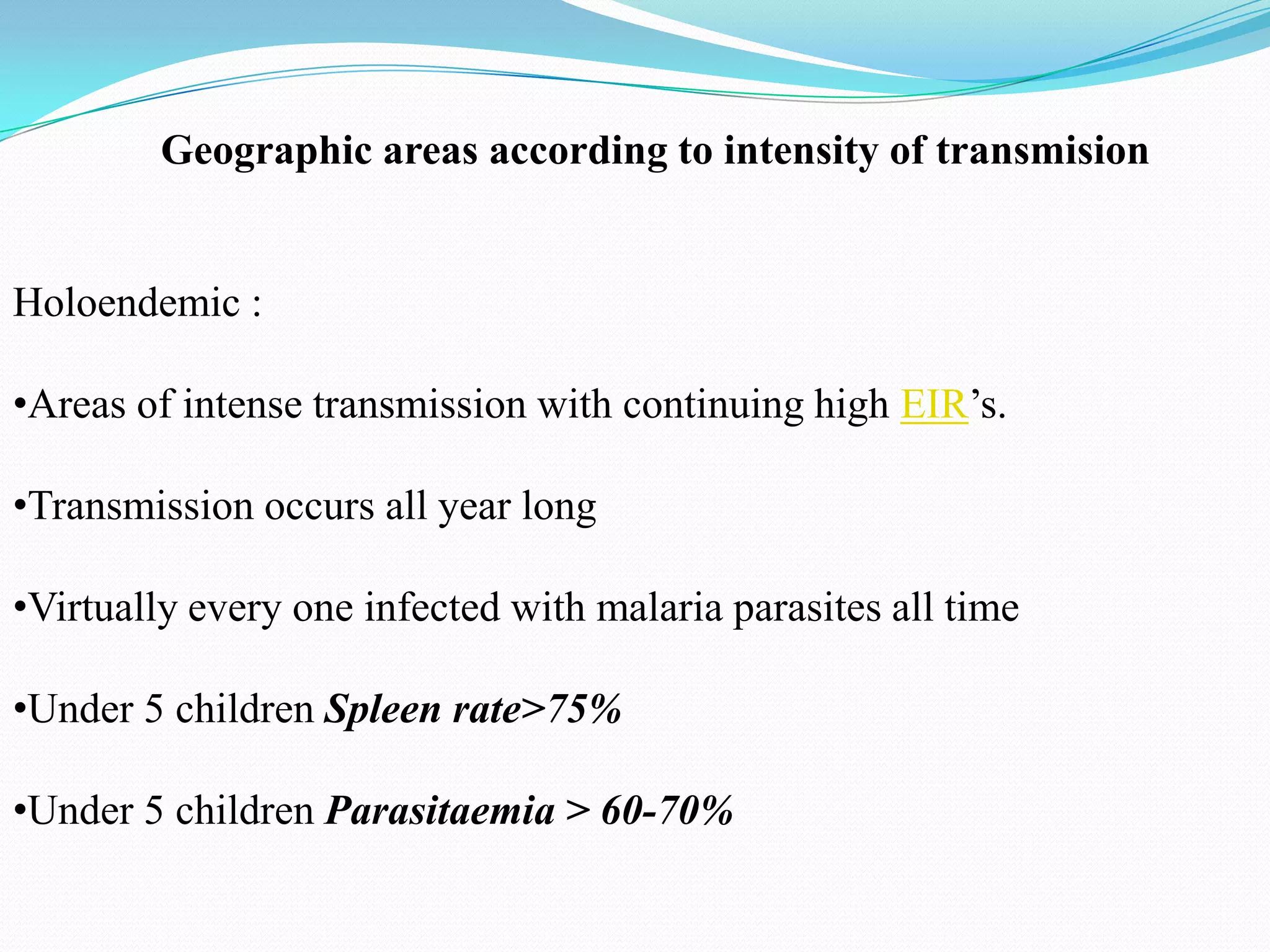
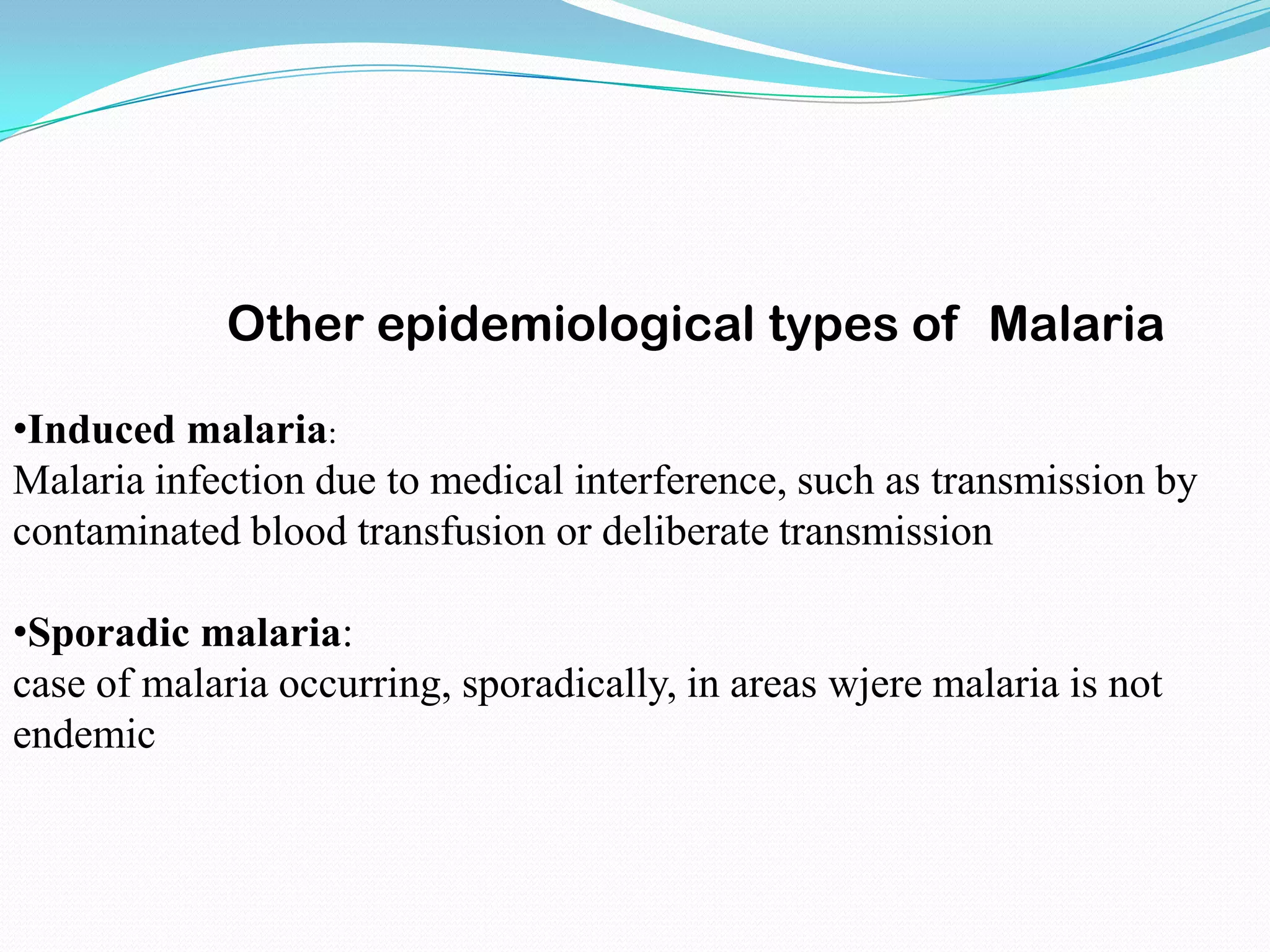
Malaria is a major public health problem that affects many countries and causes nearly 1 million deaths annually. It is caused by a protozoan parasite (Plasmodium) transmitted via the bites of infected Anopheles mosquitoes. There are four human malaria parasite species, with P. falciparum being the most deadly. Malaria transmission is influenced by factors like temperature, human and mosquito behavior, drug resistance, and control measures. The WHO classifies malaria epidemiology into several types based on transmission patterns and intensity in different geographic areas.