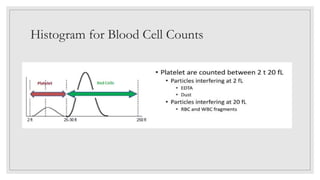
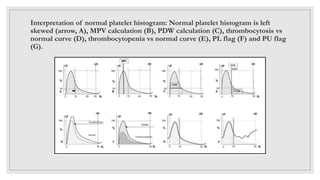
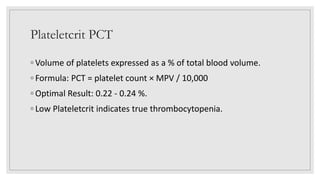
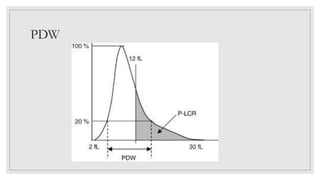
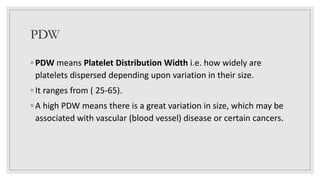
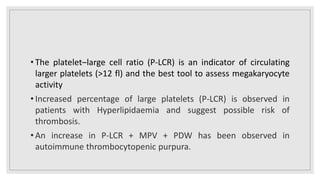
This document discusses various platelet indices used in interpreting platelet histograms and their clinical significance. It defines plateletcrit (PCT) as the volume of platelets expressed as a percentage of total blood volume, with a normal range of 0.22-0.24%. It describes platelet distribution width (PDW) as measuring the variation in platelet size, with a normal range of 25-65, and higher values associated with vascular disease or cancer. It also defines platelet large cell ratio (P-LCR) as measuring larger platelets between 12-30 femtoliters, with increased levels seen in hyperlipidemia and autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Mean platelet volume (MPV) is defined as the average