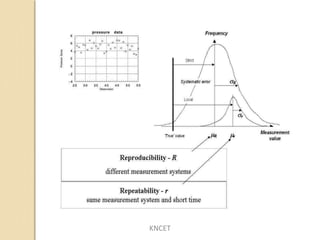
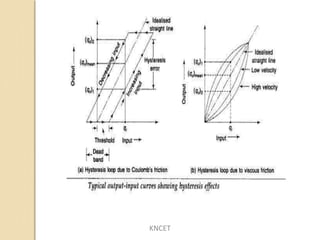
The document discusses the static and dynamic characteristics of instruments. The main static characteristics are accuracy, sensitivity, reproducibility, drift, static error, dead zone, precision, threshold, linearity, stability, range, bias, tolerance and hysteresis. The dynamic characteristics include speed of response, fidelity, lag, and dynamic error. Dynamic inputs can be transient or steady state periodic like step, ramp, parabolic or sinusoidal. Lag causes a delay or retardation in the instrument's response to changing inputs.