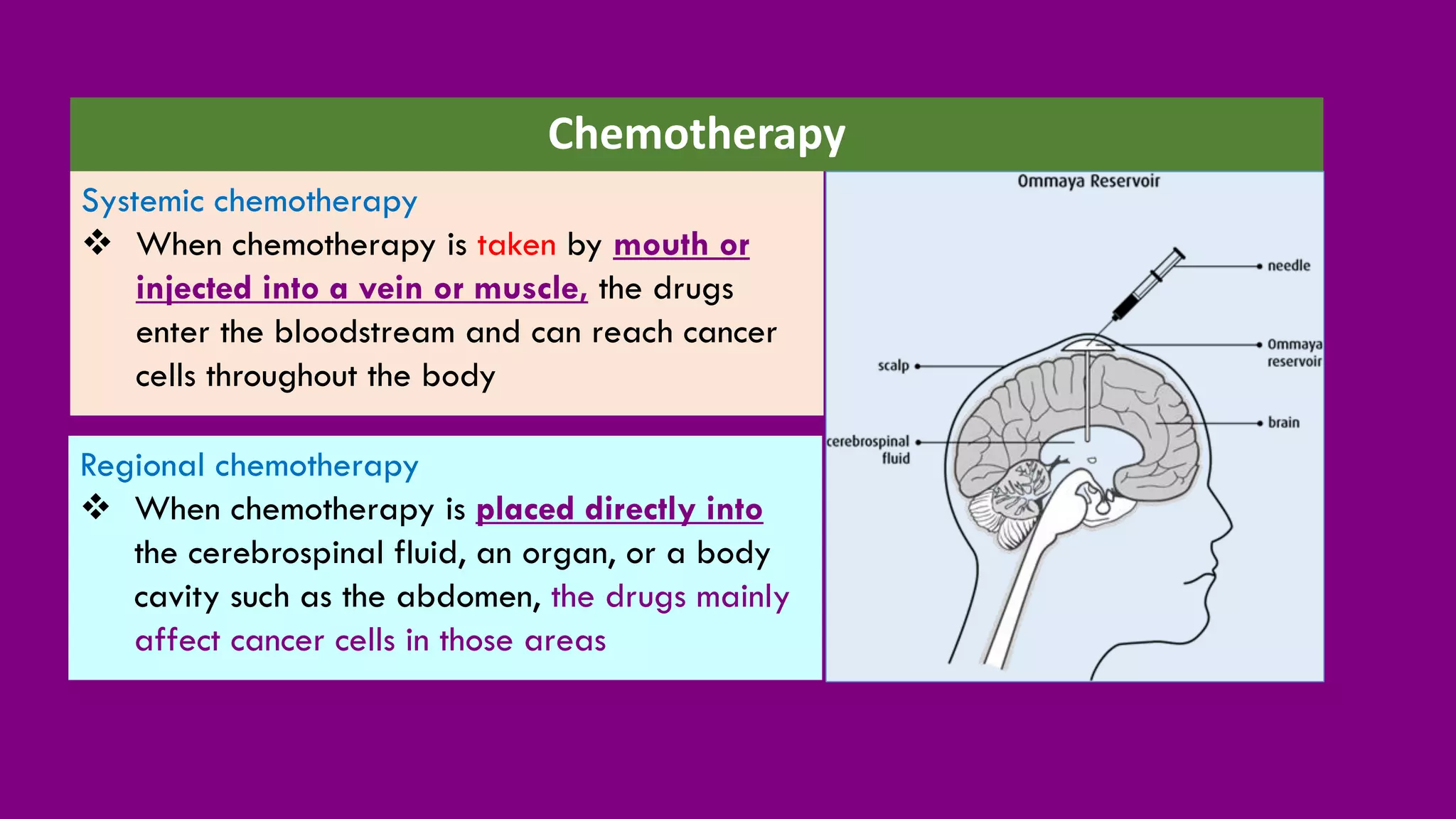
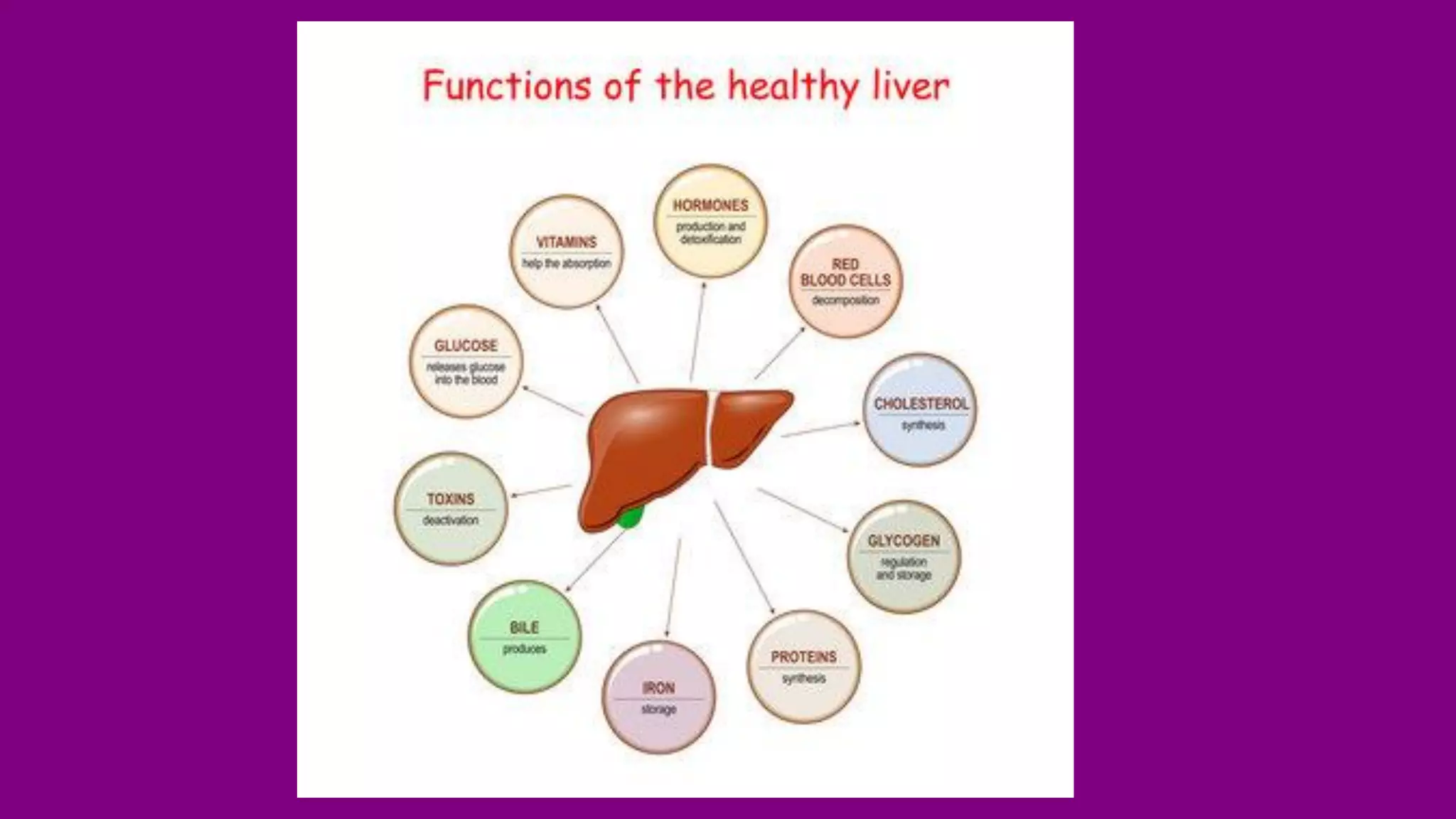
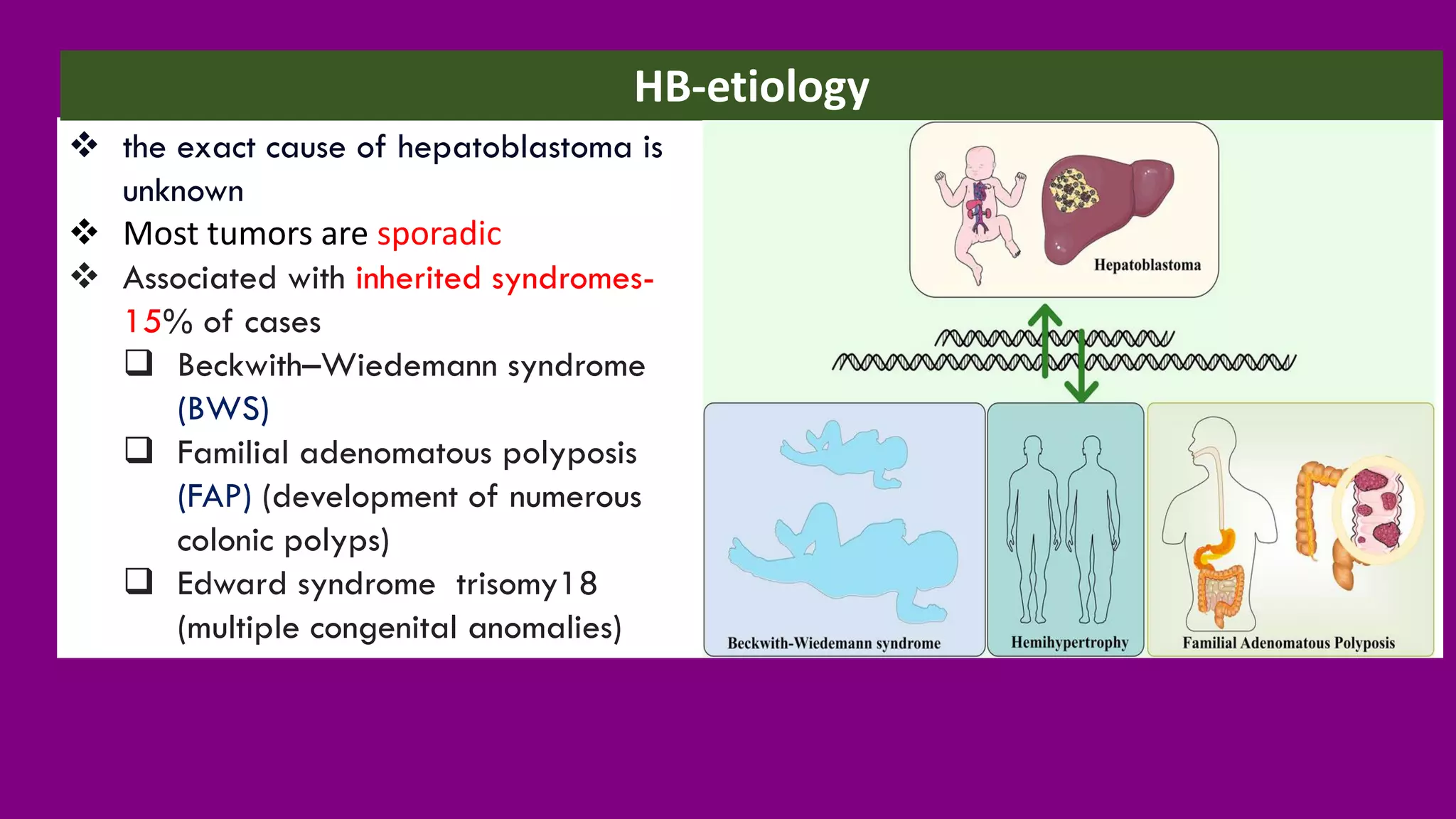
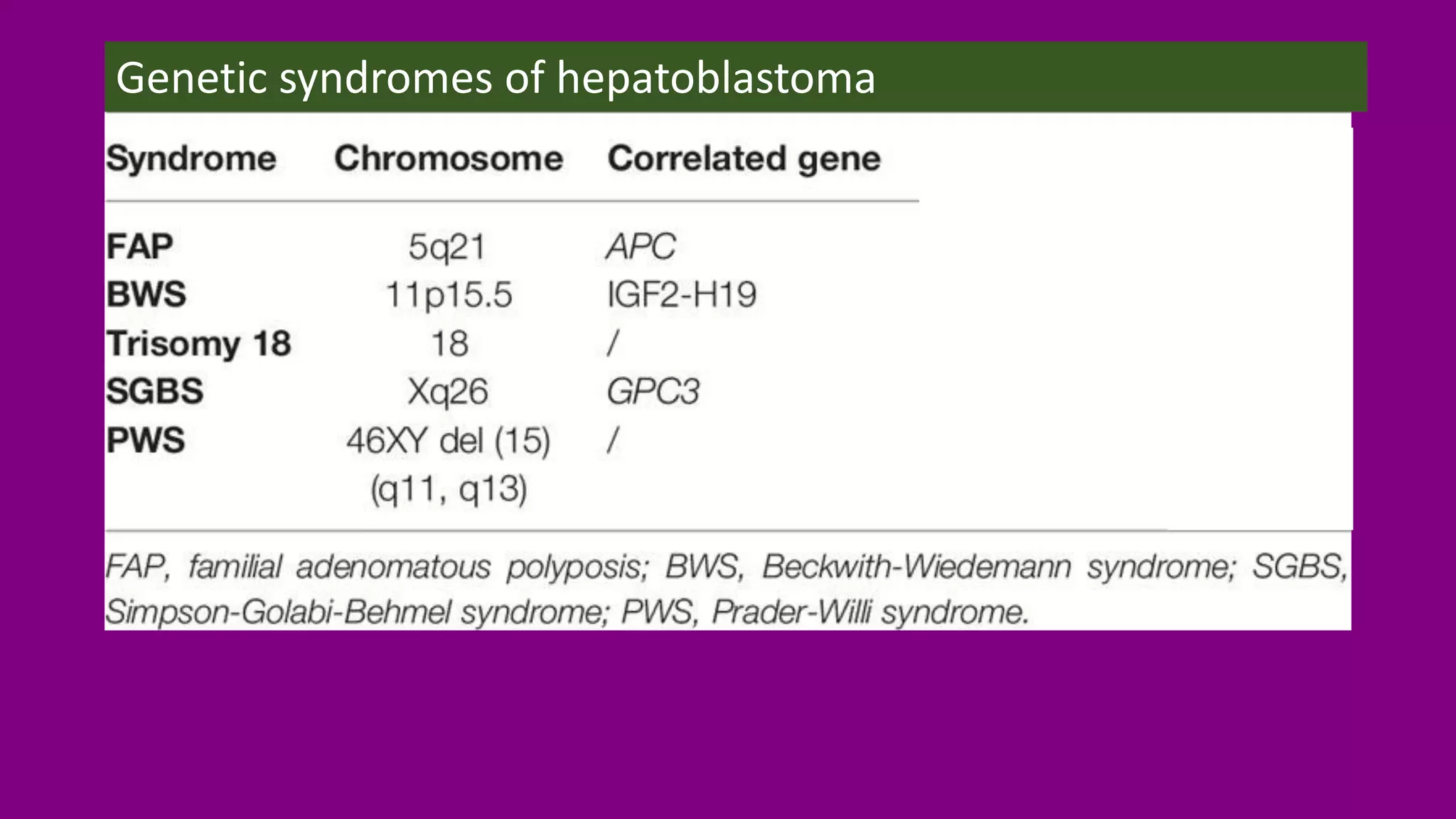
Hepatoblastoma (HB) is the most common malignant liver tumor in early childhood, primarily affecting children under five years old, and is often treated with a combination of chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapies. The document outlines various treatments including neoadjuvant chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and different forms of radiation therapy, as well as the importance of tumor staging for treatment planning. Genetic mutations, particularly in the CTNNB1 and APC genes, play a significant role in the development of hepatoblastoma, which has both hereditary and non-hereditary risk factors.