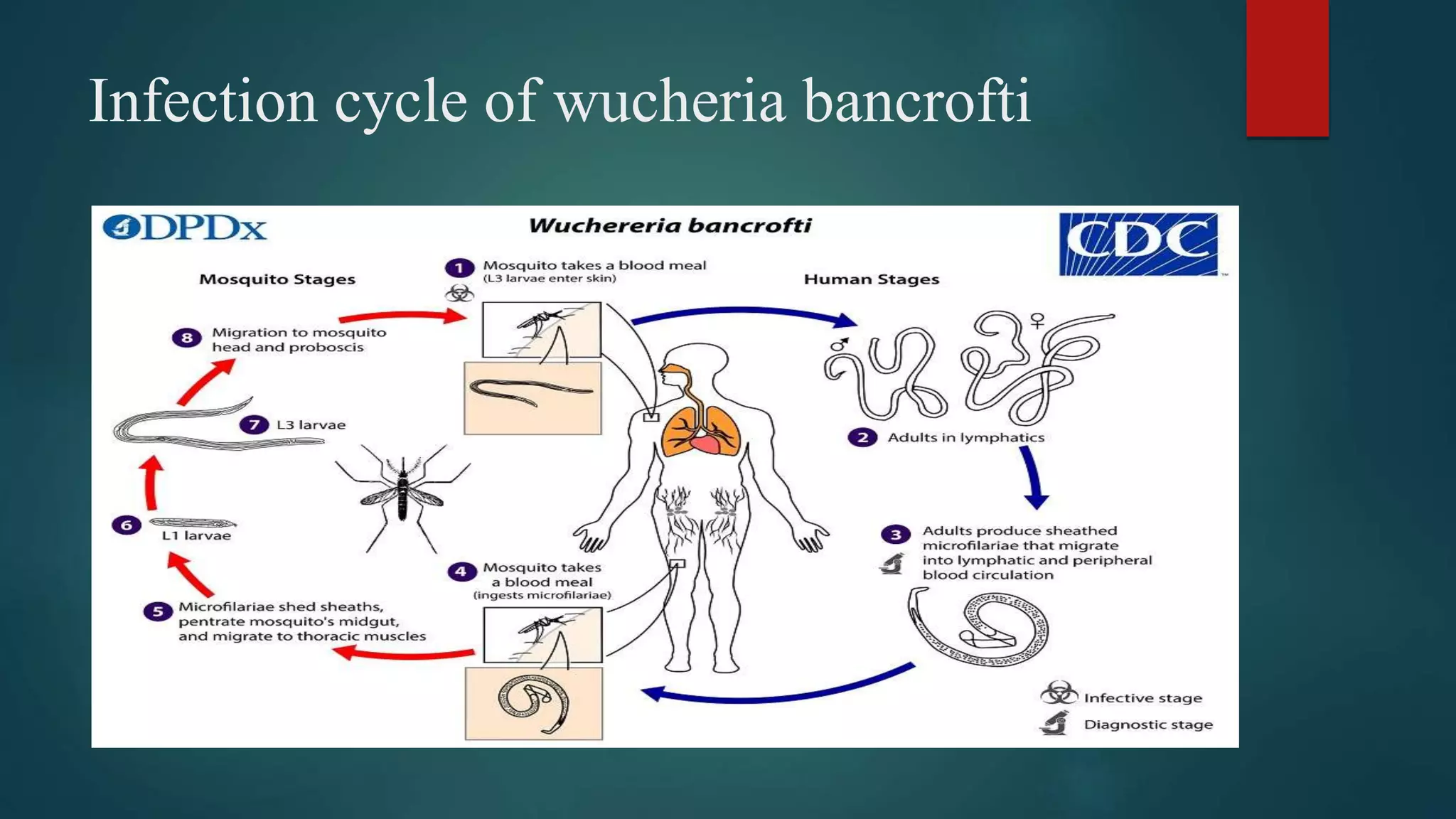
Lymphatic filariasis is caused by parasitic roundworms transmitted through mosquito bites. The adult worms live in the human lymphatic system and produce microfilariae that circulate in the bloodstream, infecting mosquitoes that bite infected individuals. When an infected mosquito bites a person, the larvae are deposited and mature over 6 months into adult worms that reside in the lymphatics. This can lead to lymphedema and elephantiasis, causing swelling of body parts. Diagnosis involves blood smears to detect microfilariae. Treatment uses diethylcarbamazine to kill the microfilariae while prevention focuses on avoiding mosquito bites through nets and repellents.