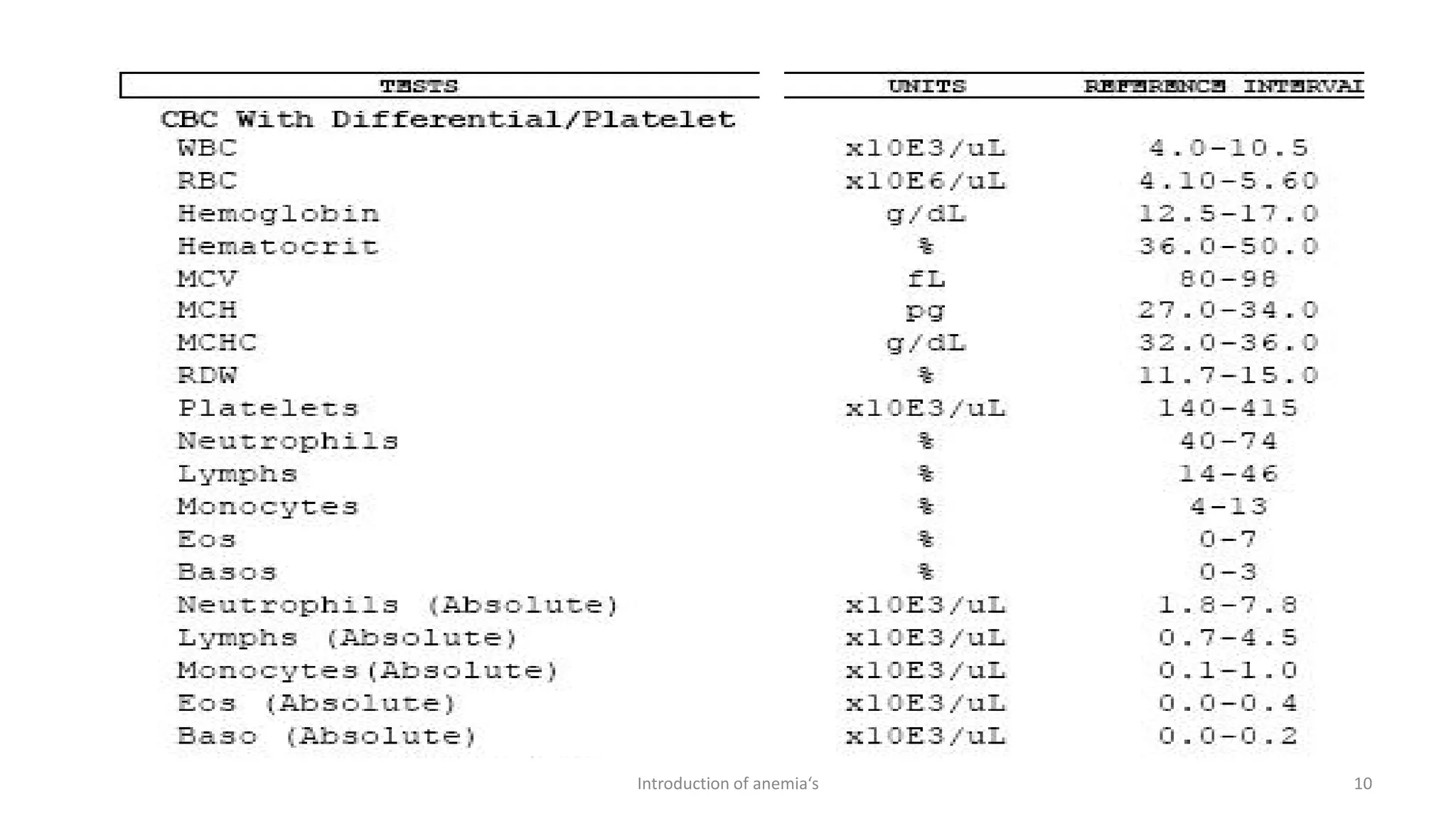
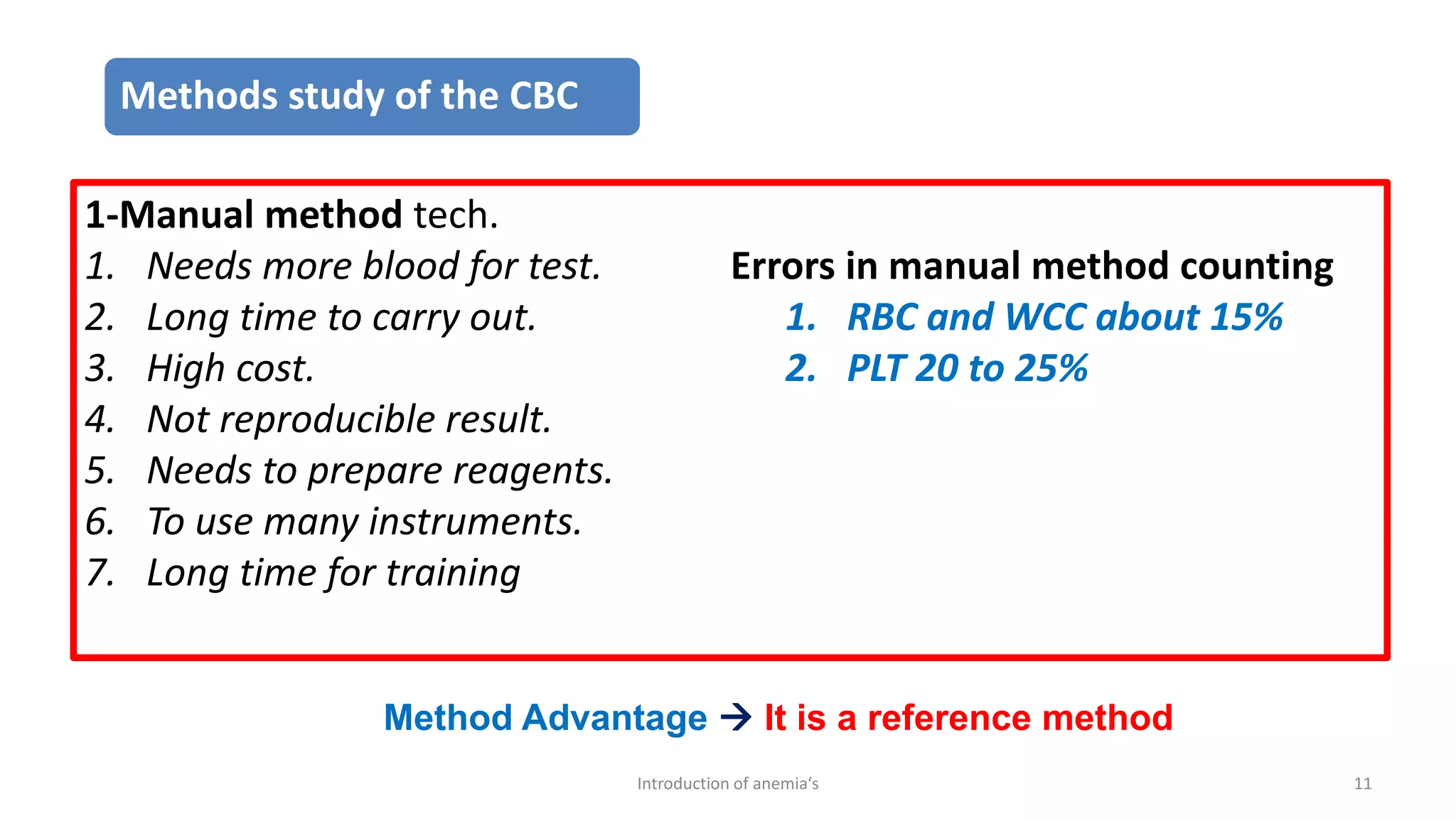
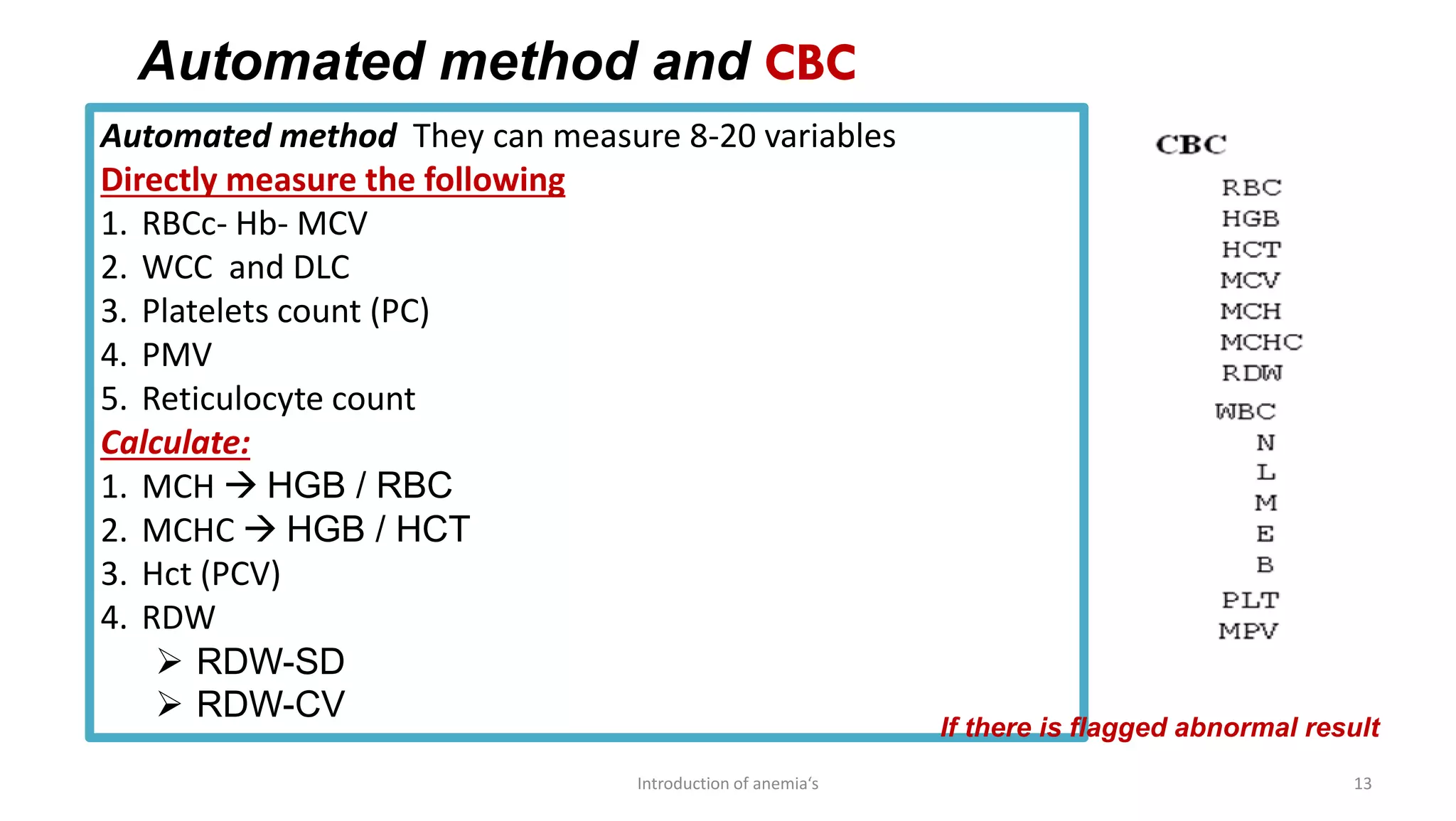
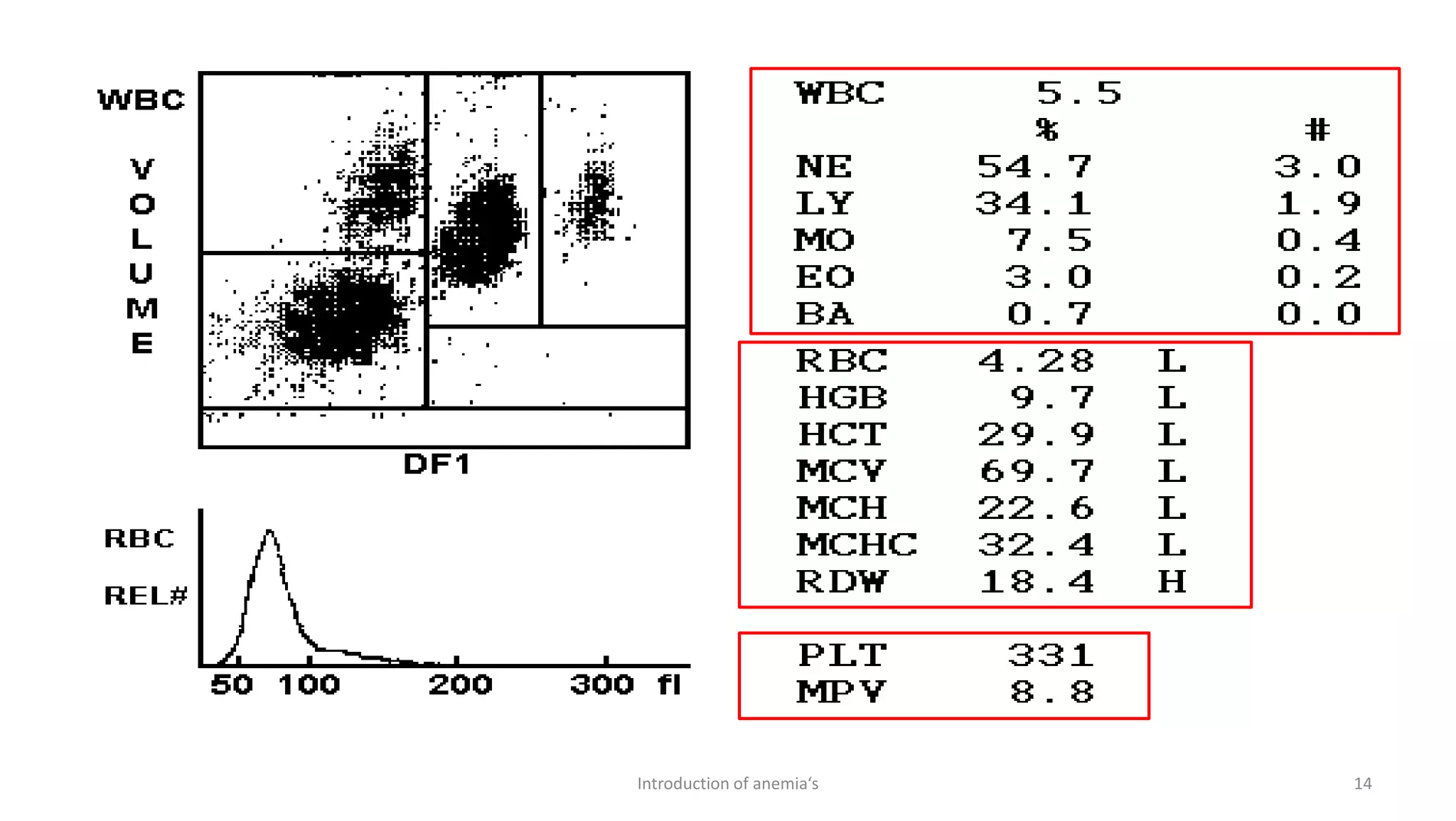
This document discusses complete blood count (CBC) tests, which are commonly used to evaluate important components in the blood. A CBC provides information about red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and can help diagnose diseases affecting the blood. It discusses how CBC results are used to diagnose anemia and other disorders. The document also compares manual and automated methods for performing CBC tests, noting advantages of automation like speed, reduced costs, and producing more reproducible results. Indices derived from CBC results, like MCV, MCH, and MCHC are also introduced as they can provide clues to the type of anemia present.