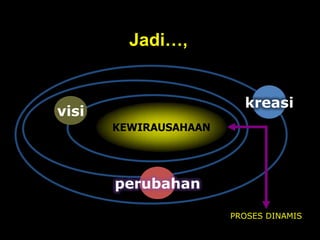
The document discusses various concepts related to entrepreneurship. It defines entrepreneurship as taking calculated risks in terms of time, equity or career, and having the ability to form effective teams and manage resources creatively with a vision for opportunity. It discusses different types of entrepreneurship including technopreneurship (applying technical skills to create wealth), agripreneurship (controlling production assets in agriculture), political entrepreneurship (seeking political benefits by providing public goods), knowledge entrepreneurship (improving knowledge production not for profit), social entrepreneurship (creating social change), and intrapreneurship (using entrepreneurial skills within an organization). It also discusses entrepreneurship education and digital entrepreneurship.