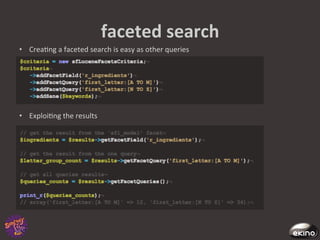
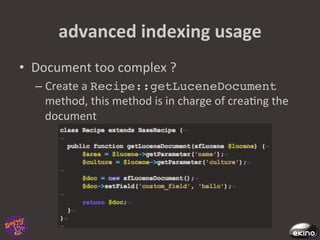
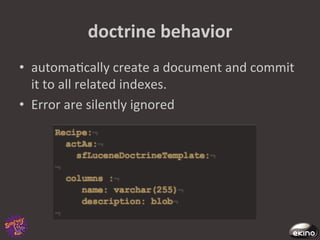
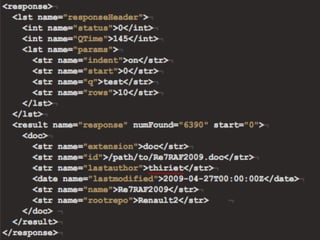
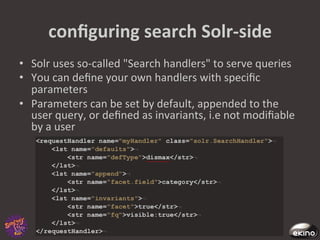
The document discusses Thomas Rabaix's involvement with Symfony including developing plugins, writing a book, and now working for Ekino. It also provides an overview of a talk on Solr including indexing, searching, administration and deployment of Solr. The talk covers what Solr is, indexing documents, filtering queries, and how Solr integrates with Apache projects like Nutch and Tika.


















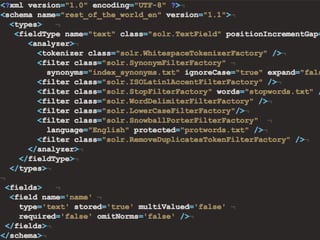



















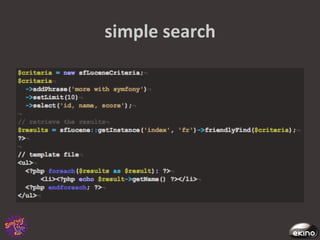
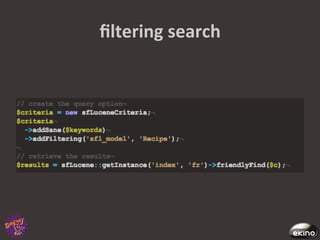
![query
parsing
:
lucene
• The
Lucene
query
parser
performs
all
the
Lucene
syntax
tricks
:
– Logical
opera8ons
:
term1
AND
NOT
term2,(term1
OR
term2)
and
TERM3
– Targe8ng
a
special
field
:
my_field_name:term1
– Range
queries
:
date_field:[*
TO
NOW
–
2
DAYS],
int_field:[0
TO
50]
– Phrase
queries
:
"term1
term2",
or
"term1
term2"~5
with
a
slop
factor
– Keyword
boos8ng
:
term1^1.5
term2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symfonylive-110304045042-phpapp02/85/Integrating-the-Solr-search-engine-47-320.jpg)