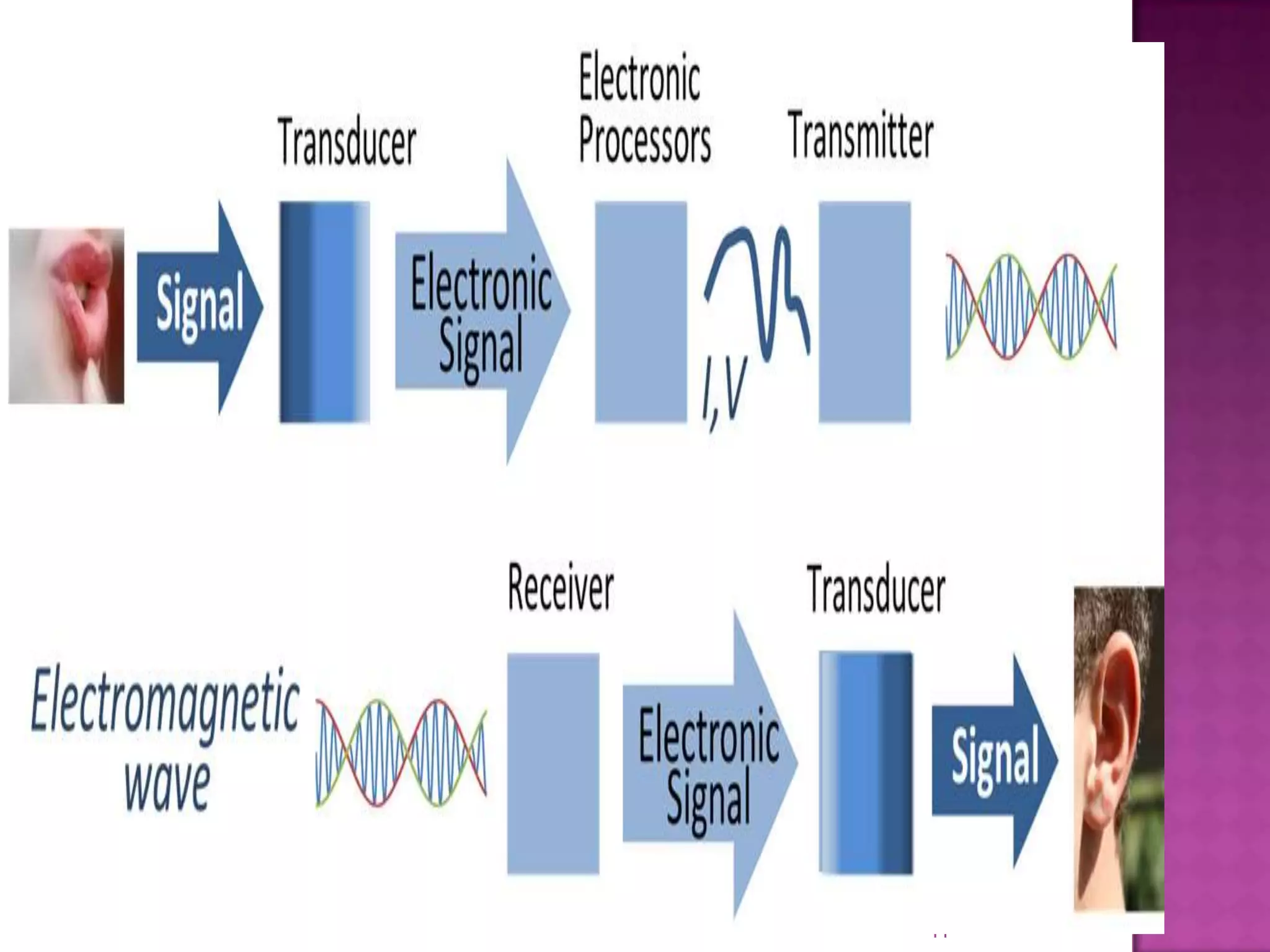
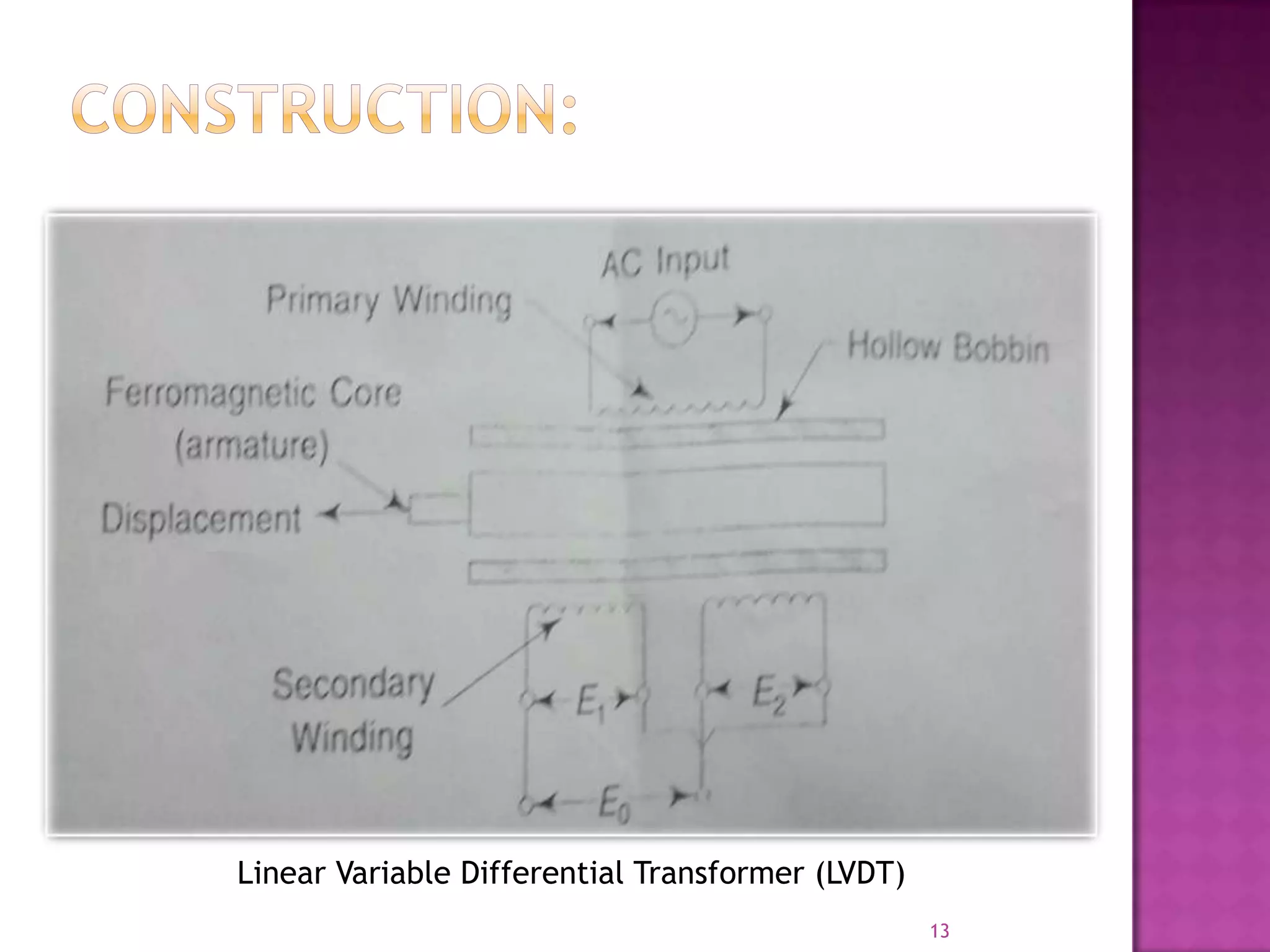
This document discusses transducers and the linear variable differential transformer (LVDT). It defines a transducer as a device that converts one form of energy to another, and classifies transducers based on their principles and whether they are active, passive, primary or secondary. LVDTs are introduced as the most widely used inductive transducer to convert linear motion to an electrical signal. The document proceeds to describe the construction, operating principle, and advantages/disadvantages of LVDTs, and concludes by outlining their applications in measuring small displacements.