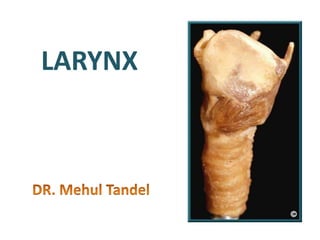
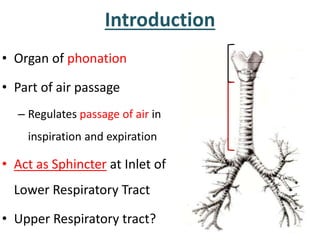
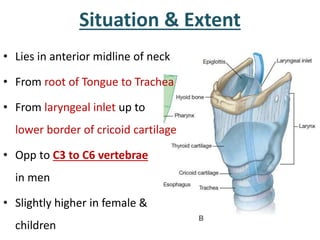
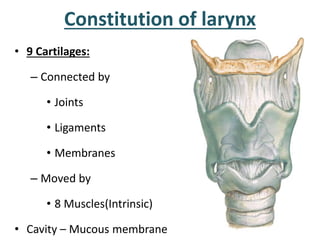
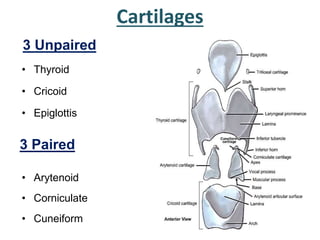
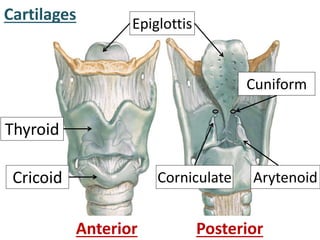
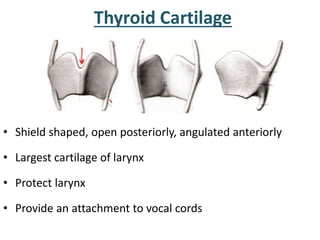
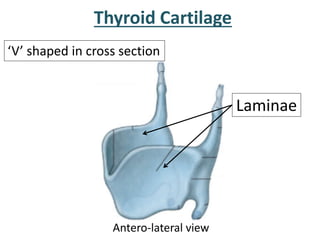
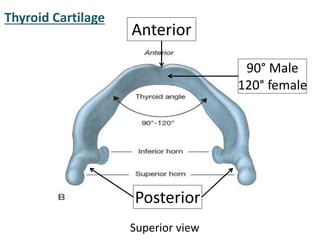
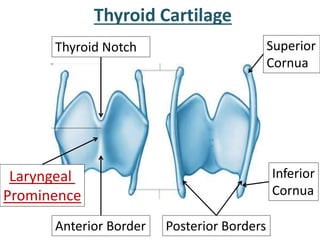
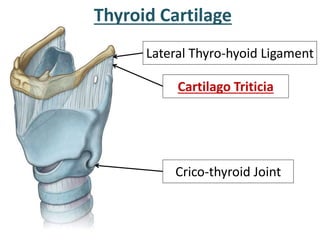
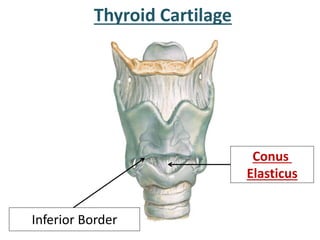
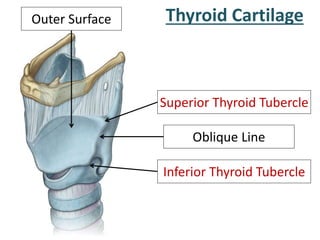
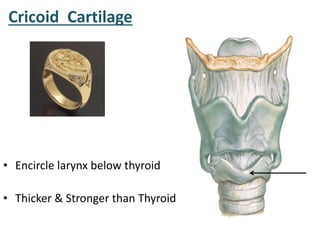
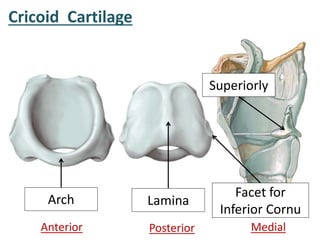
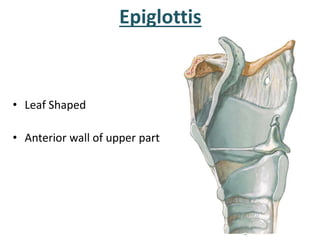
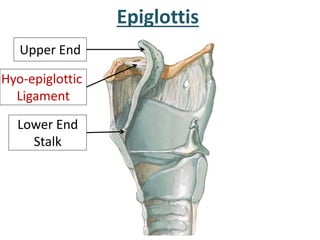
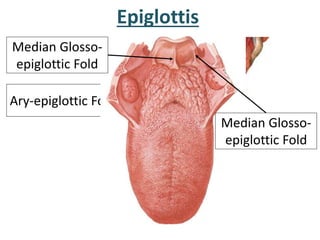
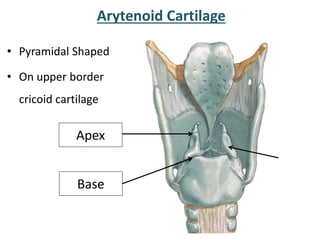
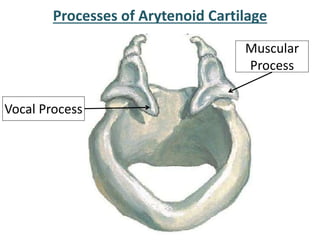
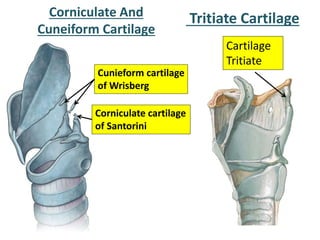
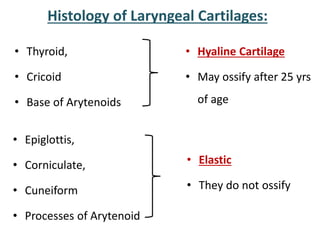
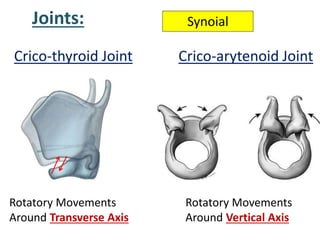
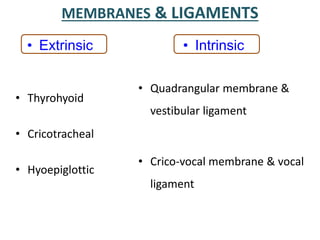
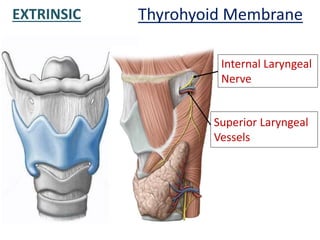
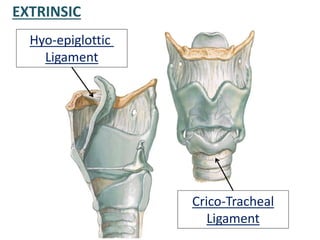
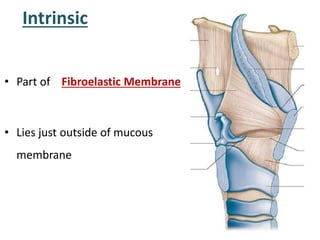
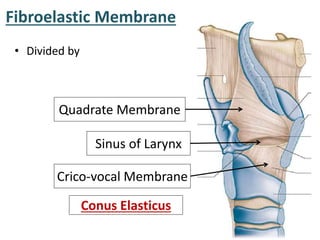
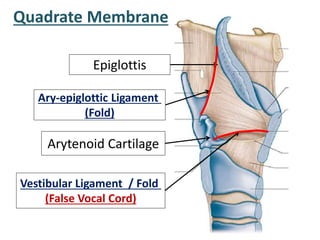
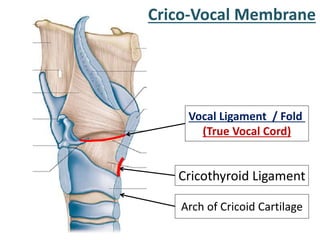
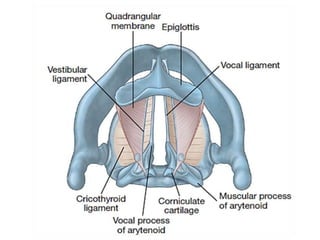
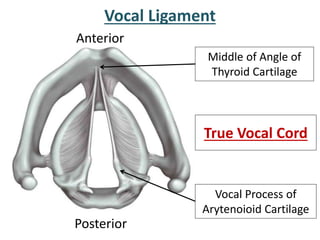
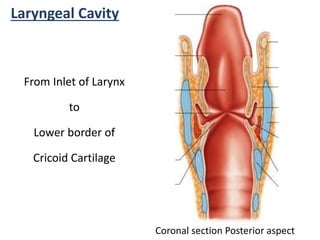
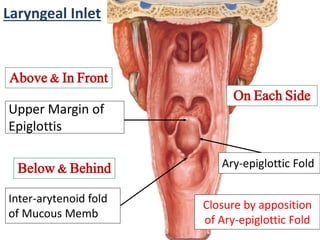
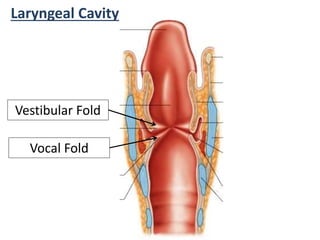
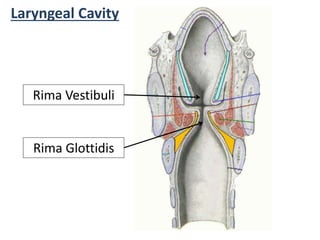
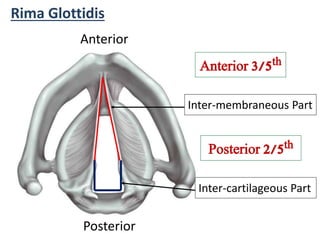
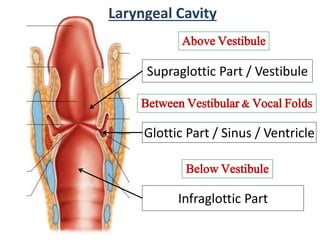
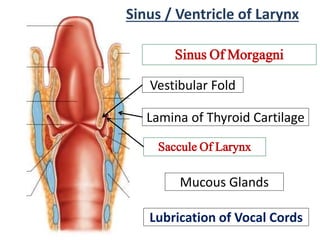
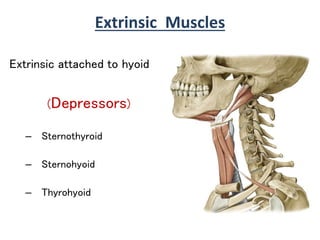
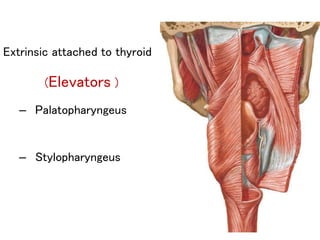
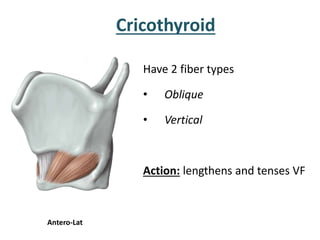
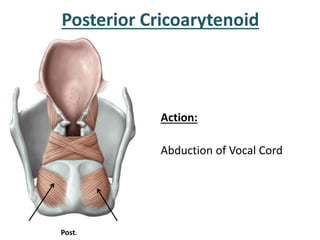
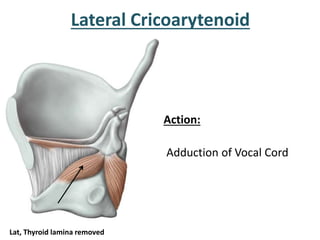
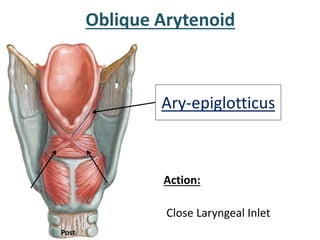
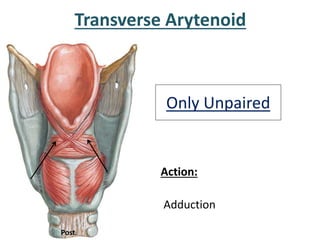
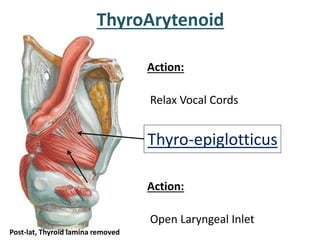
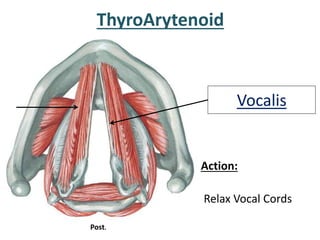
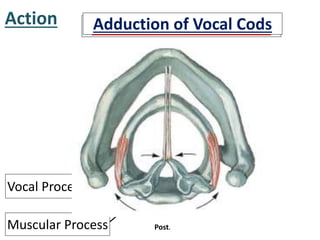
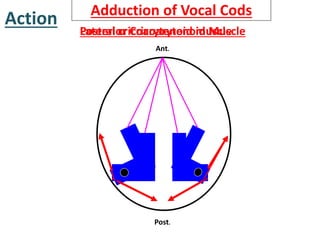
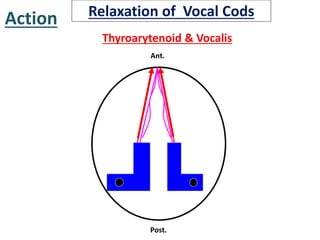
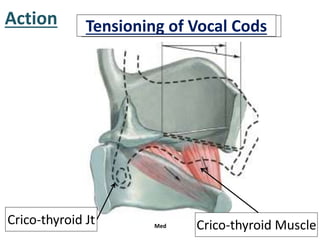
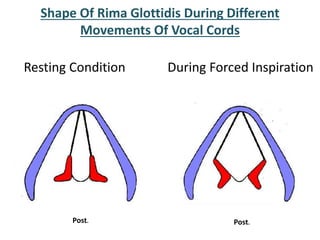
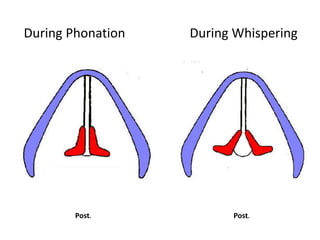
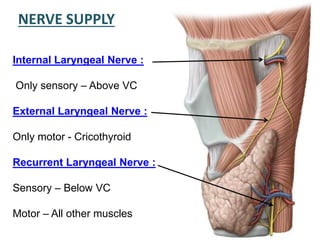
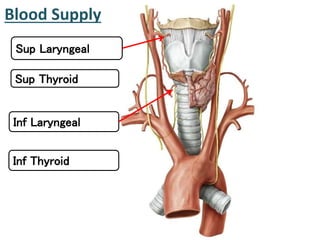
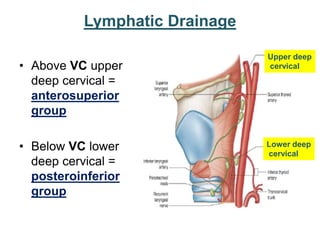
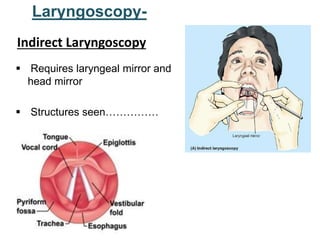
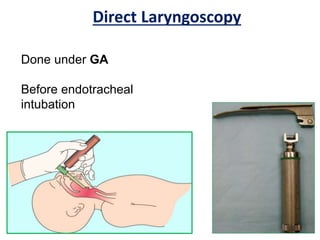
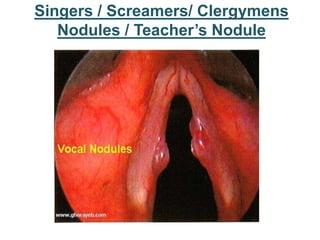
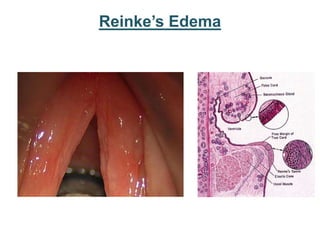
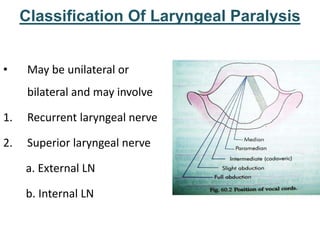
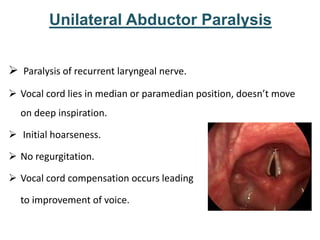
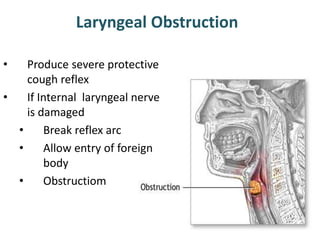
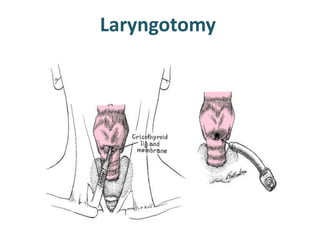
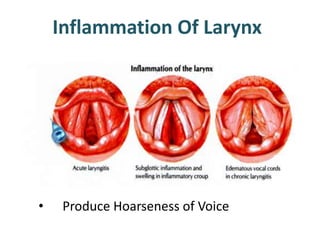
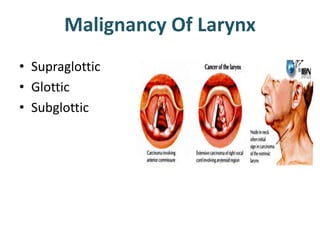
The larynx is located in the neck and regulates airflow during breathing and phonation. It contains 9 cartilages including the thyroid and cricoid cartilages which provide the skeletal framework. Intrinsic muscles like the cricothyroid and thyroarytenoid act on the vocal cords to produce sound. The larynx is supplied by the recurrent and internal laryngeal nerves and drains lymphatically into cervical nodes. Examination of the larynx provides insight into vocal cord function and pathology.