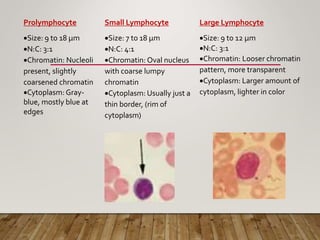
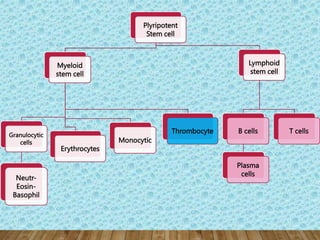
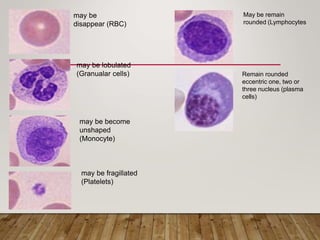
The document outlines lymphopoiesis, detailing the development of lymphoid stem cells into B and T lymphocytes, with specific sites of development such as the bone marrow and thymus. It describes the regulatory role of interleukins in the maturation process and provides characteristics of various cell types including lymphocytoblasts, prolymphocytes, and plasma cells. Additionally, it highlights changes in cell morphology during maturation and the origin of different cell types.