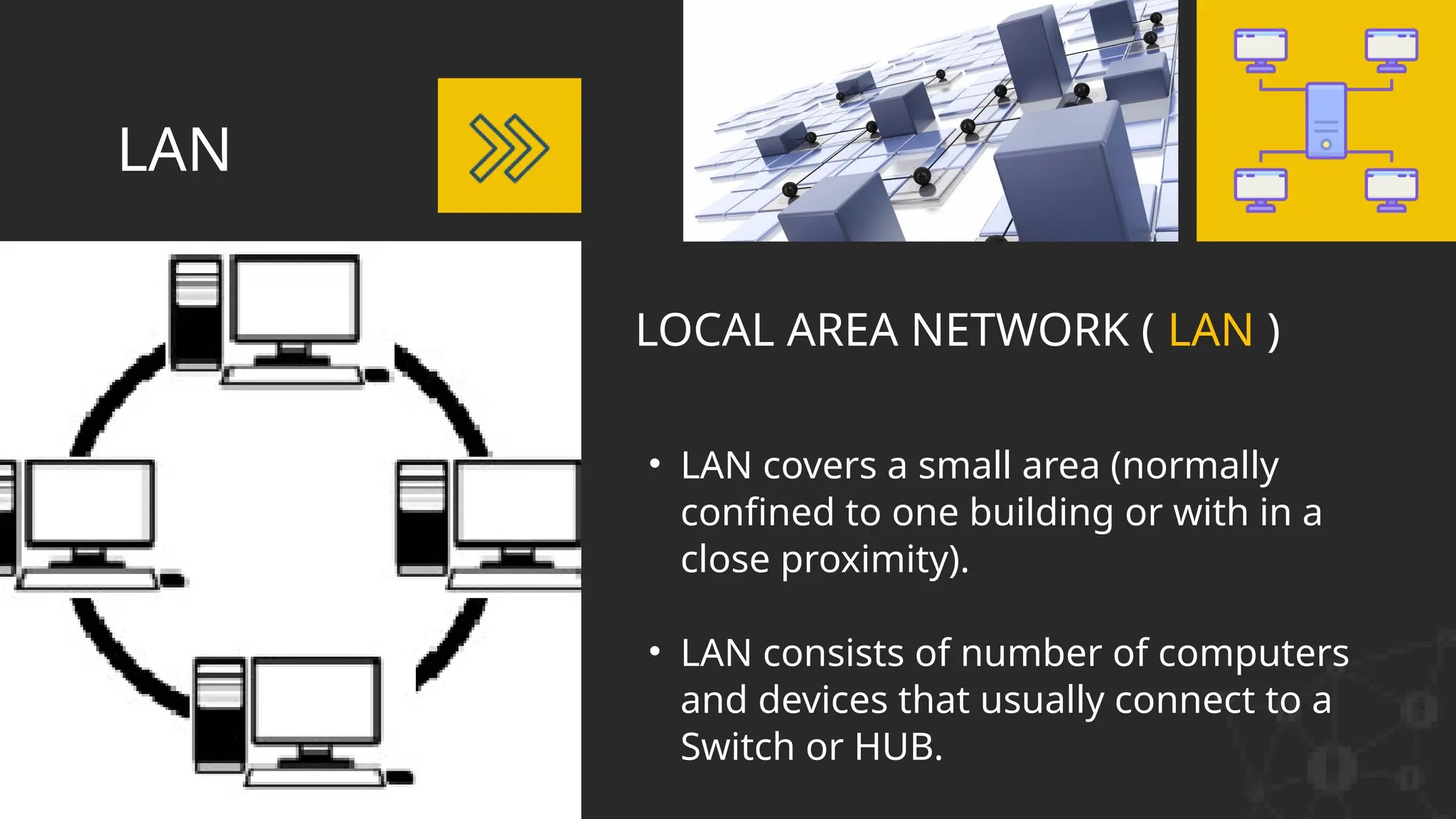
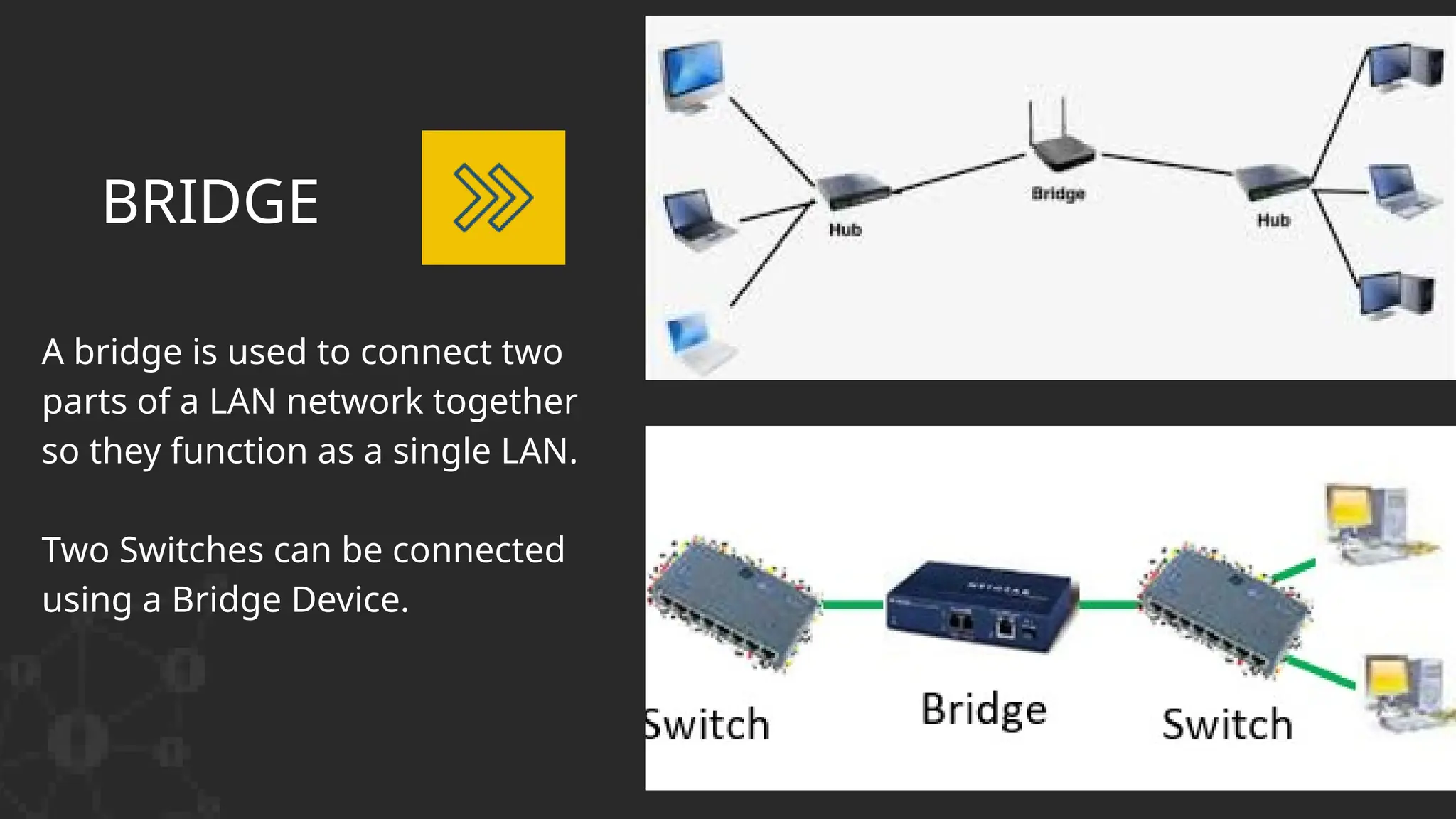
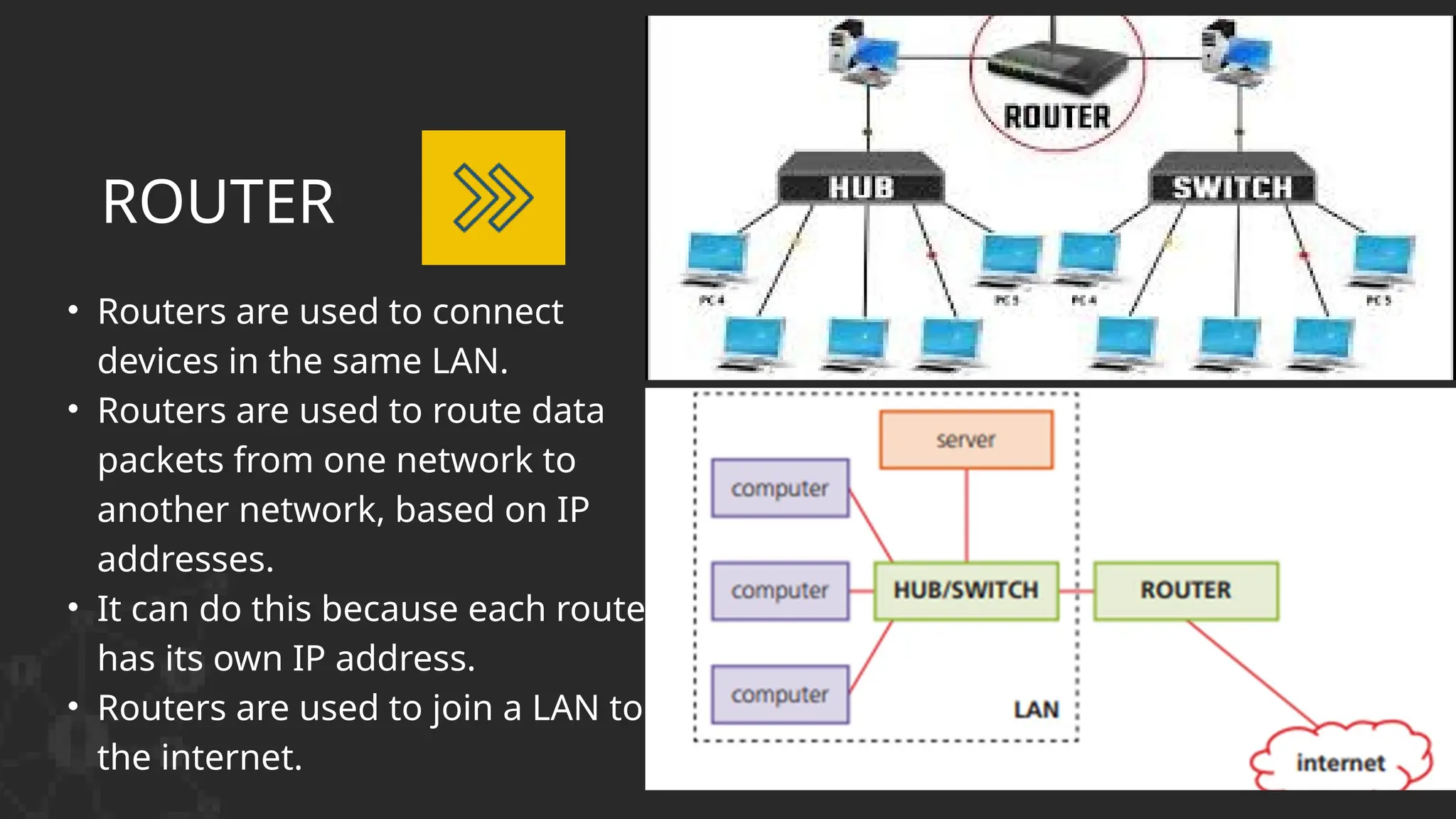
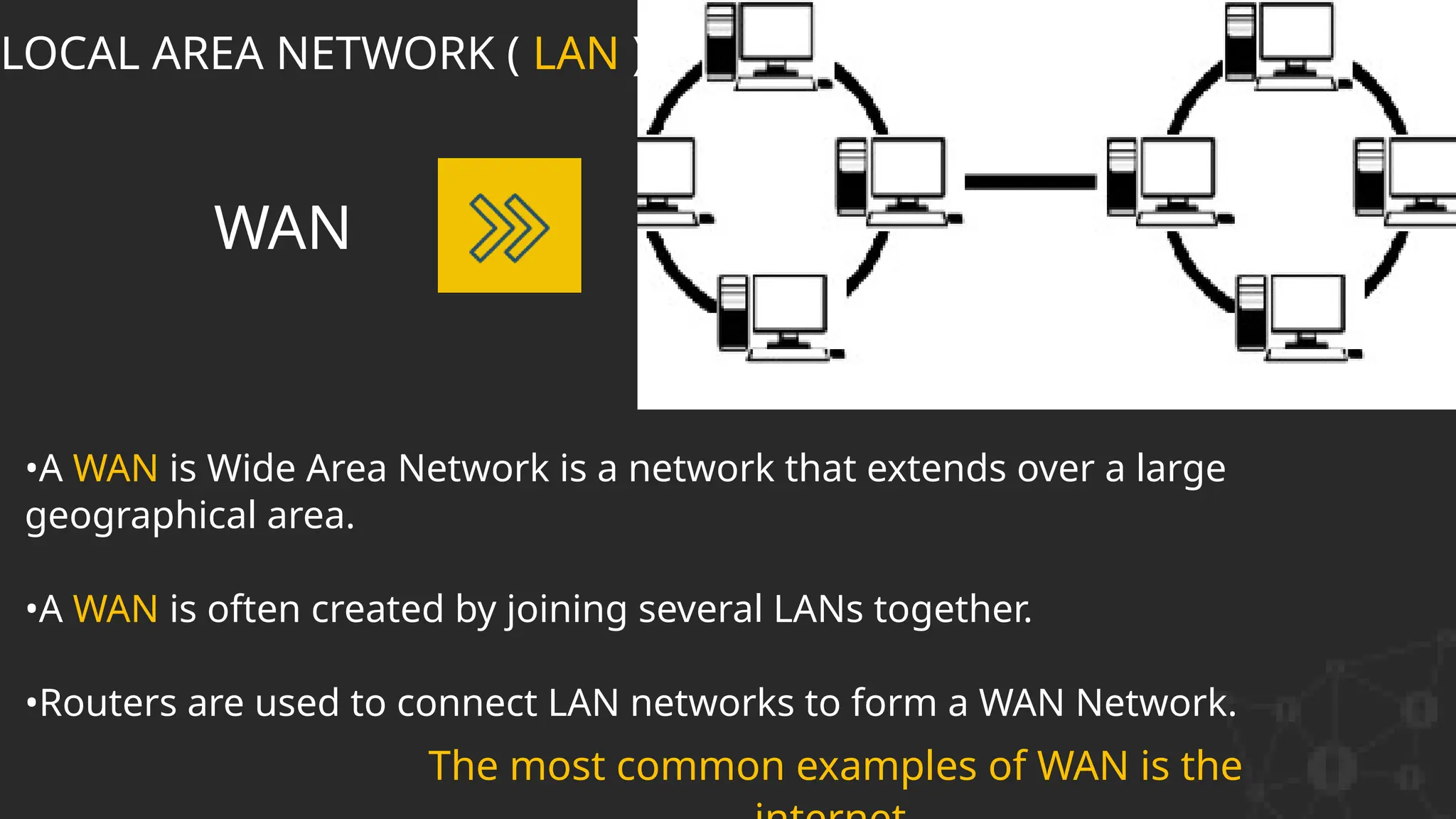
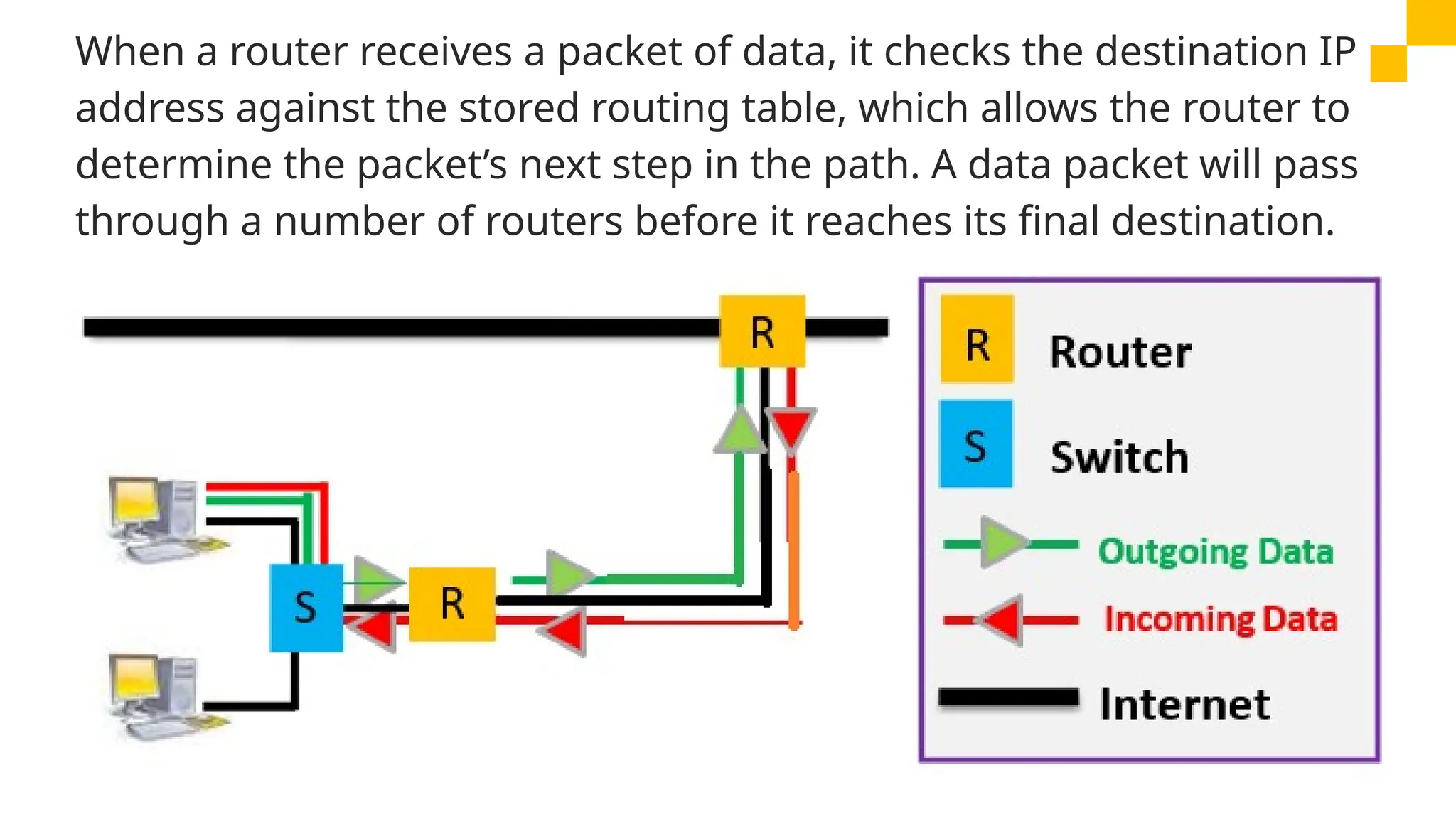
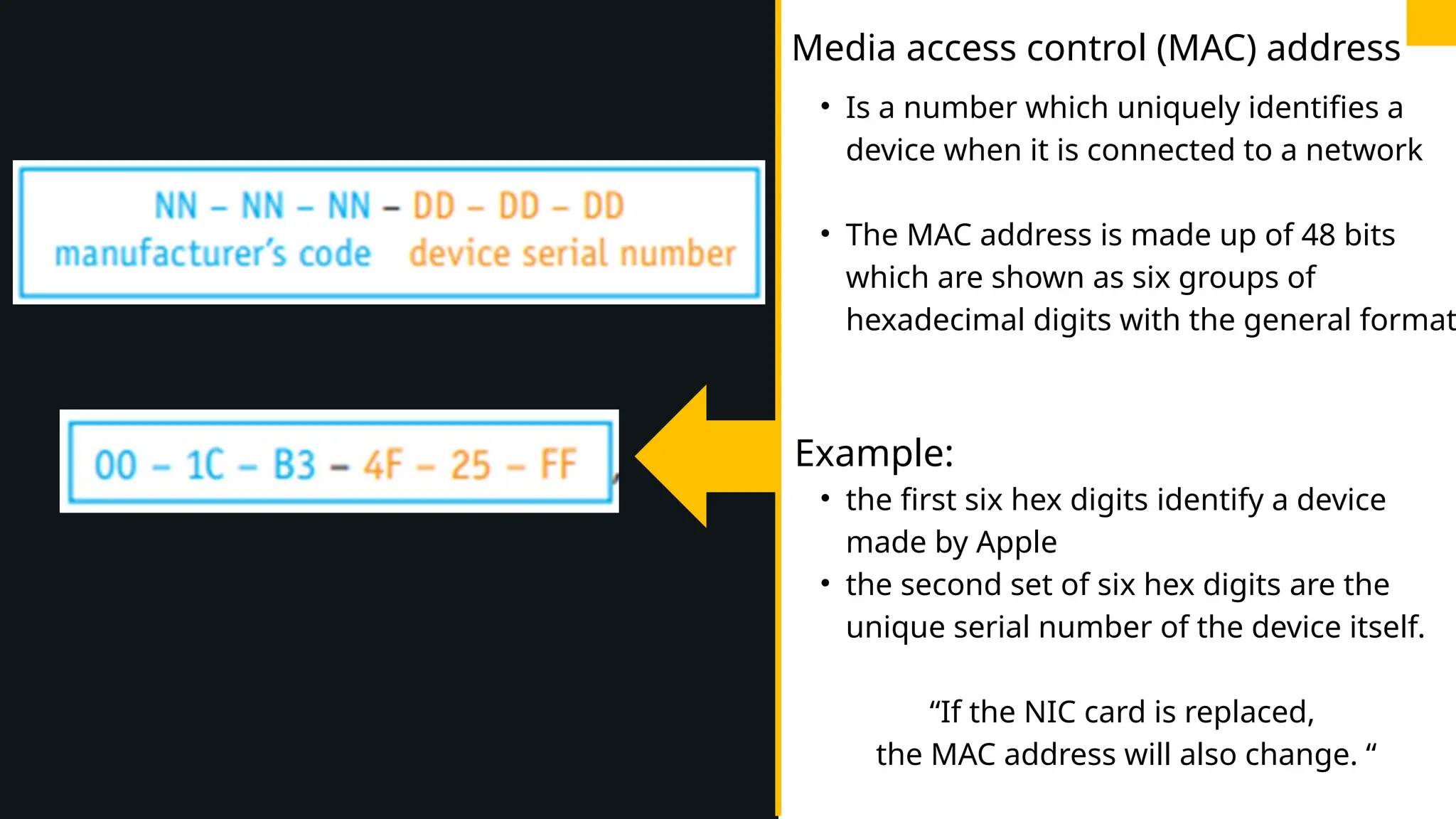
The document discusses computer networks, detailing different types, advantages, and disadvantages. It explains key network components such as NICs, switches, routers, and the differences between LANs and WANs. Additionally, it describes how data is transmitted in packets across networks using MAC and IP addresses for identification.