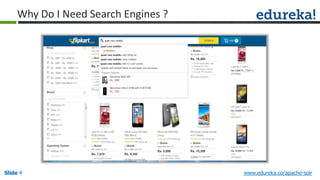
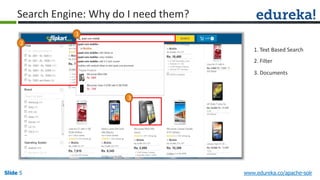
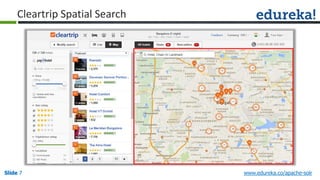
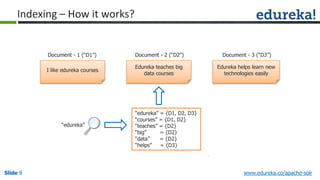
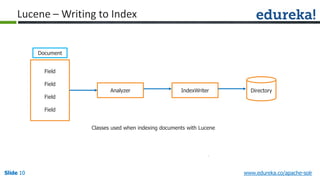
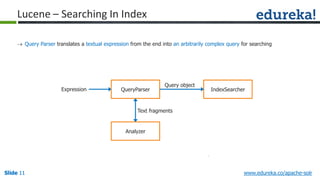
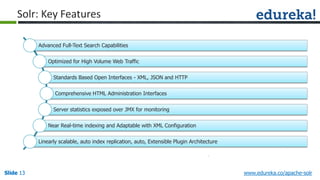
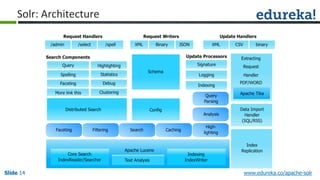
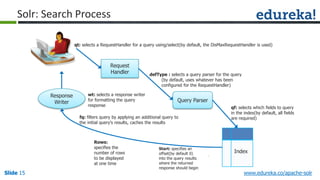
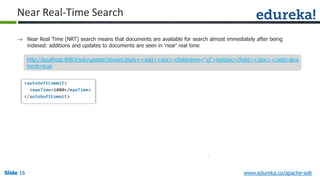
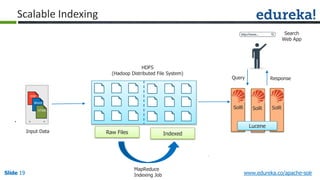
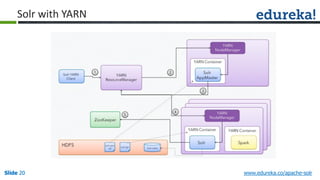
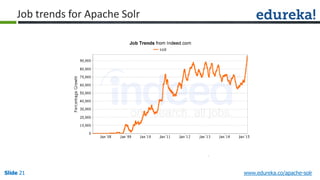
The document provides an overview of a course on Apache Solr, an enterprise search server that utilizes the Lucene search library for efficient indexing and searching. It covers the importance of search engines, Solr's architecture, features, and integration with Hadoop for scalable indexing. Additionally, it highlights job opportunities for Solr developers and offers post-class support and certification for participants.