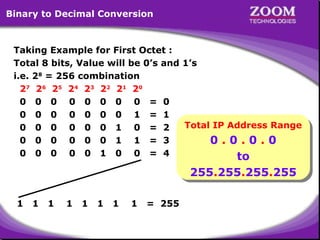
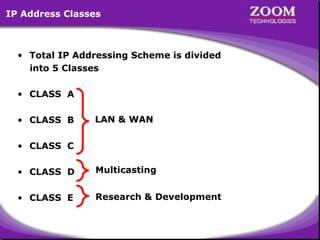
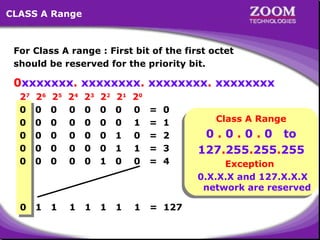
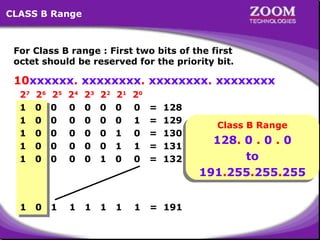
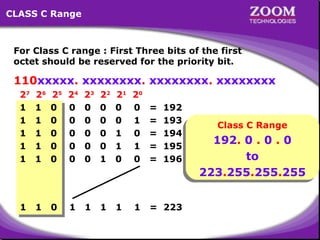
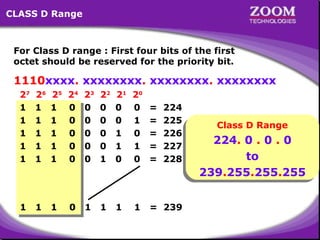
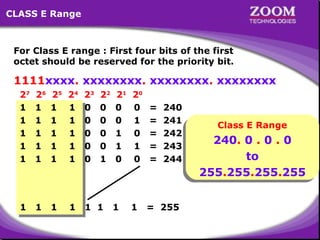
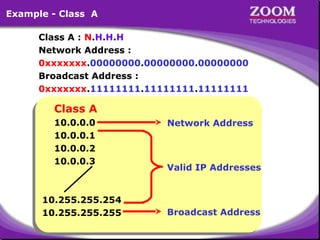
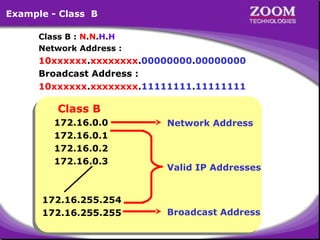
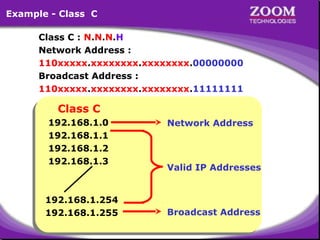
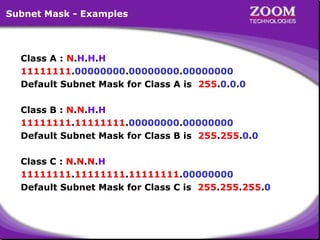
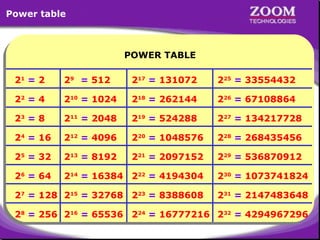
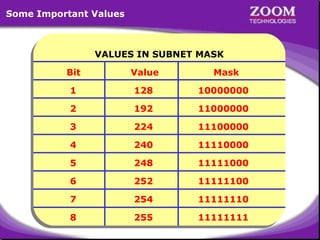
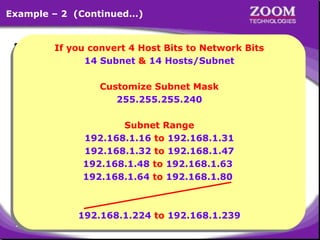
The document provides an overview of IP addressing, detailing both IPv4 and IPv6, their structure, and the different classes of IP addresses (A, B, C, D, E). It explains the concept of subnetting, subnet masks, and their usages within local area networks, as well as private address ranges for home and office use. Additionally, it discusses practical scenarios for implementing these concepts effectively.