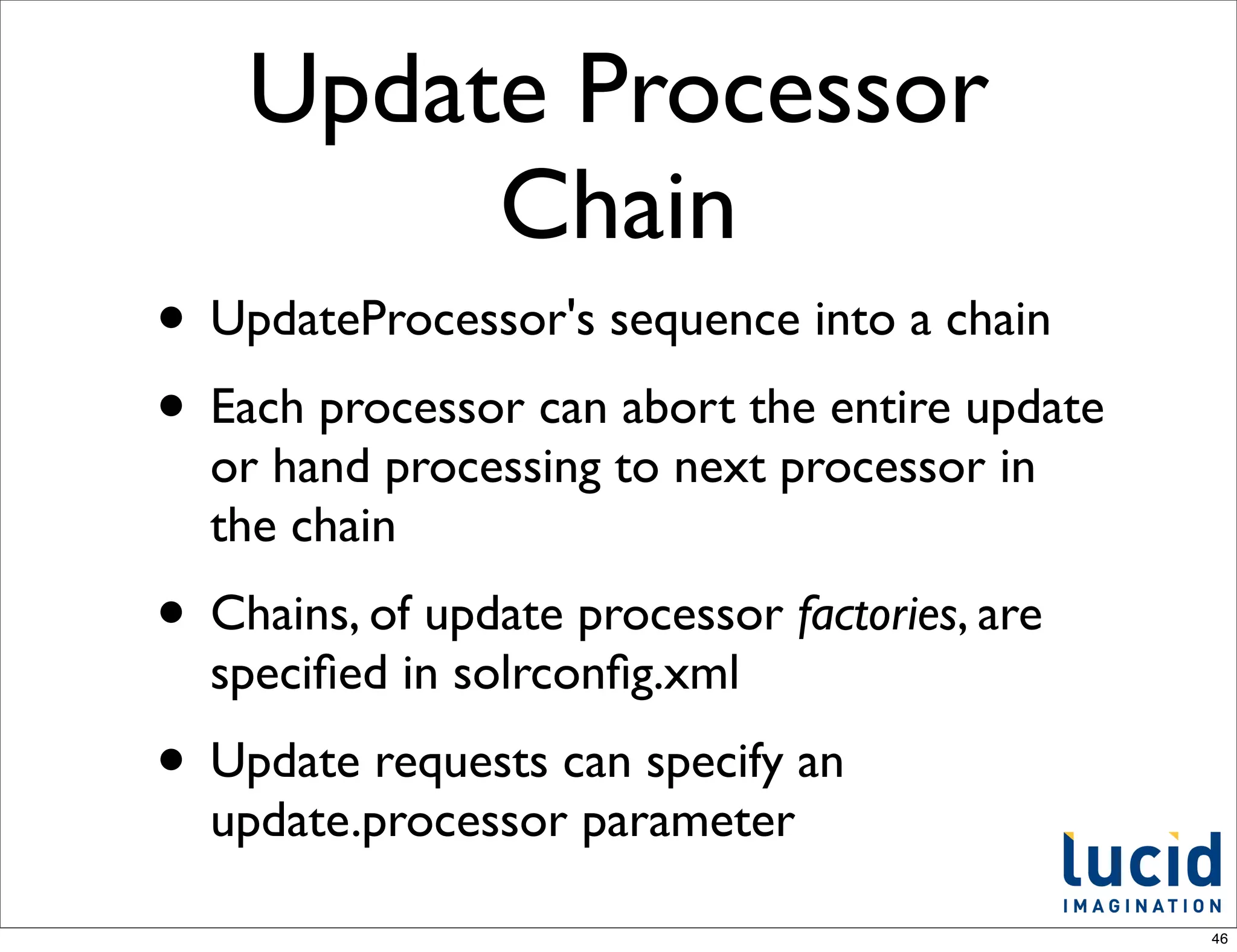
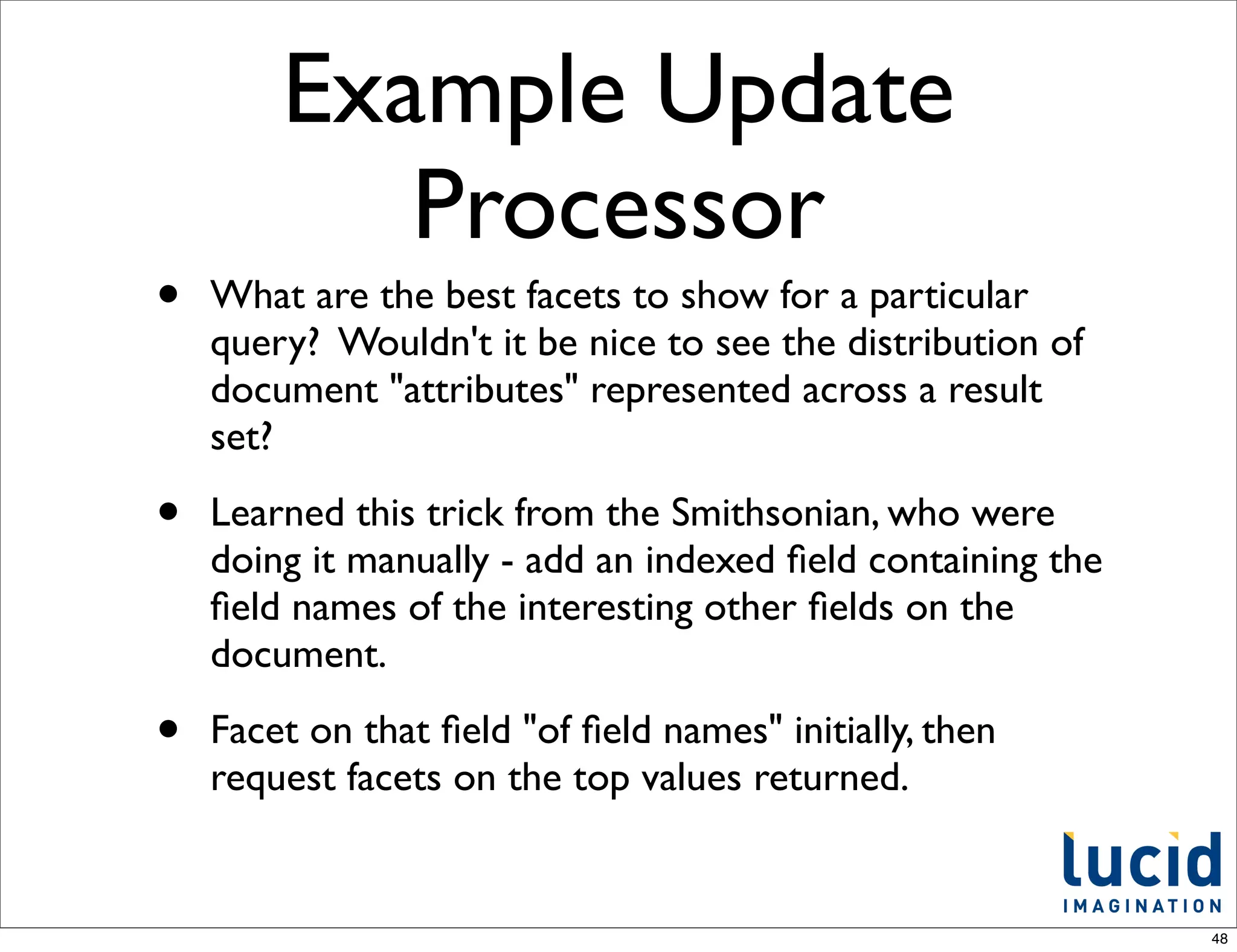
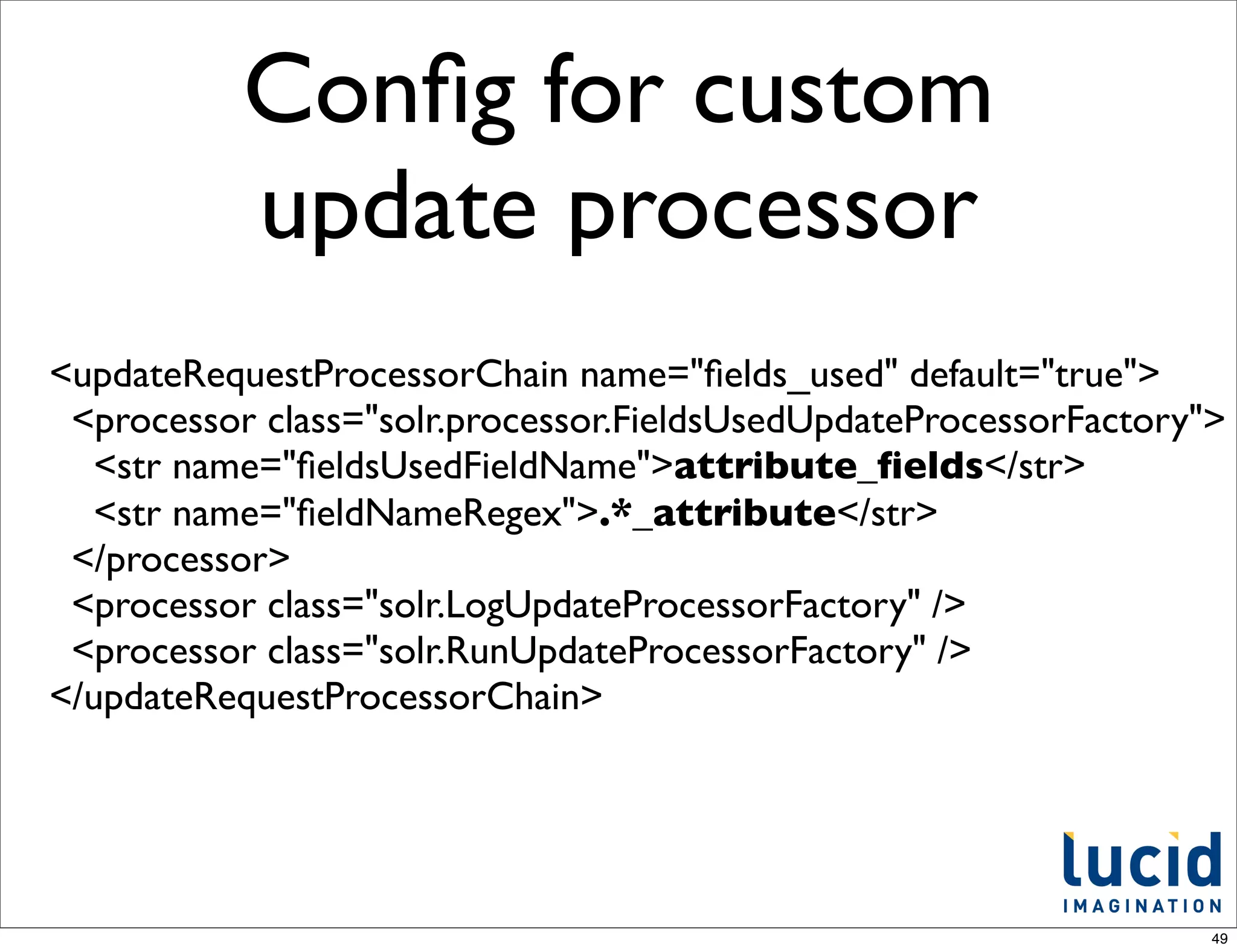
The document discusses recent developments in renewable energy technologies. It highlights advancements in solar and wind energy, focusing on their efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The document emphasizes the importance of transitioning to sustainable energy sources for environmental and economic benefits.












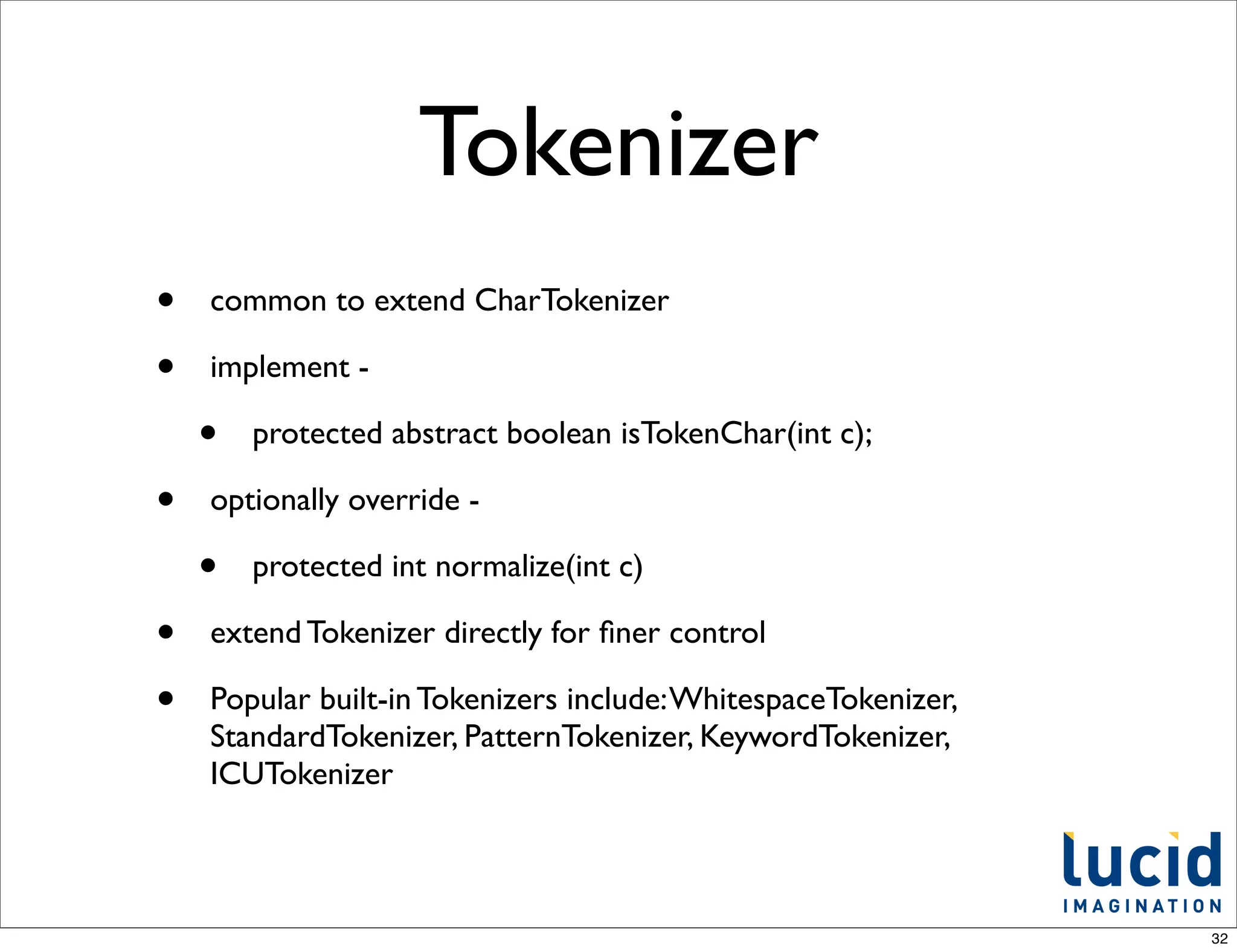

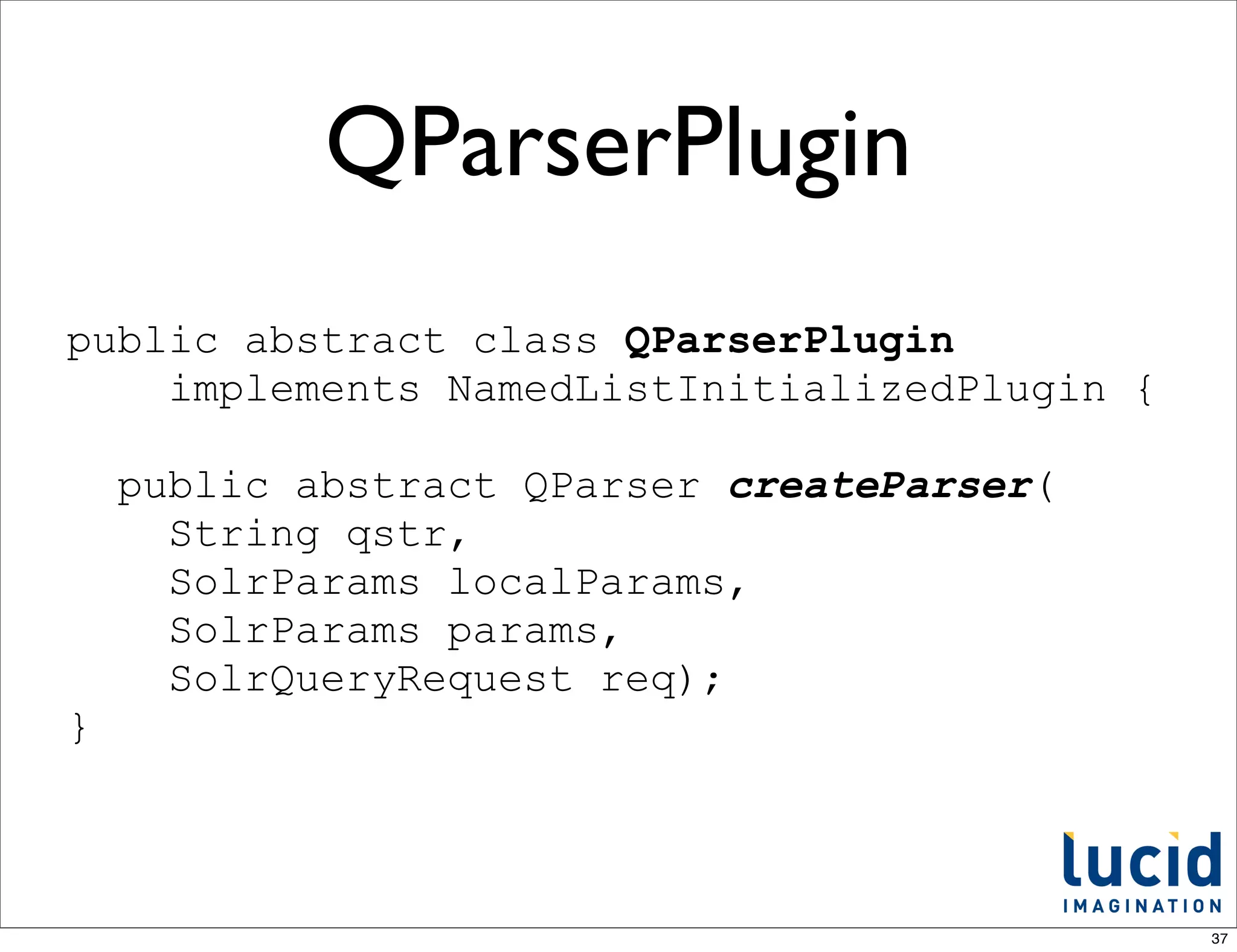
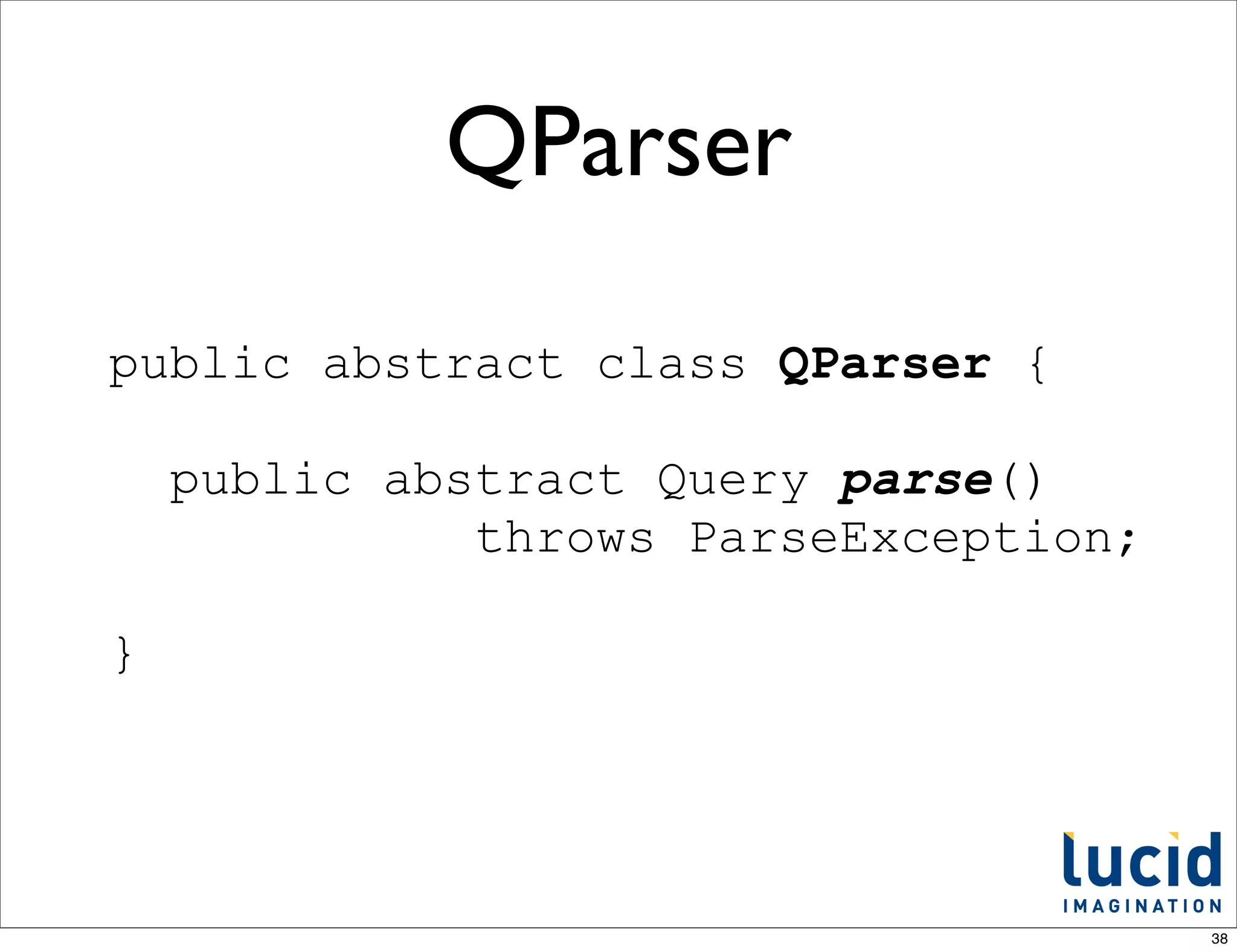
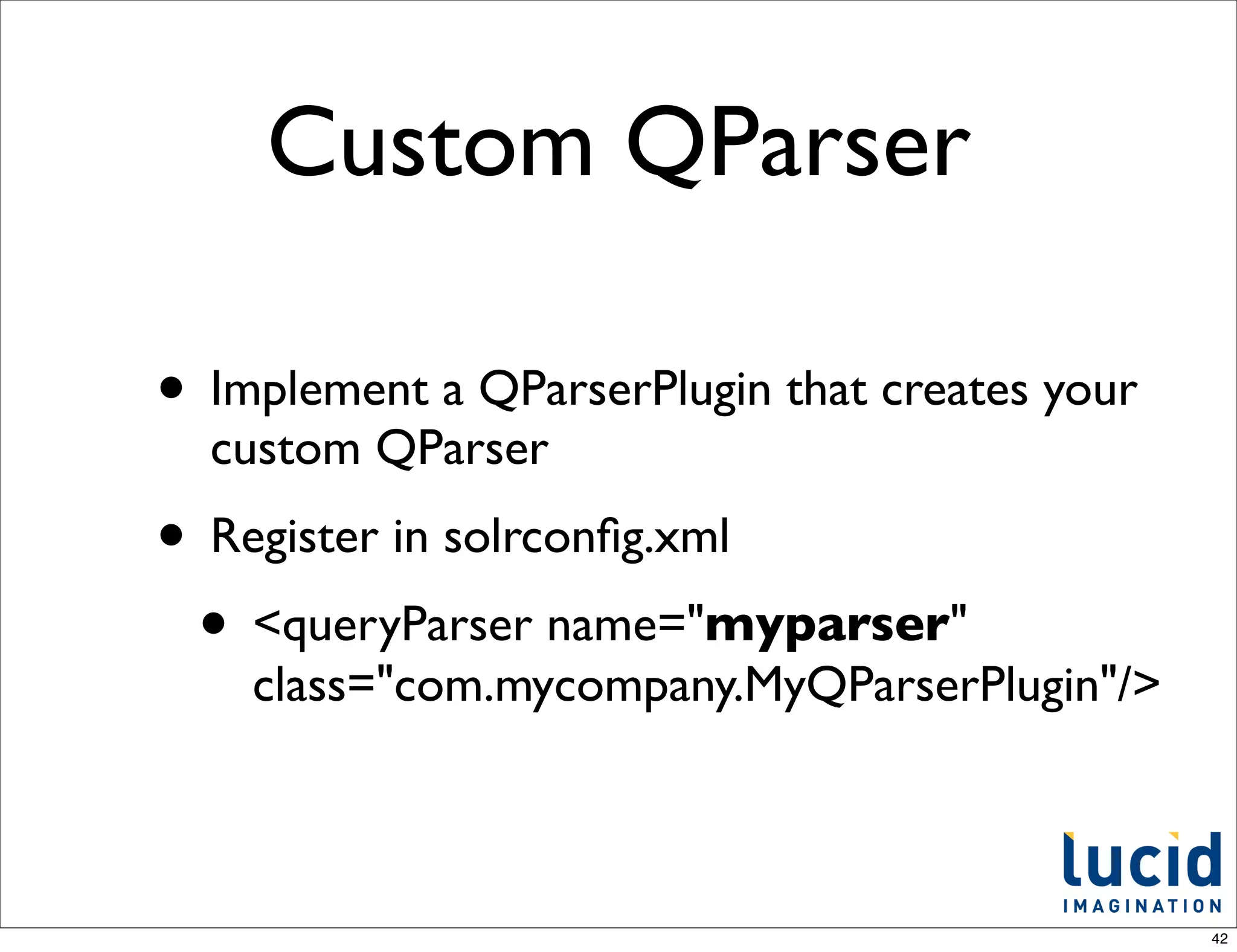
![Built-in QParsers
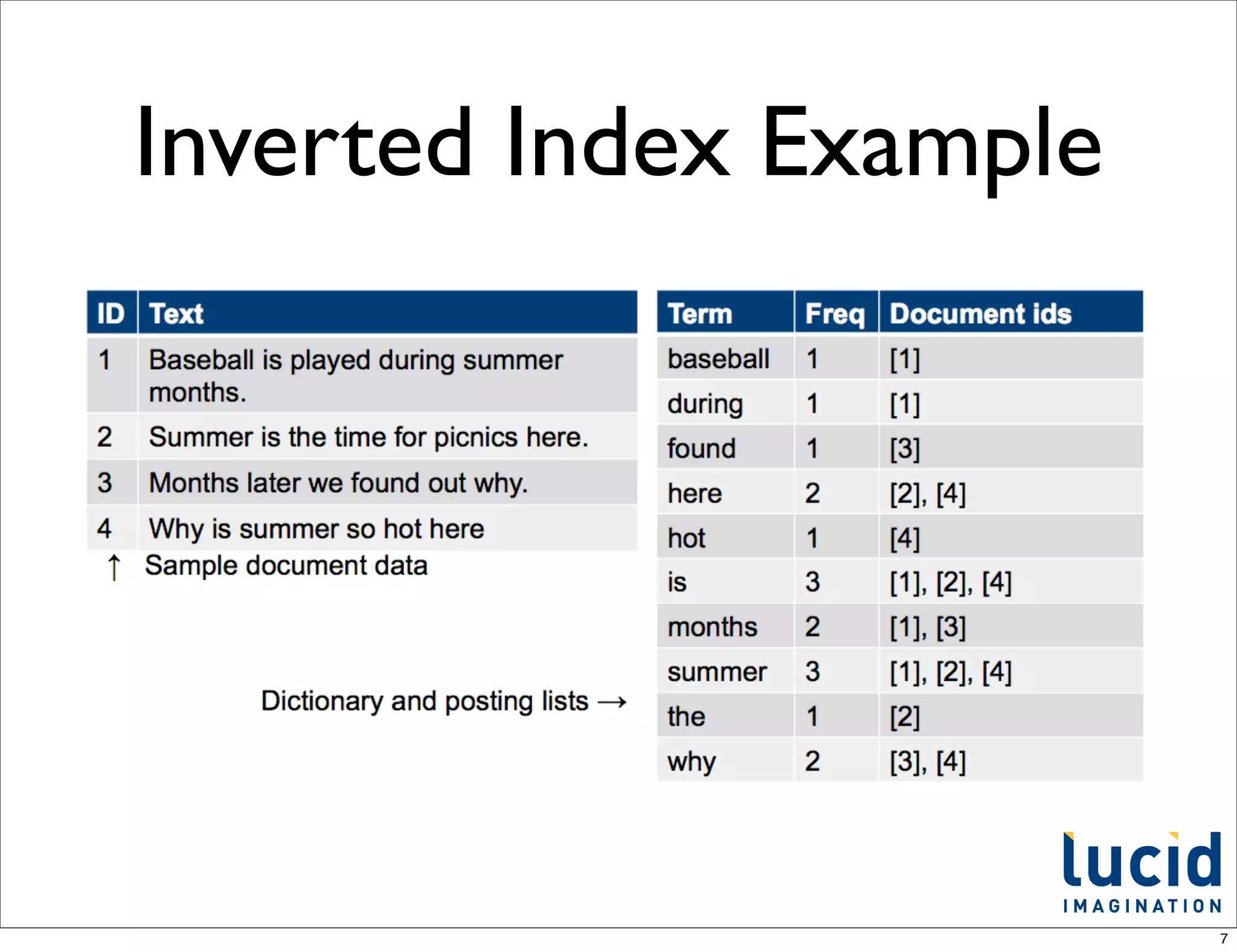
from QParserPlugin.java
/** internal use - name to class mappings of builtin parsers */
public static final Object[] standardPlugins = {
LuceneQParserPlugin.NAME, LuceneQParserPlugin.class,
OldLuceneQParserPlugin.NAME, OldLuceneQParserPlugin.class,
FunctionQParserPlugin.NAME, FunctionQParserPlugin.class,
PrefixQParserPlugin.NAME, PrefixQParserPlugin.class,
BoostQParserPlugin.NAME, BoostQParserPlugin.class,
DisMaxQParserPlugin.NAME, DisMaxQParserPlugin.class,
ExtendedDismaxQParserPlugin.NAME, ExtendedDismaxQParserPlugin.class,
FieldQParserPlugin.NAME, FieldQParserPlugin.class,
RawQParserPlugin.NAME, RawQParserPlugin.class,
TermQParserPlugin.NAME, TermQParserPlugin.class,
NestedQParserPlugin.NAME, NestedQParserPlugin.class,
FunctionRangeQParserPlugin.NAME, FunctionRangeQParserPlugin.class,
SpatialFilterQParserPlugin.NAME, SpatialFilterQParserPlugin.class,
SpatialBoxQParserPlugin.NAME, SpatialBoxQParserPlugin.class,
JoinQParserPlugin.NAME, JoinQParserPlugin.class,
};
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/luceneforsolrdevelopers-111203091216-phpapp02/75/Lucene-for-Solr-Developers-39-2048.jpg)
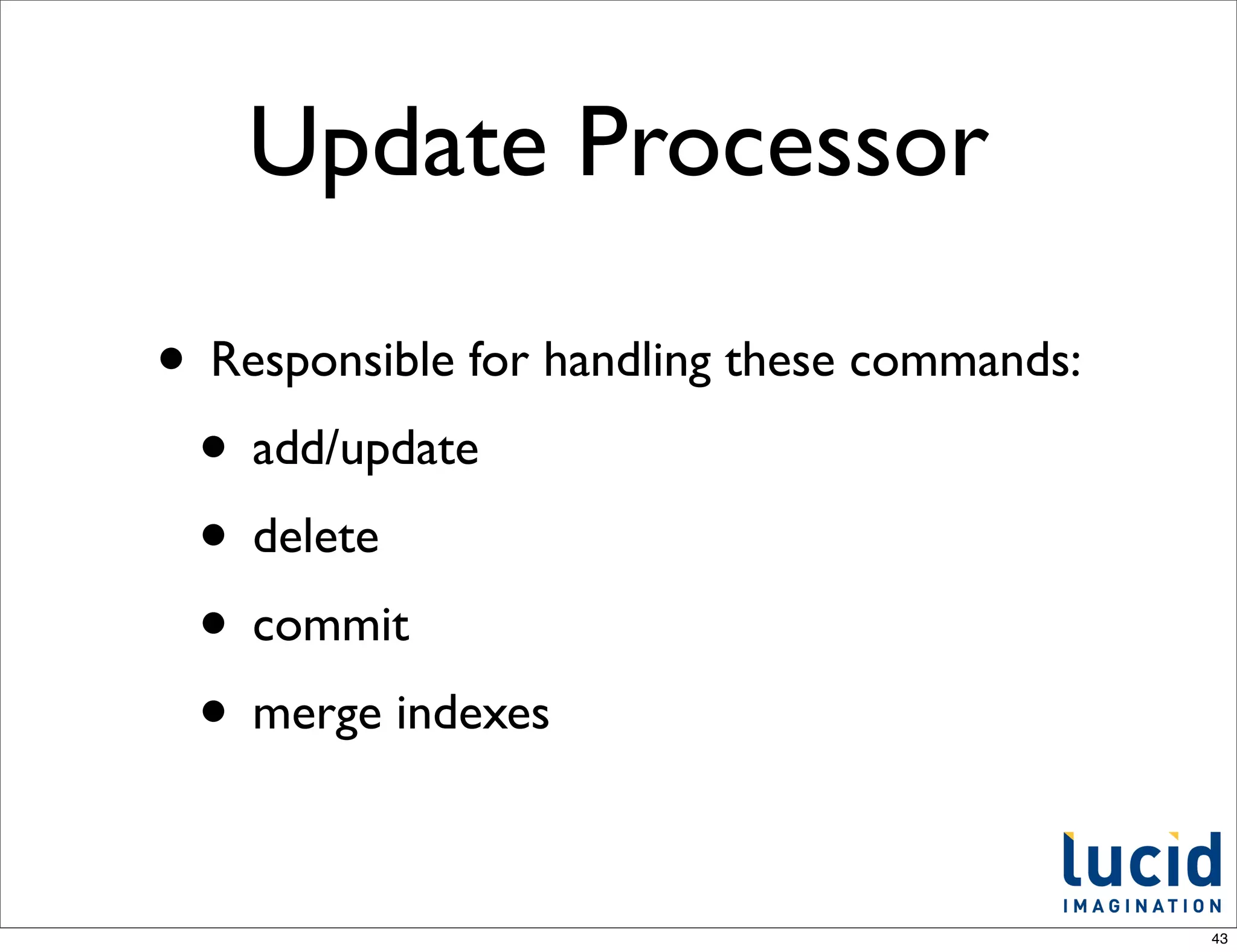
![Default update
processor chain
From SolrCore.java
// construct the default chain
UpdateRequestProcessorFactory[] factories =
new UpdateRequestProcessorFactory[]{
new RunUpdateProcessorFactory(),
new LogUpdateProcessorFactory()
};
Note: these steps have been swapped on trunk recently
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/luceneforsolrdevelopers-111203091216-phpapp02/75/Lucene-for-Solr-Developers-47-2048.jpg)
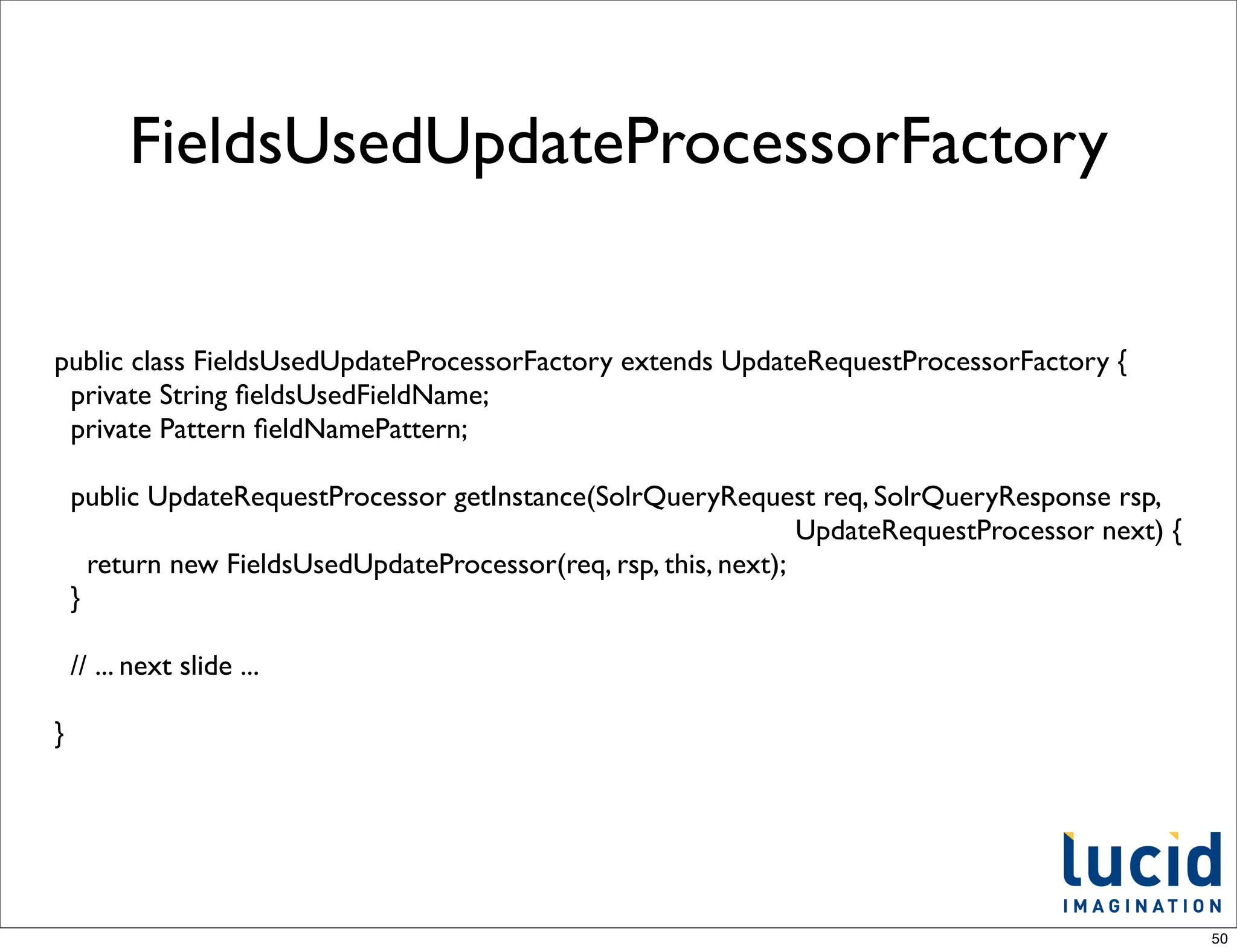
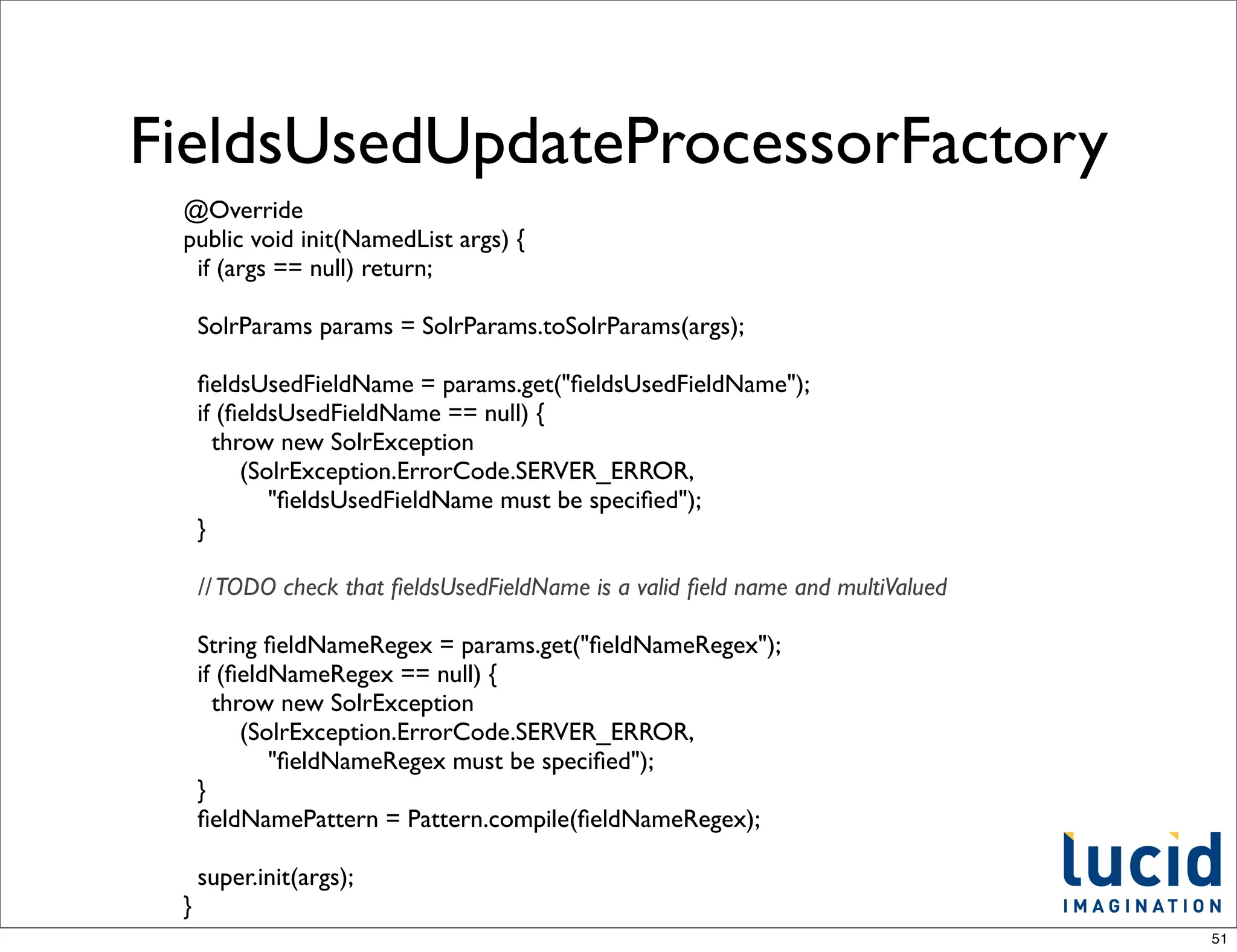

![FieldsUsedUpdateProcessor
in action
schema.xml
<dynamicField name="*_attribute" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
Add some documents
solr.add([{:id=>1, :name => "Big Blue Shoes", :size_attribute => 'L', :color_attribute => 'Blue'},
{:id=>2, :name => "Cool Gizmo", :memory_attribute => "16GB", :color_attribute => 'White'}])
solr.commit
Facet on attribute_fields
- http://localhost:8983/solr/select?q=*:*&facet=on&facet.field=attribute_fields&wt=json&indent=on
"facet_fields":{
"attribute_fields":[
"color_attribute",2,
"memory_attribute",1,
"size_attribute",1]}
53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/luceneforsolrdevelopers-111203091216-phpapp02/75/Lucene-for-Solr-Developers-53-2048.jpg)




![autofacet success
http://localhost:8983/solr/searchplus
?q=*:*&facet=on&autofacet.field=attribute_fields&wt=json&indent=on
{
"response":{"numFound":2,"start":0,"docs":[
{
"size_attribute":["L"],
"color_attribute":["Blue"],
"name":"Big Blue Shoes",
"id":"1",
"attribute_fields":["size_attribute",
"color_attribute"]},
{
"color_attribute":["White"],
"name":"Cool Gizmo",
"memory_attribute":["16GB"],
"id":"2",
"attribute_fields":["color_attribute",
"memory_attribute"]}]
},
"facet_counts":{
"facet_queries":{},
"facet_fields":{
"color_attribute":[
"Blue",1,
"White",1],
"memory_attribute":[
"16GB",1]}}}
58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/luceneforsolrdevelopers-111203091216-phpapp02/75/Lucene-for-Solr-Developers-58-2048.jpg)