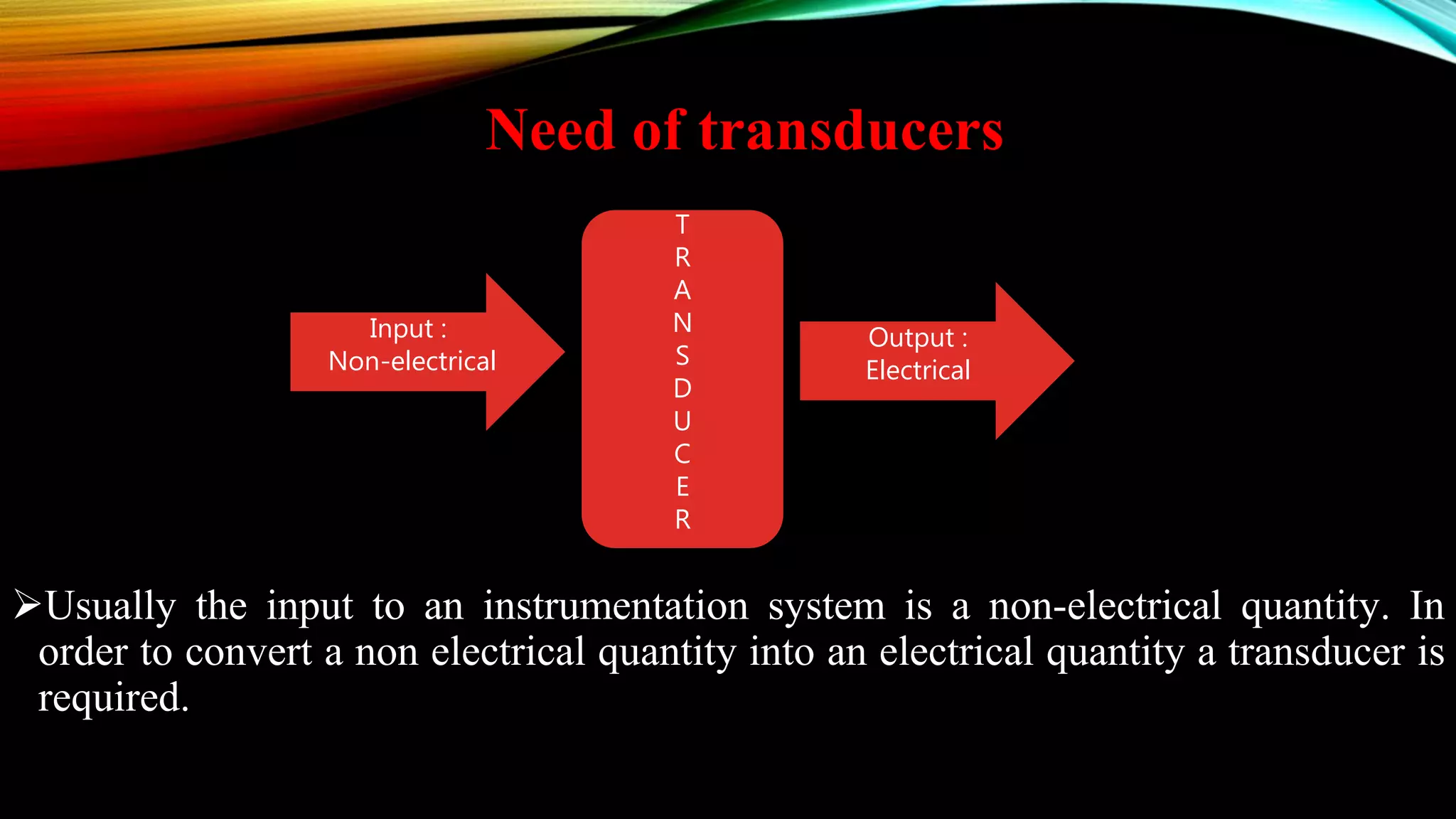
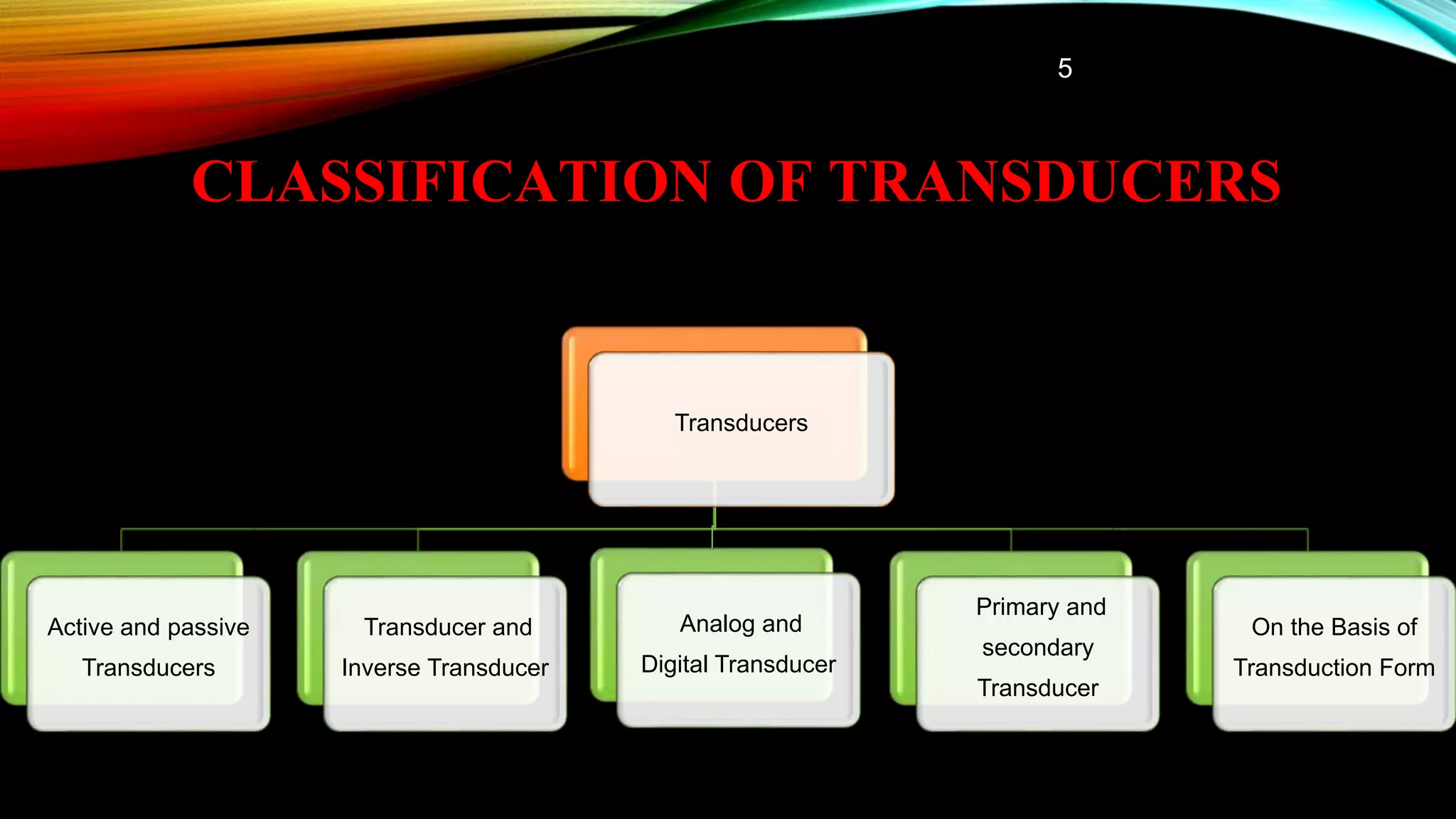
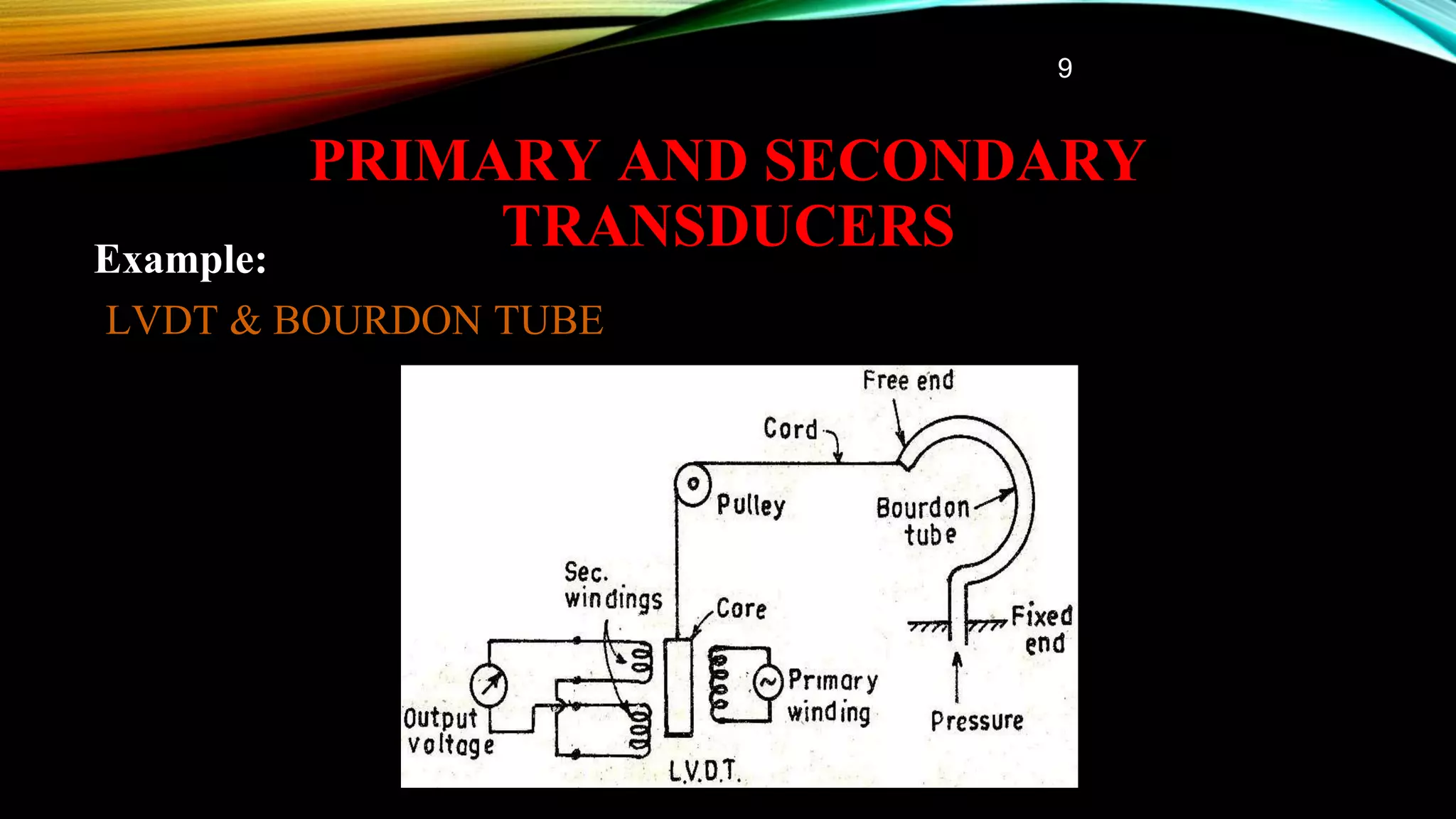
This document presents a classification of transducers. It begins by defining a transducer as a device that converts one form of energy into another. The document then discusses several classifications of transducers including active vs passive, transducer vs inverse transducer, analog vs digital, and primary vs secondary. Examples are provided for each classification. The document also covers advantages and disadvantages of transducers as well as common applications. In conclusion, transducers are useful devices for converting one energy form to another for various applications.