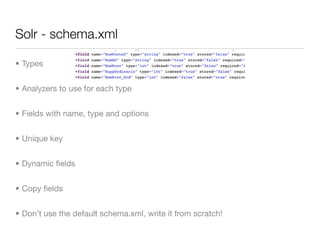
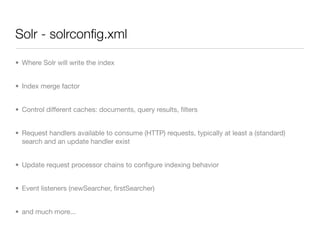
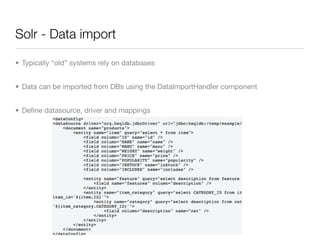
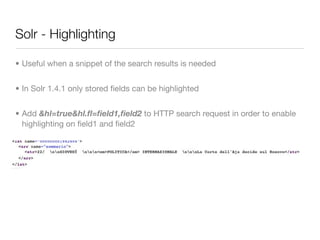
The document provides an overview of building scalable enterprise search services using Apache Lucene and Solr. It covers key aspects such as Lucene's indexing capabilities, Solr's architecture, query syntax, configuration, and advanced features like faceting and replication. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of using Solr as a ready-to-use enterprise search server leveraging Lucene's power.






![Solr - Query syntax
• Default operator is OR (you can override adding &q.op=AND to the HTTP req)
• You can query fields with fieldname:value
• Common + - AND OR NOT modifiers
• Range queries on date or numeric fields timestamp:[* TO NOW]
• Boost terms, i.e.: roma^2 inter
• Fuzzy search roam~0.6
• ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vers1-100924022755-phpapp02/85/Apache-Solr-Enterprise-search-platform-14-320.jpg)