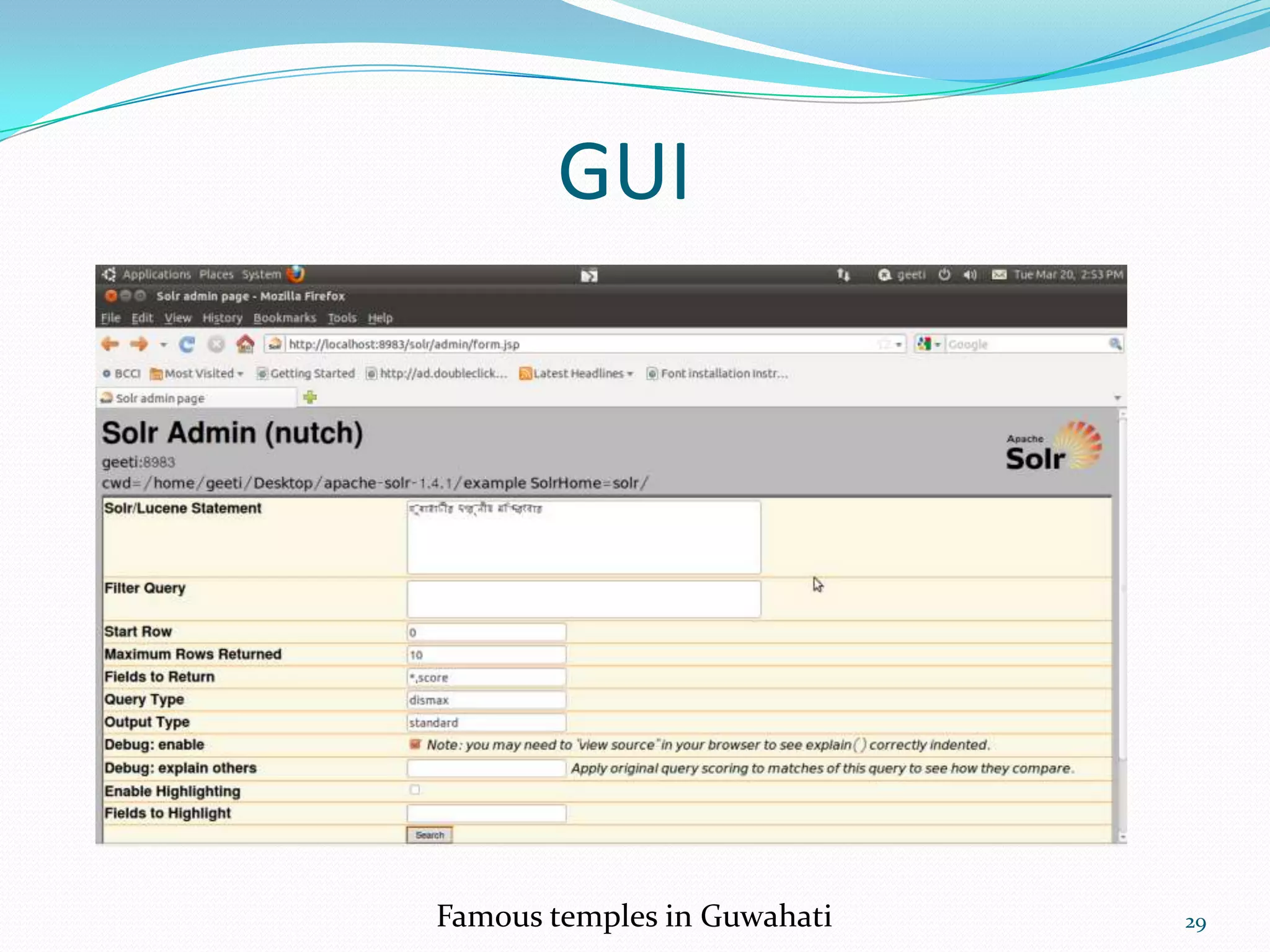
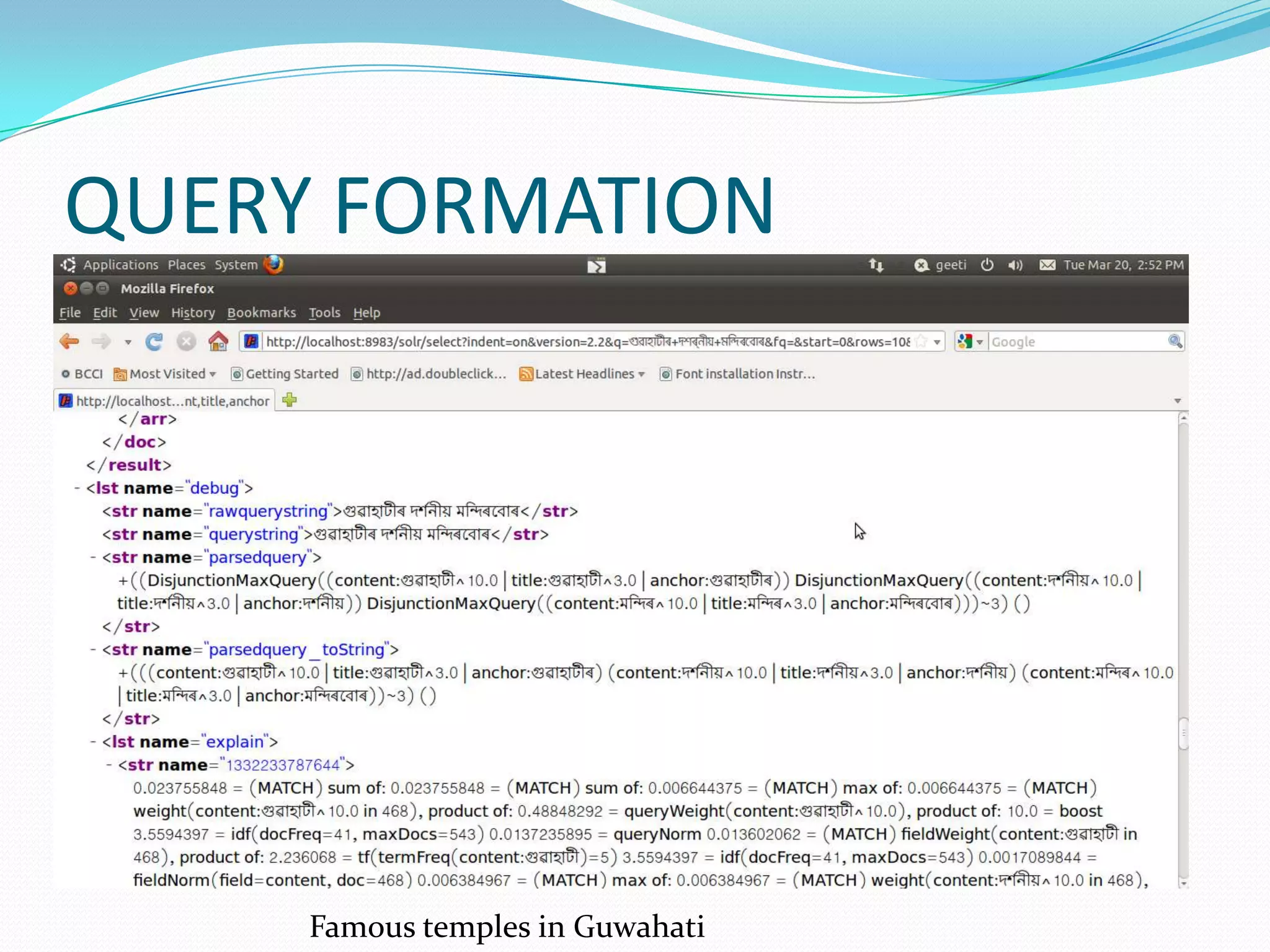
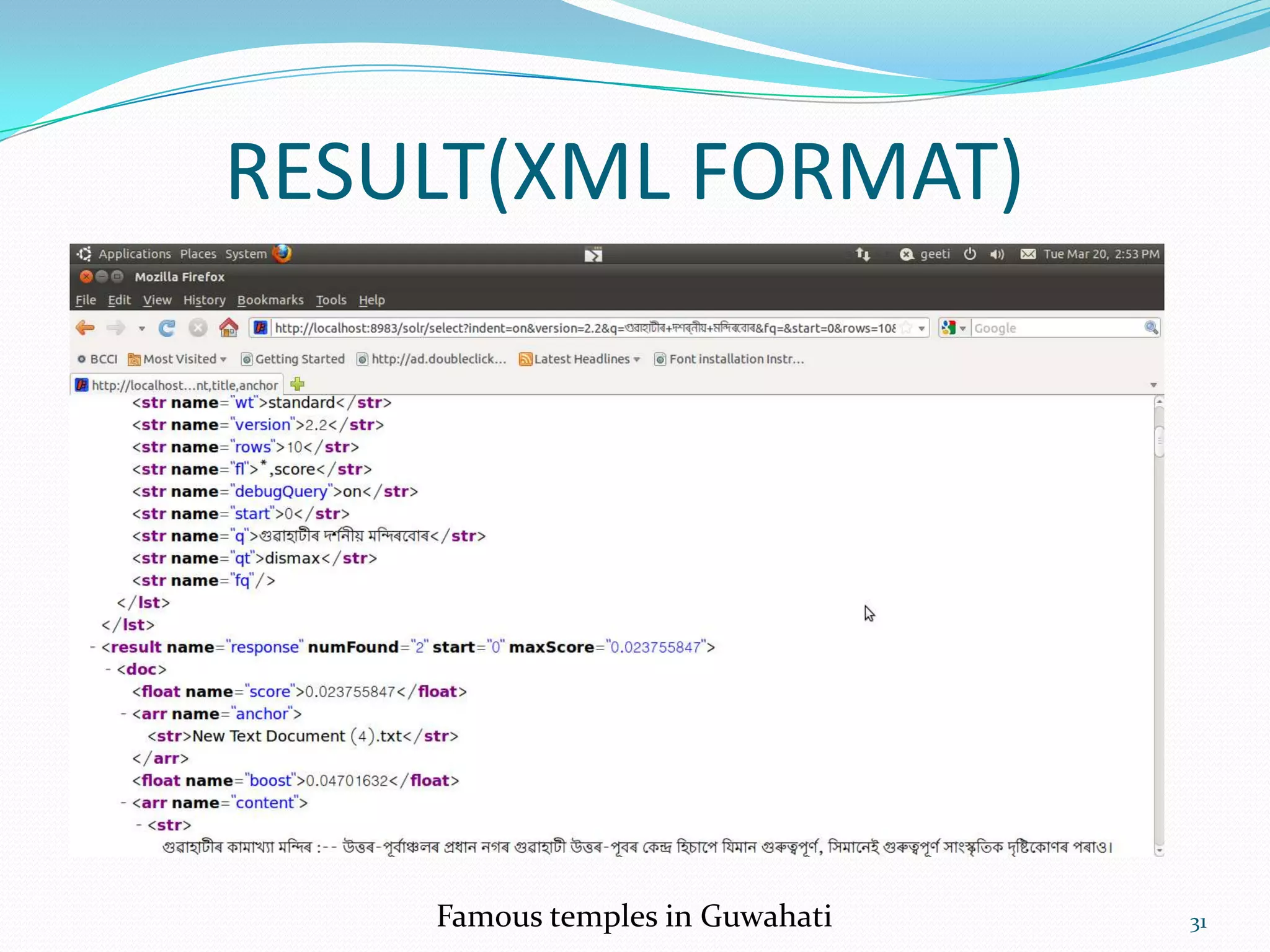
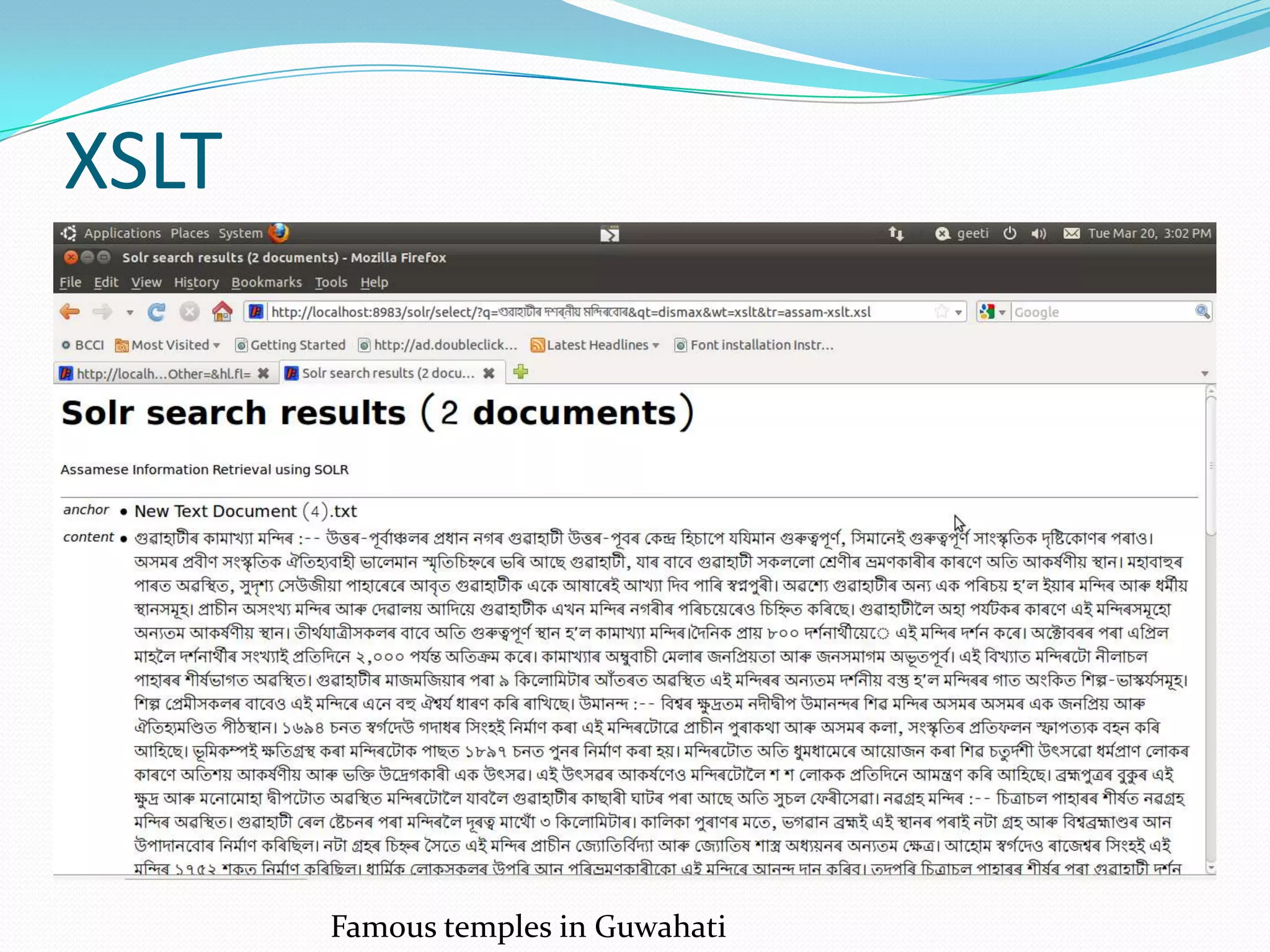
The document provides an overview of Solr, an open-source enterprise search platform built on the Lucene library, highlighting its features such as hit highlighting, faceted search, and distributed searching. It discusses the indexing process, configuration through schema.xml, and querying functionalities with request handlers. Additionally, the document addresses the implementation of Solr for Assamese and cross-lingual search, as well as future work and conclusions regarding its flexibility and features.


![What is Solr?
Solr is an open source enterprise search platform from
the Apache Lucene project.[1]
Solr=Lucene + added features
Allows for faster, more comprehensive searches on a
large volume of data
7/15/2012 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assamesesearchengine-120715042044-phpapp02/75/Assamese-search-engine-using-SOLR-by-Moinuddin-Ahmed-moin-3-2048.jpg)



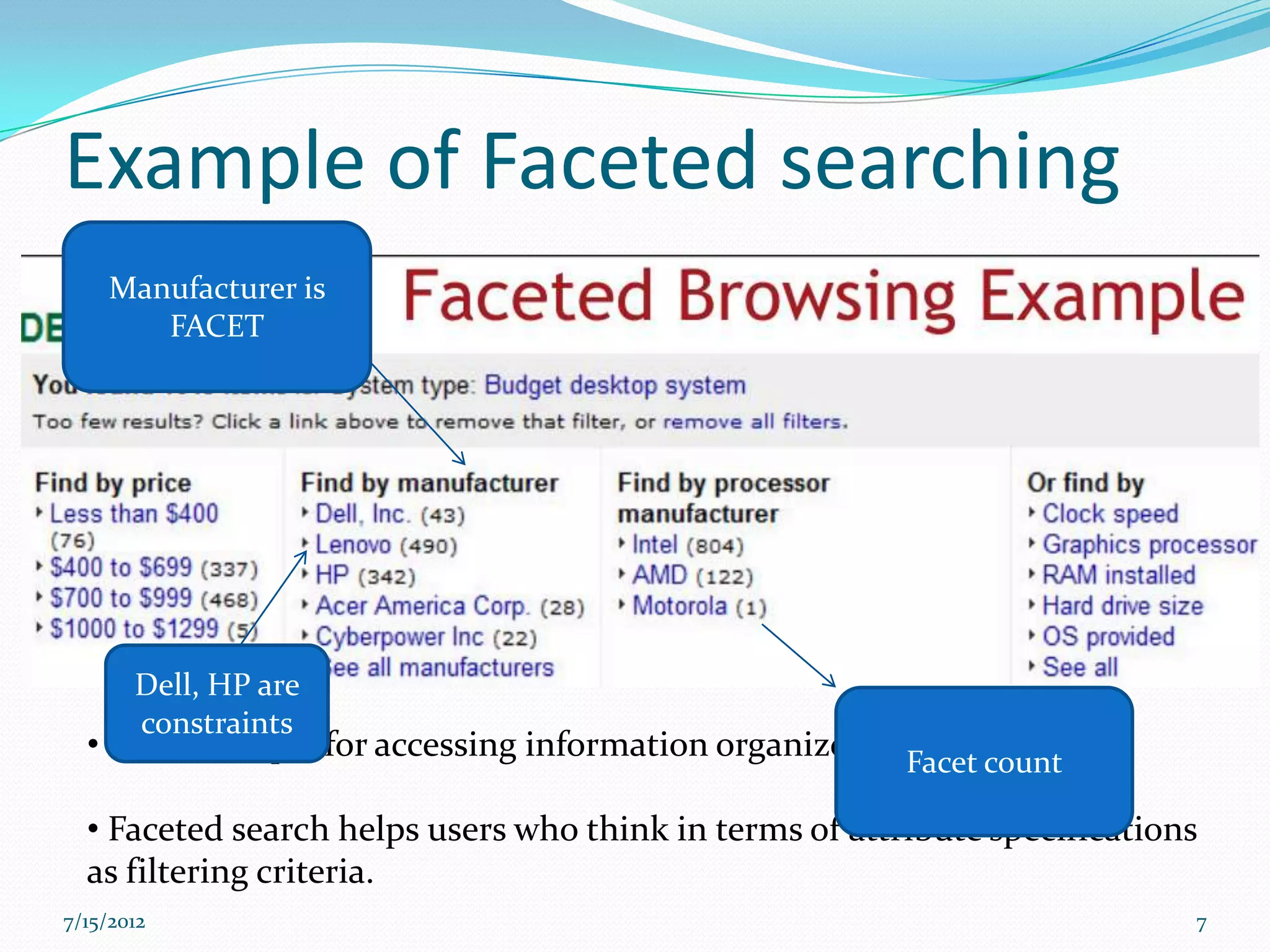

![Distributed Search
When an index becomes too large to fit on a single system, an index can be
split into multiple shards[2]
A single shard receives the query, distributes the query to other shards
Solr can query and merge results across those shards.
7/15/2012 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assamesesearchengine-120715042044-phpapp02/75/Assamese-search-engine-using-SOLR-by-Moinuddin-Ahmed-moin-9-2048.jpg)









![SOLR REQUEST HANDLER
A SolrRequestHandler is a Solr Plugin that defines the logic
executed for any request.[4]
Can be implemented either in solrconfig.xml or directly
in the url/user interface.
List of Request Handlers utilized
StandardRequestHandler
DisMaxRequestHandler
LukeRequestHandler
MoreLikeThisHandler](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assamesesearchengine-120715042044-phpapp02/75/Assamese-search-engine-using-SOLR-by-Moinuddin-Ahmed-moin-21-2048.jpg)
![DismaxRequestHandler
It is designed to process simple user entered phrases and search for the
individual words across several fields using different weighting (boosts)
based on the significance of each field. [4]
Some parameters of DismaxRequestHandler:
qf(query fields), fl(fields), pf(phrase fields), bq(boost query), etc.
Example
<requesthandler=dismax>
<str name="fl">
title,content,anchor,host,url
</str>
<str name="qf">
url^3.0 anchor content^10.0 title^3.0 host^2.0
</str>
</requesthandler>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assamesesearchengine-120715042044-phpapp02/75/Assamese-search-engine-using-SOLR-by-Moinuddin-Ahmed-moin-22-2048.jpg)
![Response Writers
A QueryResponseWriter is a Solr Plugin that defines
the response format for any request[3].
Uses a default format XmlResponseFormat.
Also has several others response formats like Xslt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assamesesearchengine-120715042044-phpapp02/75/Assamese-search-engine-using-SOLR-by-Moinuddin-Ahmed-moin-23-2048.jpg)
![XSLT RESPONSE WRITER..
The XSLT Response Writer captures the output of the XML
Response Writer and applies an XSLT transform to it.[3]
http://localhost:8983/solr/select/?q=‘user query’&wt=xslt&tr=example.xsl
Parameters:
Wt: writer used
Tr: Selects the XSLT transformation to use, which must be found in
Solr's conf/xslt directory.
The Content-Type of the response is set according to the <xsl:output>
statement in the XSLT transform, for example:
<xsl:output media-type="text/html"/>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assamesesearchengine-120715042044-phpapp02/75/Assamese-search-engine-using-SOLR-by-Moinuddin-Ahmed-moin-24-2048.jpg)