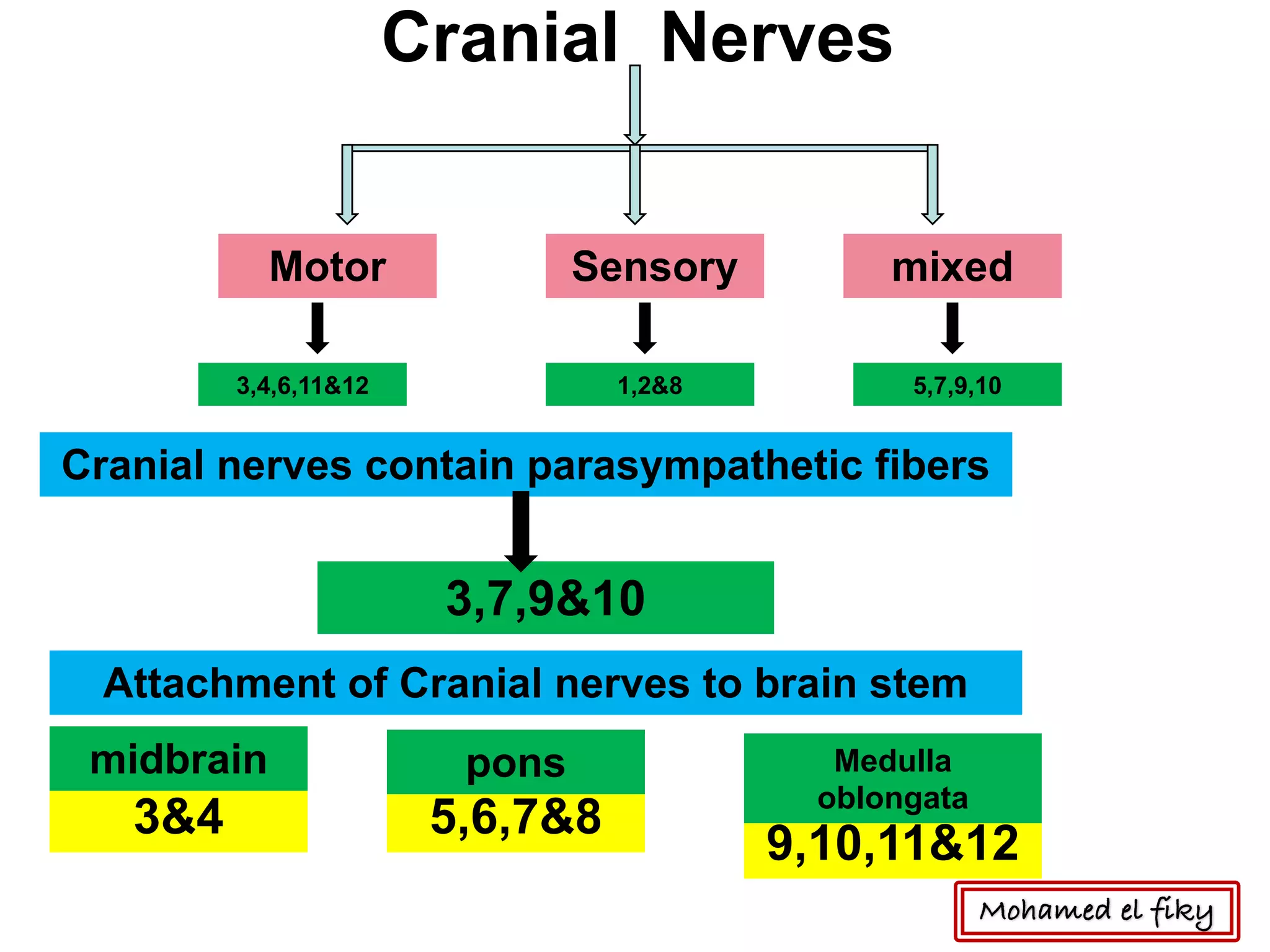
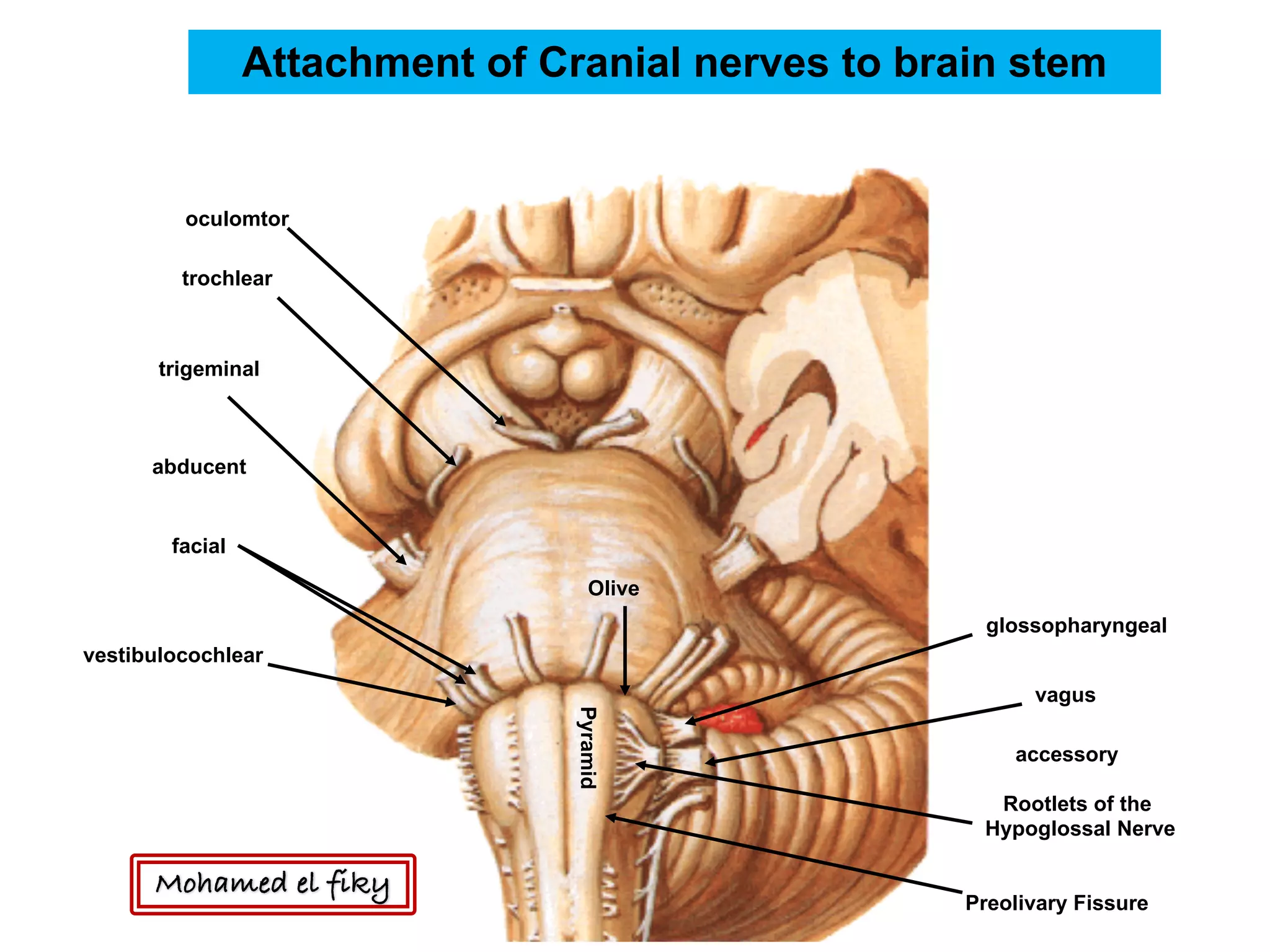
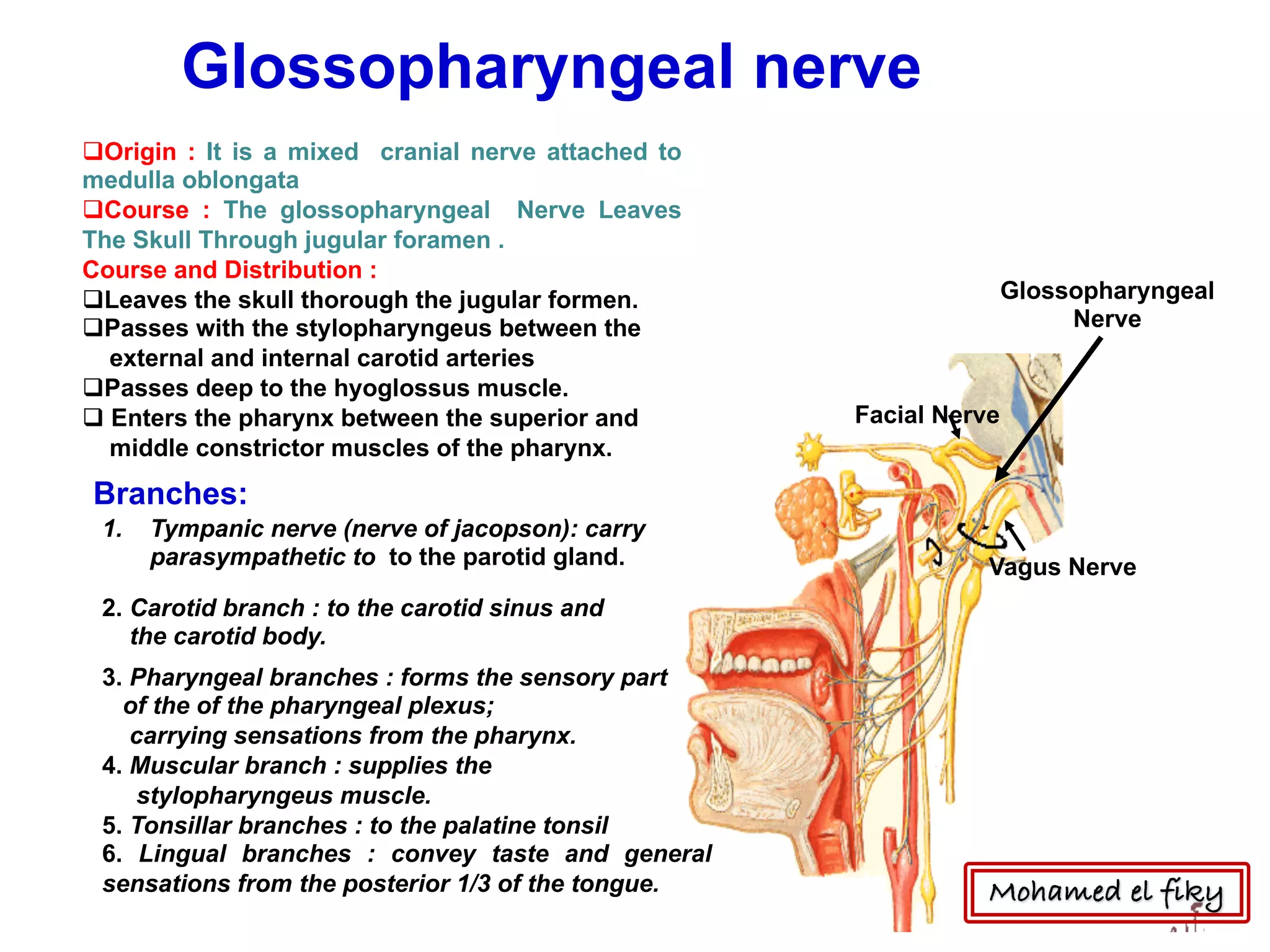
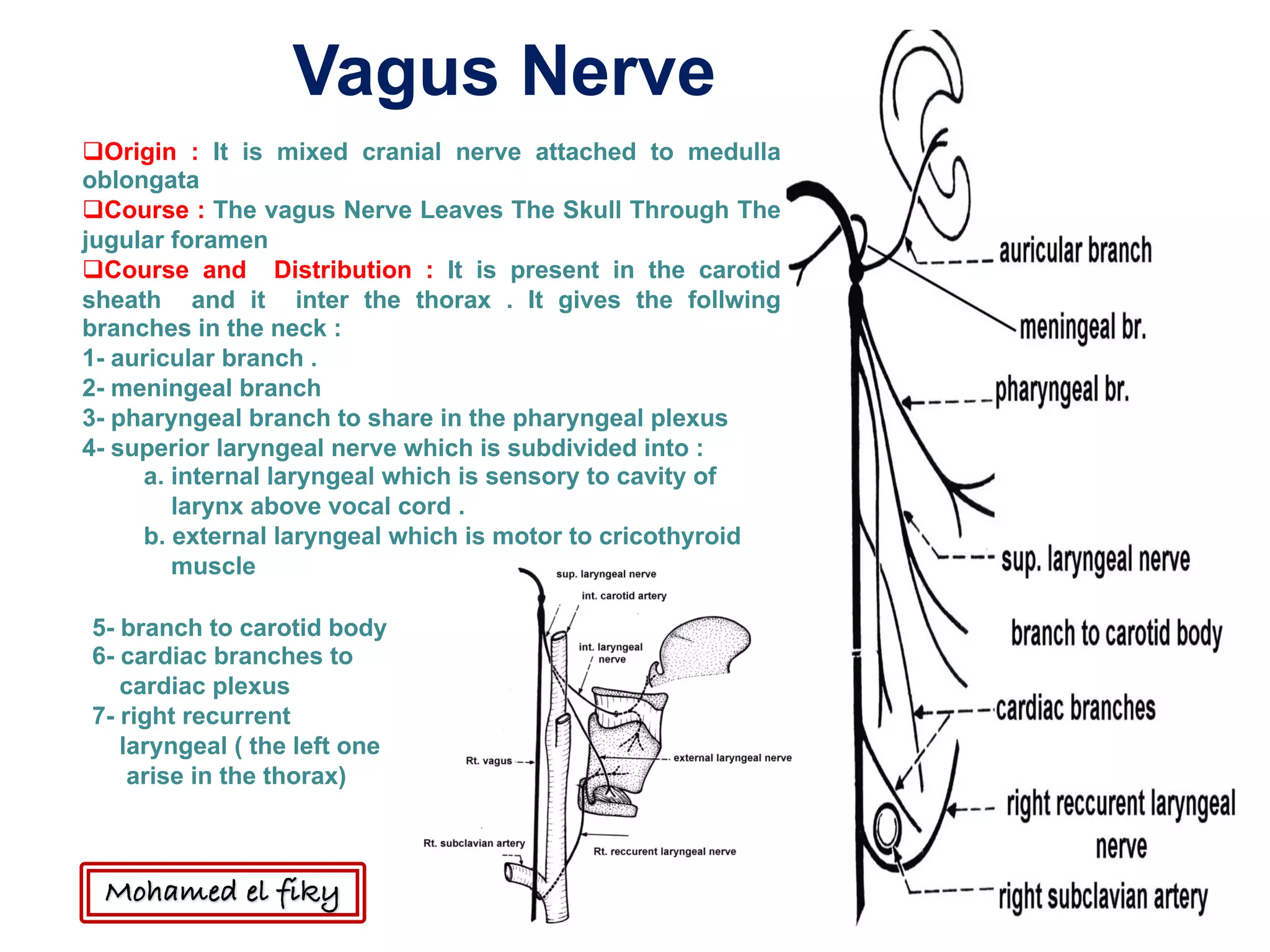
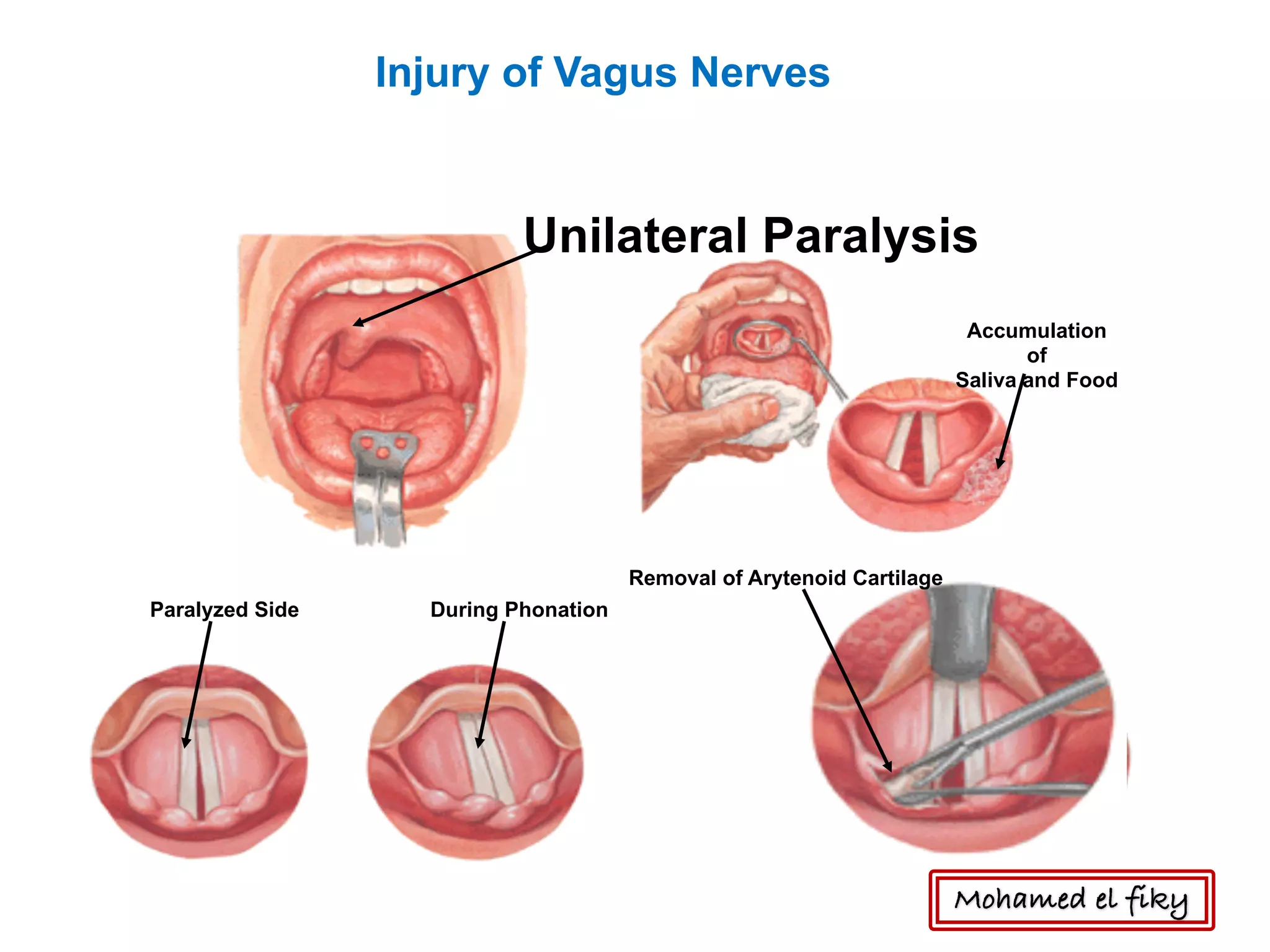
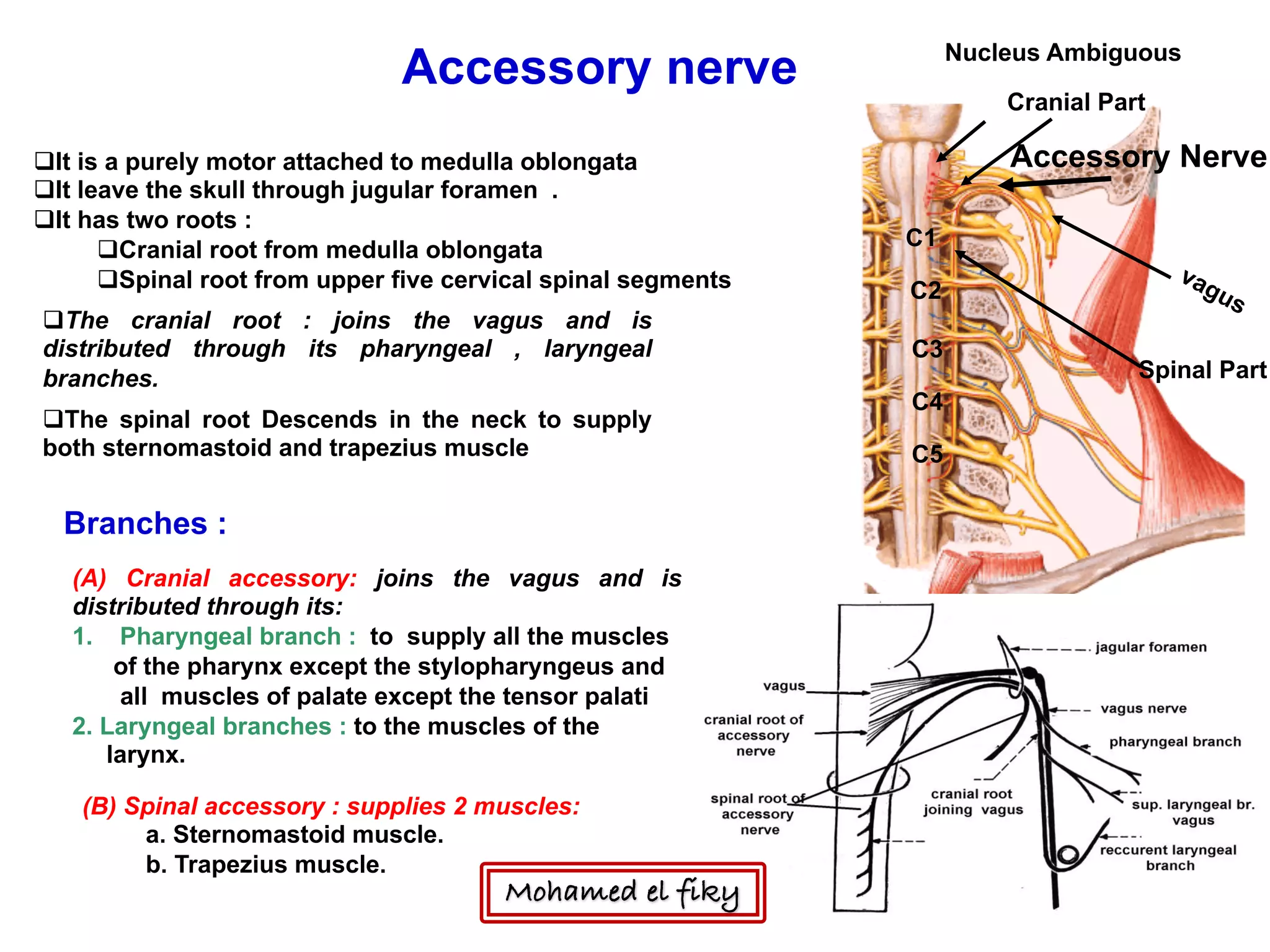
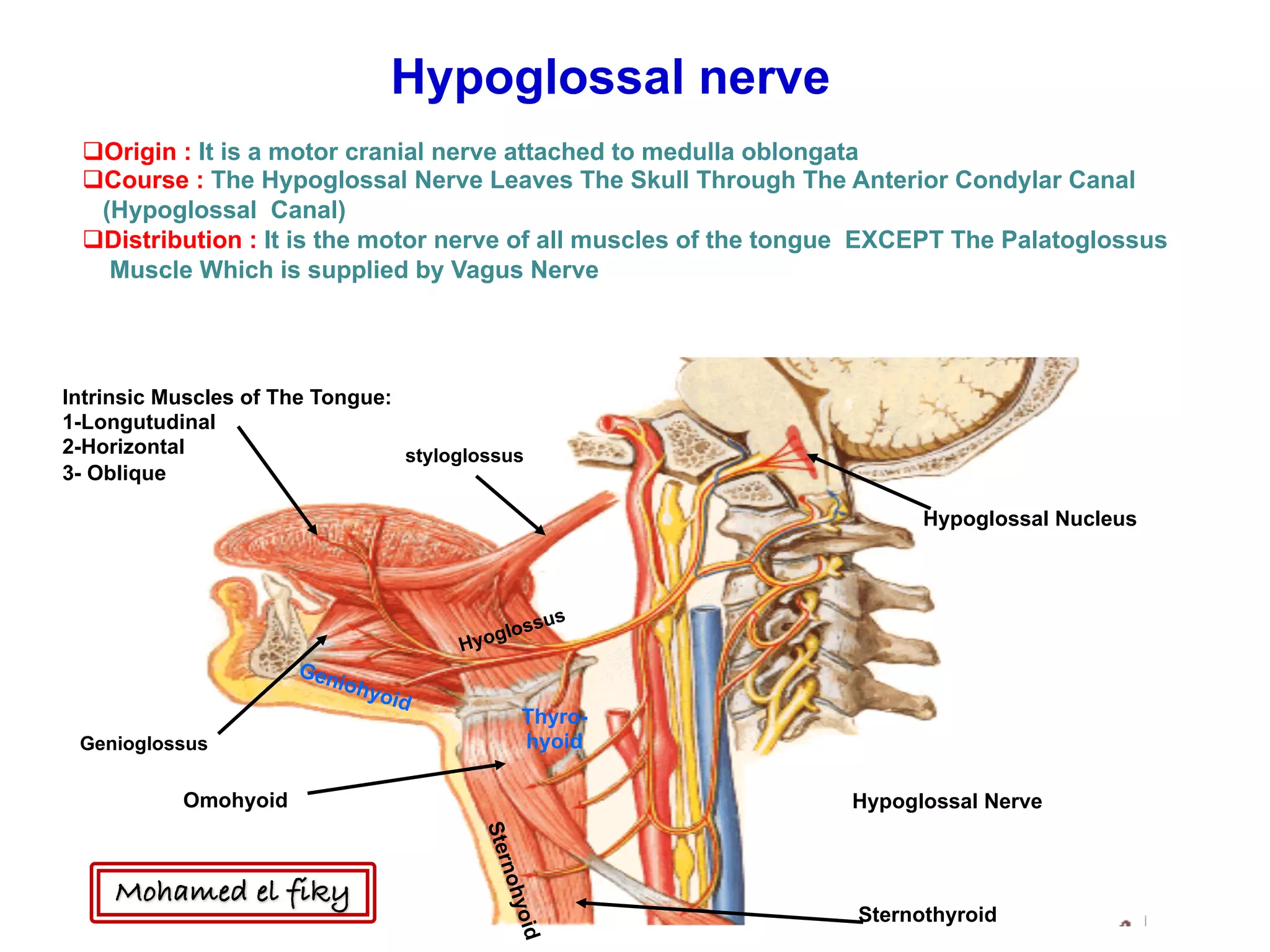
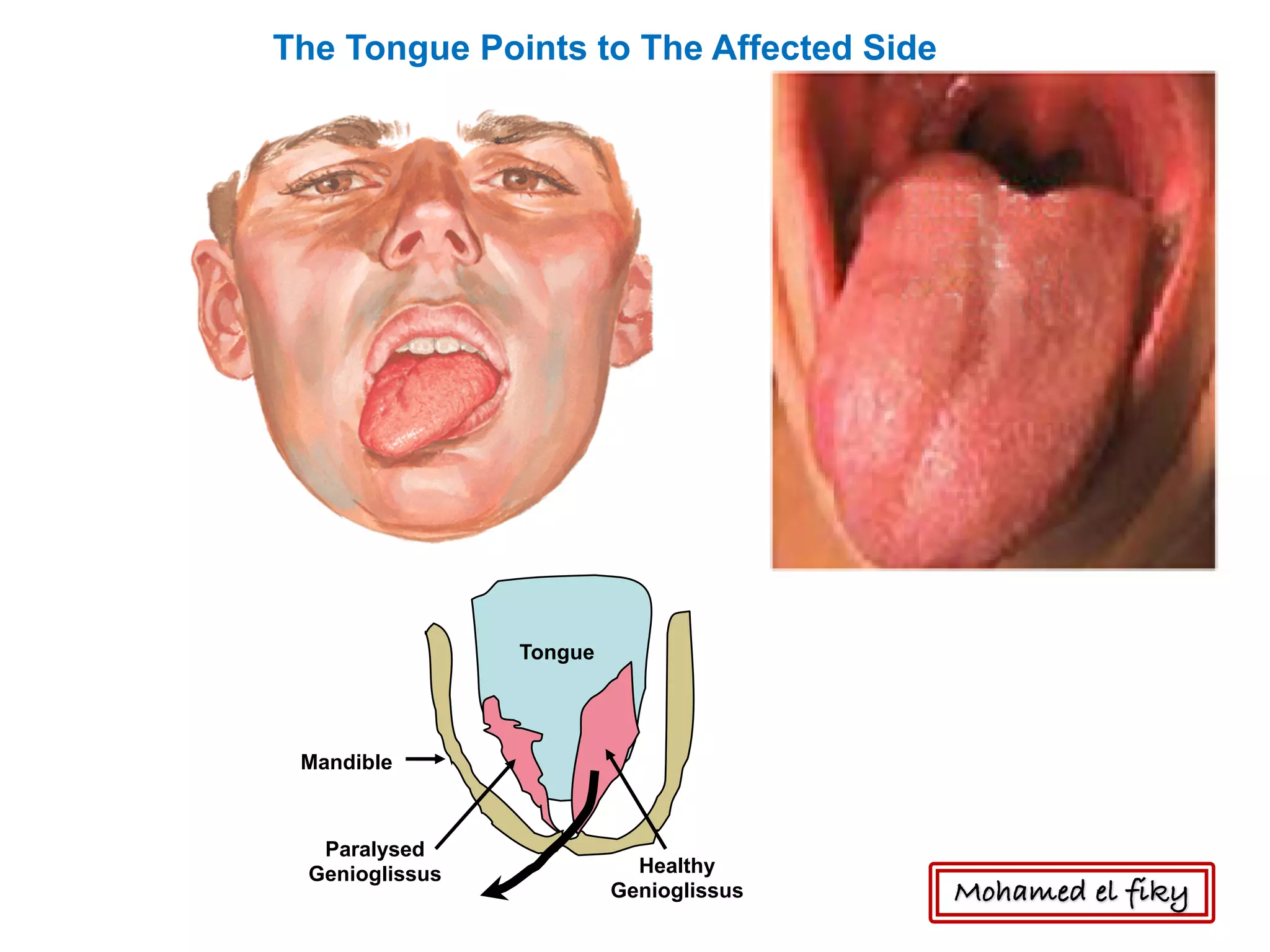
1) The document discusses several cranial nerves including their origin, course, and branches. It focuses on the glossopharyngeal nerve, vagus nerve, accessory nerve, and hypoglossal nerve.
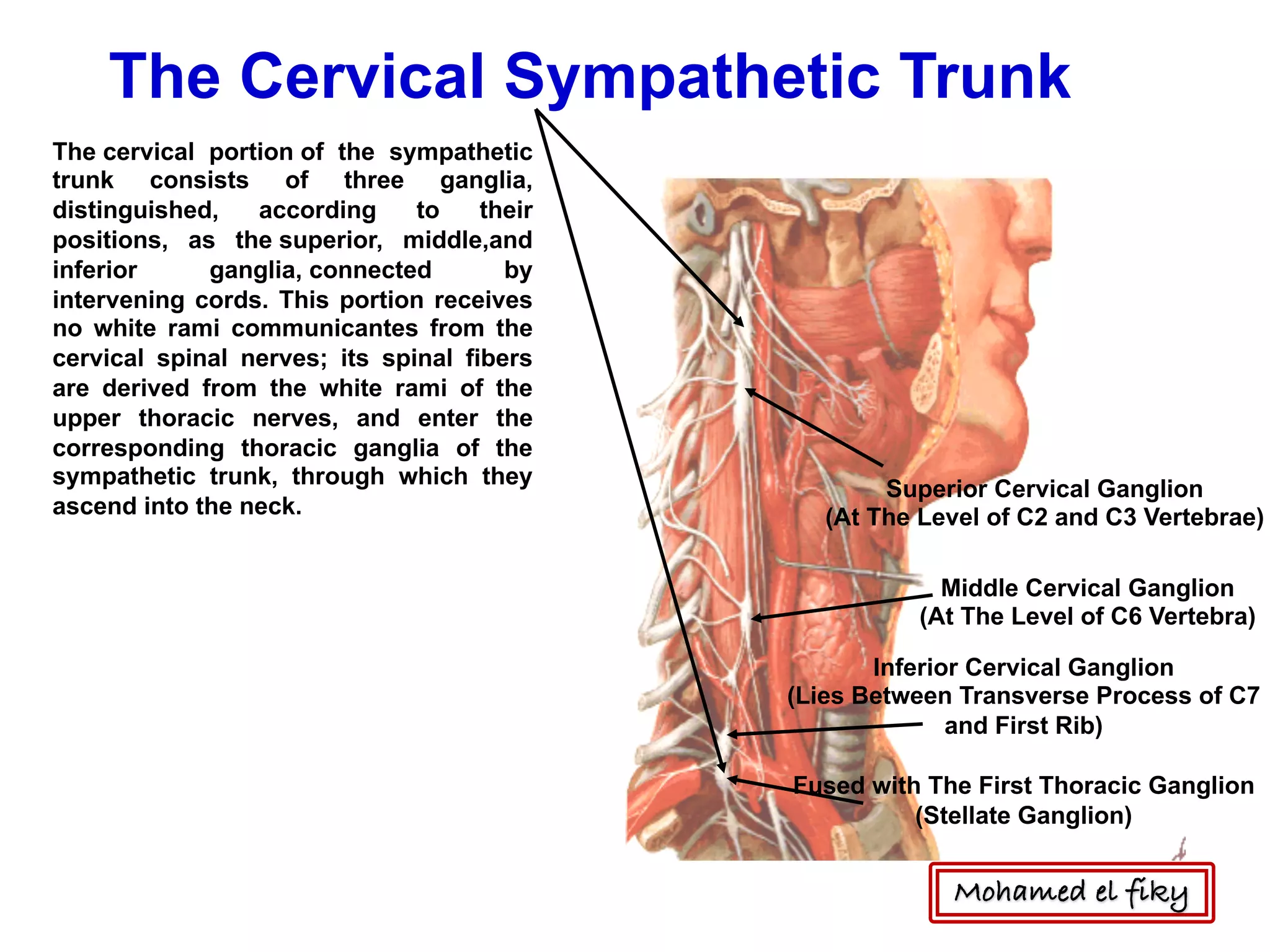
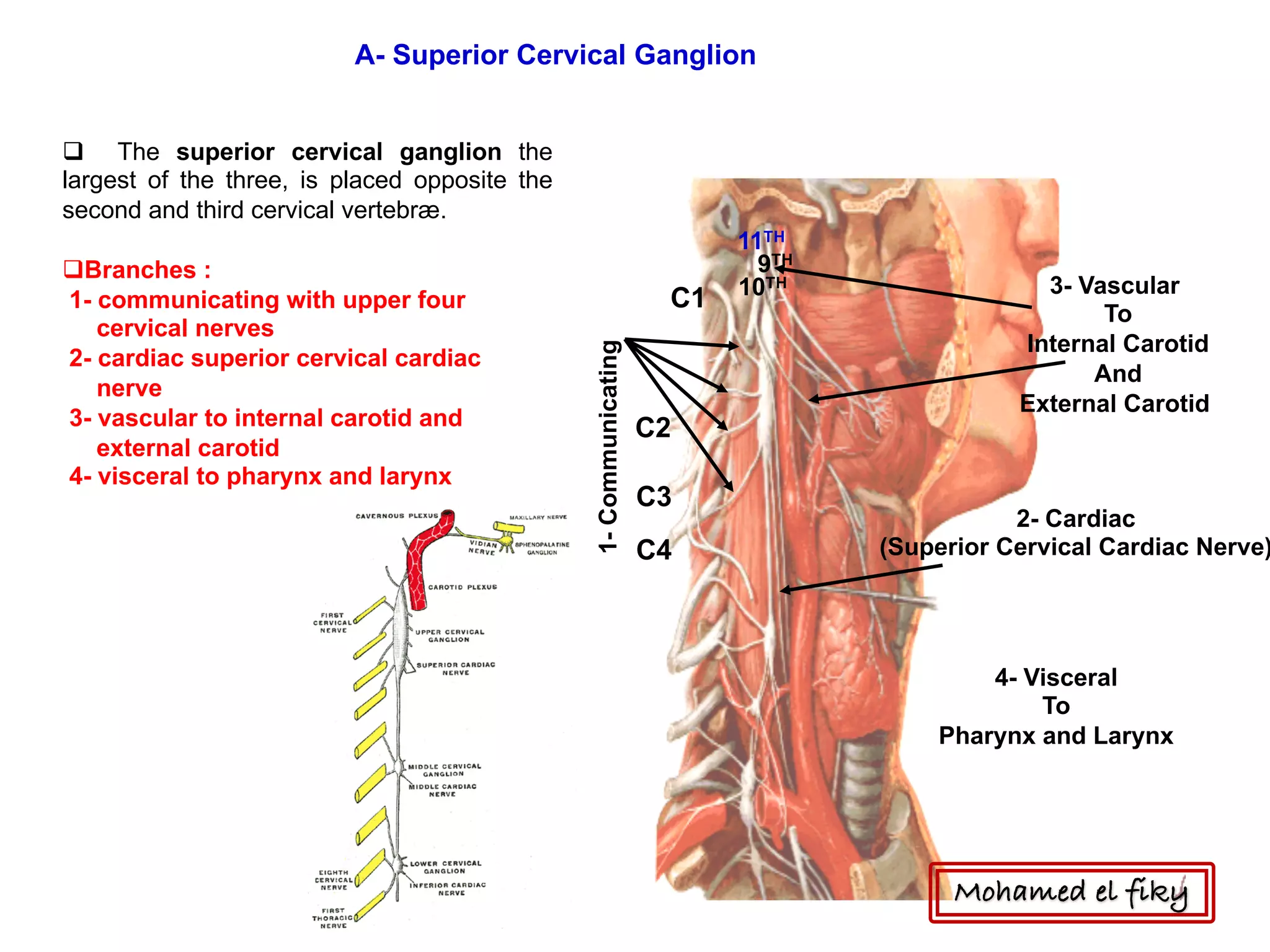
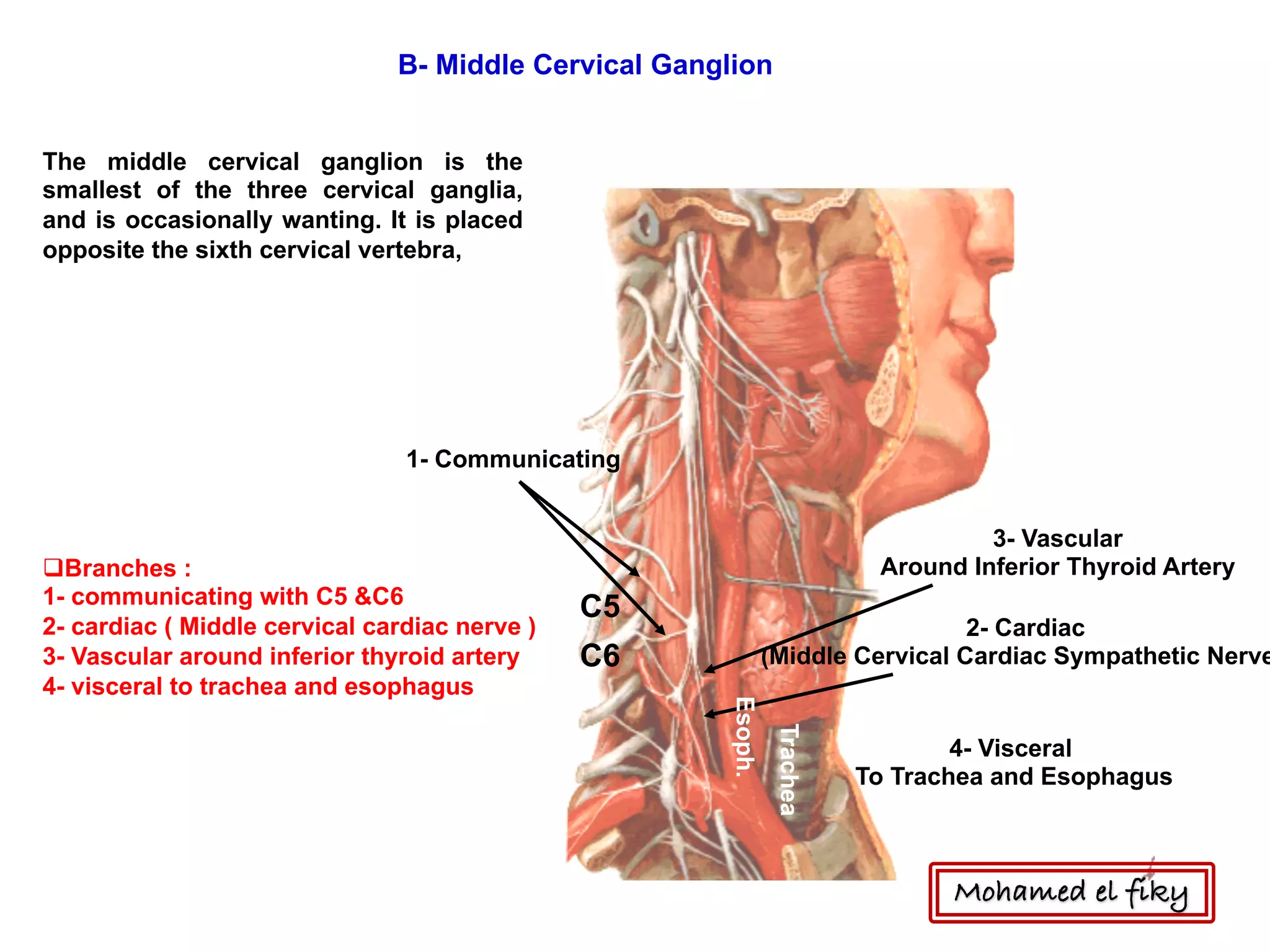
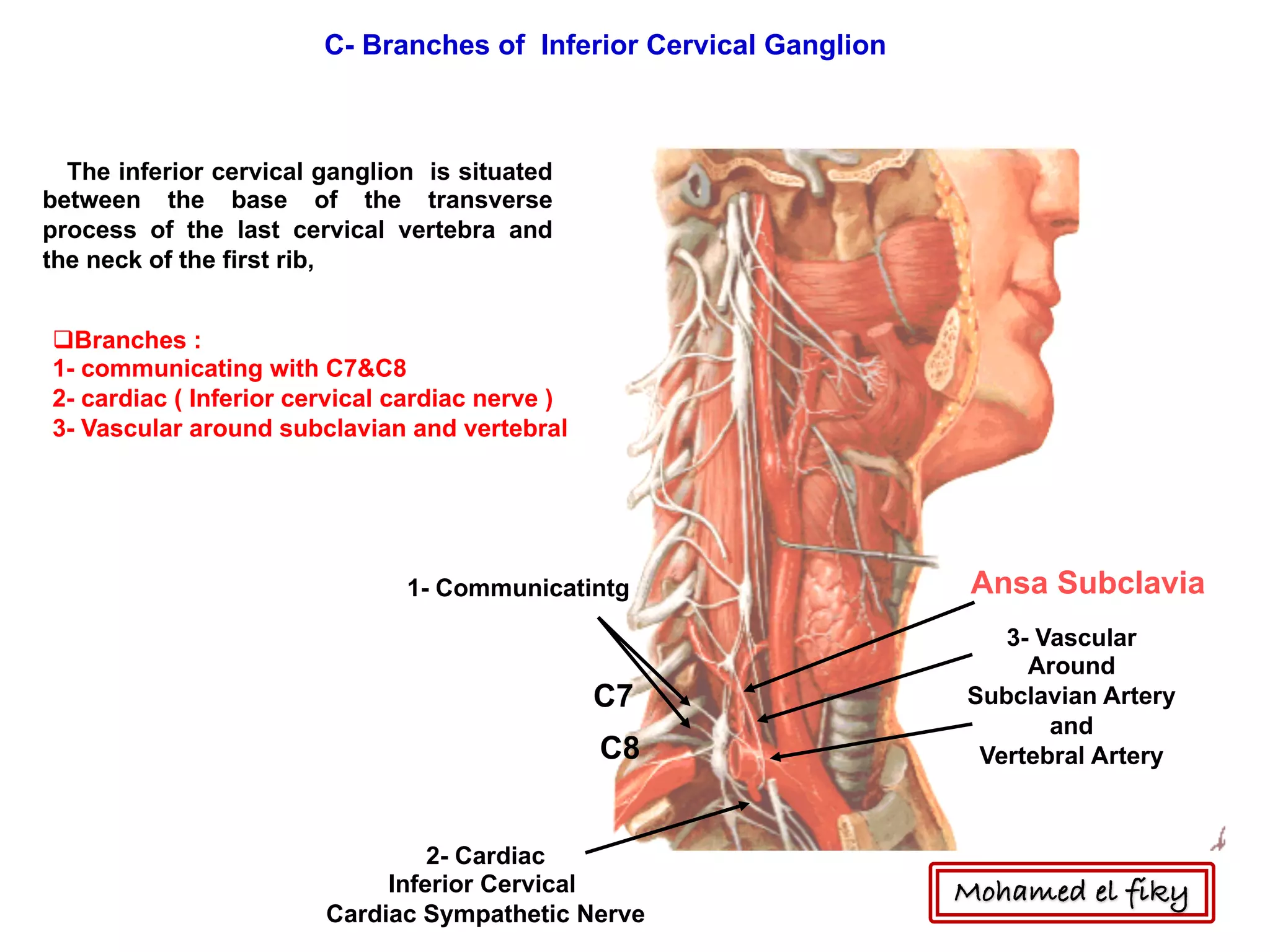
2) It also discusses the cervical sympathetic trunk, including the three cervical ganglia (superior, middle, inferior) and their branches for communication, cardiac nerves, and blood vessels.
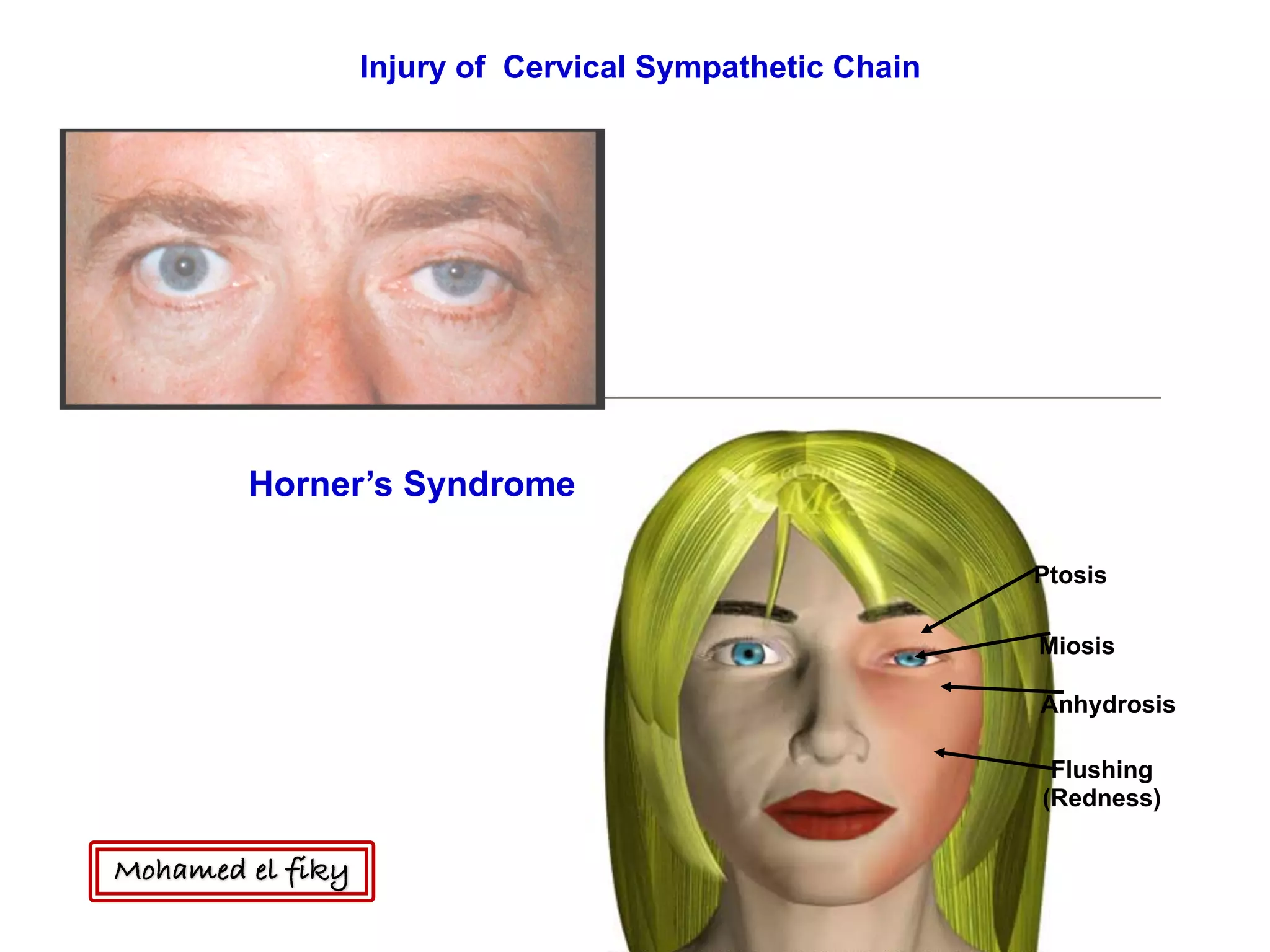
3) Horner's syndrome is mentioned as resulting from injury to the cervical sympathetic chain, causing ptosis, miosis, anhydrosis, and flushing.