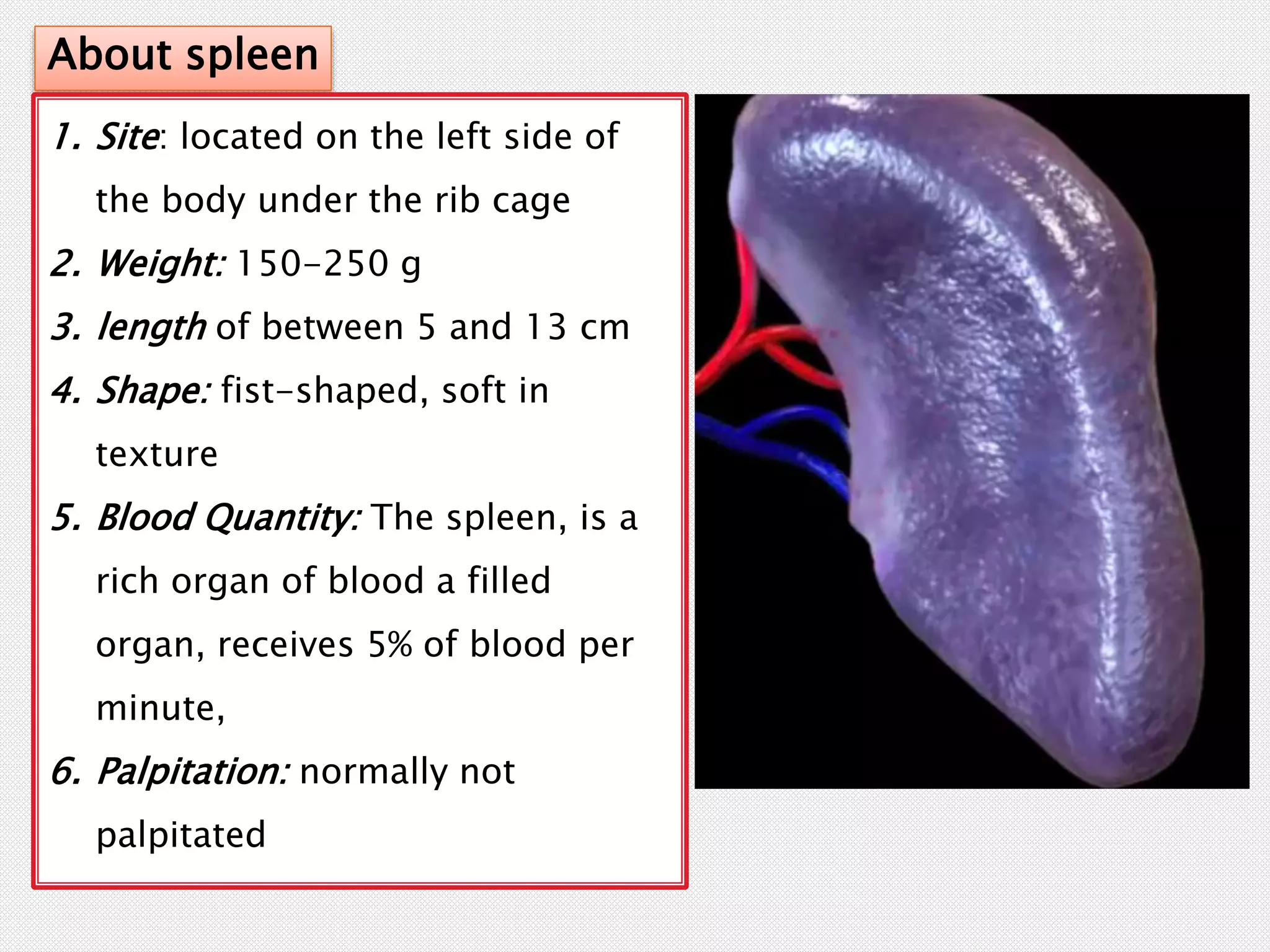
The spleen plays important roles in filtering blood and immune function. It is divided into red pulp, white pulp, and marginal zones, each with distinct functions. The spleen filters red blood cells, supports hematopoiesis, removes antigens from blood for immune processing, and stores platelets and white blood cells. Diseases can cause the spleen to enlarge (splenomegaly) or overwork (hypersplenism), requiring its surgical removal (splenectomy) to improve blood counts.