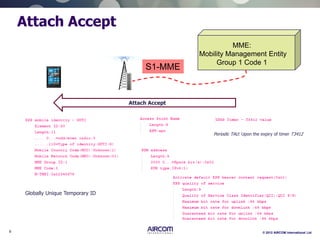
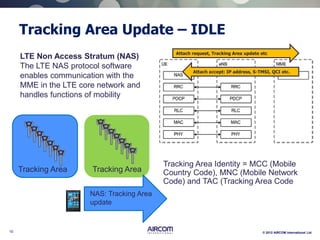
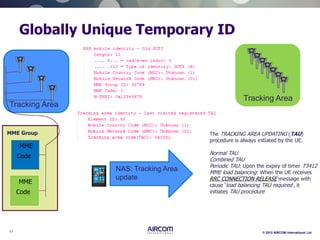
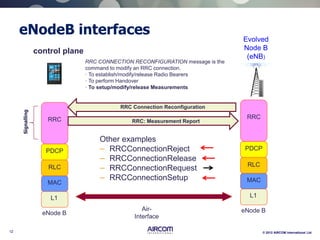
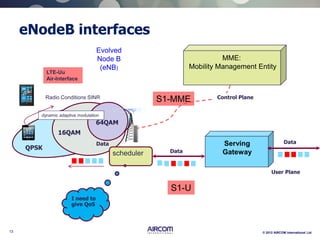
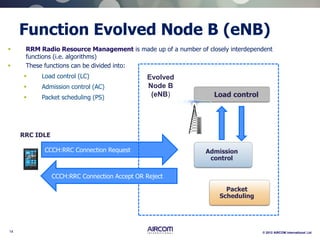
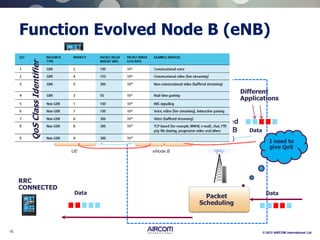
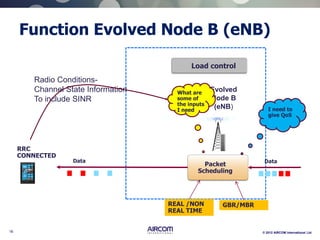
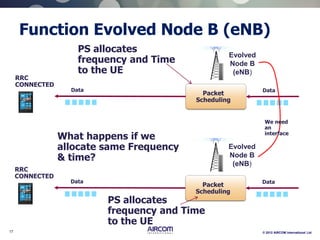
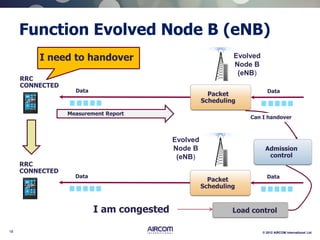
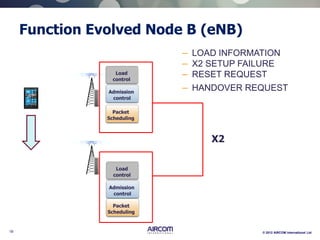
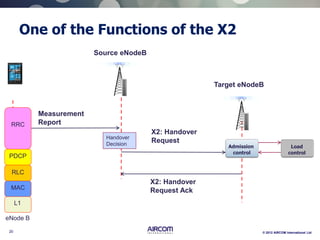
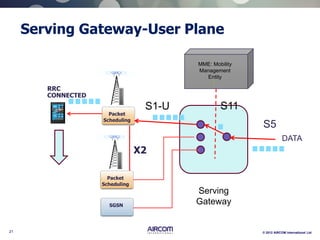
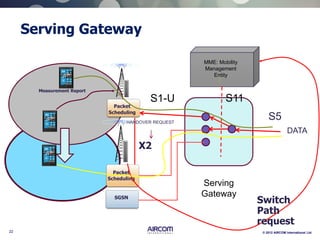
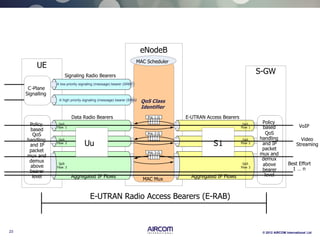
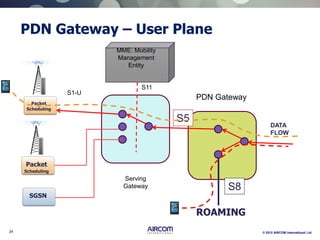
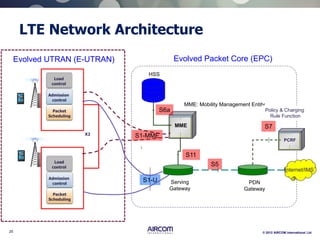
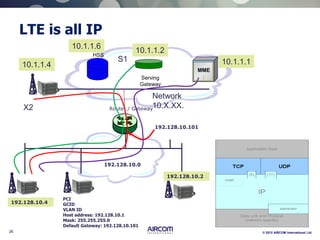
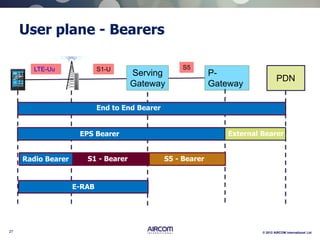
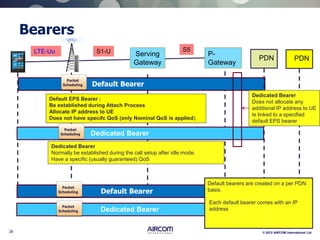
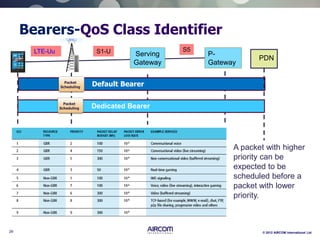
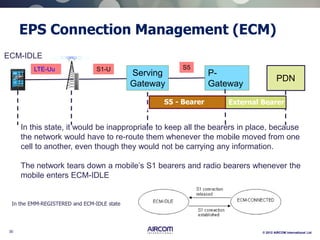
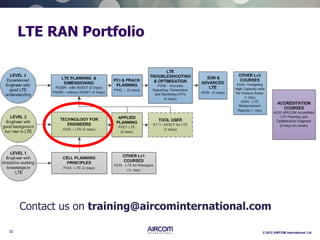
The document is a presentation on LTE network architecture by Aircom International, outlining the roles and functions of various components such as eNodeB, serving gateway, and PDN gateway. It introduces the presenters and provides an overview of Aircom's background and training offerings, emphasizing their expertise in mobile network planning and management. The presentation includes details on communication protocols and procedures relevant to LTE technology and concludes with an invitation for further engagement through upcoming webinars.